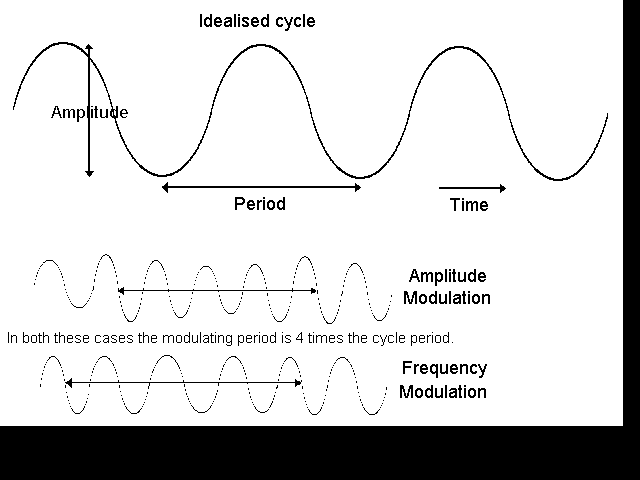
Amplitude is the range of the cycle from low to high measured in whatever units the cycle is in.
Amplitude Modulation means that the amplitude of a cycle varies over a longer cycle. For example, radio uses AM to transmit an audible sound of say 400 Hz by varying the amplitude of a radio signal with frequency 100,000 Hz.
Beats are produced by two cycles which have similar frequencies (or periods). For example if two adjacent notes are played on the piano they might have frequencies of 220 Hz and 233 Hz and they will produce beats at 13 Hz which is heard as a sort of wa-wa-wa-wa sound. Beats are equivalent to Amplitude and Frequency modulation at the same time so we may either look for multiple cycles of similar period or one with a modulating cycle. These are equivalent.
Beat Frequency is the difference between the frequencies of the two cycles that produce the beats. It is much easier to calculate beats with frequencies than with periods, as for example, periods of 3 and 4 years will produce beats of 1/(1/3)-(1/4) years or 12 years.
Calendar. In modern times the rules are: Thirty days hath September, April, June and November, all the rest have 31 except February alone which has 28 and 29 in leap years. Leap years are years which are a multiple of 4 unless they are a multiple of 100 when they are not leap years unless they divide by 400 when they are again. I hope that is perfectly clear :-)
A Filter is a device, probably mathematical, that allows some ranges of frequencies through and not others. It may partially allow some through. Simple filters can be made by using moving averages.
Fourier Analysis is a mathematical technique for turning a time series into a set of coefficients which are the amplitudes of a set of sine waves of various frequencies so that those sine waves add up to the original data.
Frequency is the number of cycles per unit time interval, e.g. 7.5 cycles per second (also called Hertz) means that there are 7.5 cycles in each second of time. Frequency is related to period by: Frequency = 1/Period
Frequency Modulation is a variation in the frequency of a cycle over a longer cycle. For example, radio uses FM to transmit an audible sound of say 400 Hz by varying the frequency of a radio signal with frequency 100,000,000 Hz.
Harmonics of a cycle are other cycles whose frequencies are exact multiples of the original frequency. Therefore the periods are exact fractions. For example, a 5.93 year cycle is the 2nd harmonic of an 11.86 year cycle.
Phase refers to the timing of the peaks or troughs. For example we might say that the phase of the 1 year temperature cycle has a maximum in January (I live in the southern hemisphere).
Phase Change refers to a variation in the phase of a cycle. This is equivalent to saying that the frequency is modulated although may refer to more extreme cases. Sometimes cycles have a 180 degree phase change, which means that peaks start happening where troughs were expected and vice versa.
Moving Average is method of smoothing by averaging n terms of the time series. A moving average may be centred in which case it is plotted at the middle of the time interval which it is the average of, or lagged in which case it is plotted at the last term included. Centred moving averages are often used for smoothing data. A moving average which has a number of terms equal to the length of a cycle will remove that cycle from the data. A moving average with a number of terms which is half the cycle period will remove shorter cycles and so emphasize the cycle. The difference between these these last two will also remove longer cycles and so emphasize cycles of about the selected period only.
Noise is any time series which has a spectrum which is continuous rather than having specific periods present. Noise comes in various types which are named after colours such as White, Brown and Pink according to the variation of amplitude with frequency. There is usually noise present in any time series in addition to any cycles.
Period is the time interval between two adjacent peaks or two adjacent troughs in a cycle, e.g. a cycle period of 4.45 years means that a full cycle occurs every 4.45 years. Period is related to frequency by: Period = 1/Frequency
Smoothing means removing the smaller random fluctuations so as to see the trend. Smoothing may be done by a moving average or by various filters which are equivalent to weighted moving averages.
Time Series. Any series of measurements of anything at all that are usually taken at regular intervals. Sometimes the intervals are not strictly regular such as calendar months, which are near enough for most purposes, or trading days which have weekends and public holidays missing which may cause some problems.
Weighted Moving Average is like a moving average but not all
terms are equal. Each moving average term is determined by weighting a
series of consecutive values, for example in the proportions 1:2:3:2:1,
before averaging.