The purpose of the charger is to trickle charge rechargable AA and AAA NiMH batteries. In order to charge the batteries, the charge voltage has to be greater than the rated voltage of the combined batteries.
Each rechargeable battery is quoted at supplying 1.2V. The charge voltage needs to exceed this. The solar panel although rated as supplying 3V will rarely achieve this! On a cloudy day, it supplies near 1V. Using 2 solar panels in series, the voltage is effectively doubled and this should be sufficient to charge a single battery. When the pair of solar panels supllies over 2.5V then pairs of batteries can be charged. Of course the voltage does not need to be doubled on a sunny day for a single battery!
Using 2 solar panels in parallel effectively doubles the current.
The schematic for the charger is:
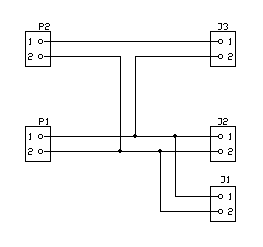
J1, J2, and J3 are 1.3mm DC sockets. P1 and P2 are Molex headers. The solar panel plugs into the J sockets and the battery holder (containing the battery to charge) plugs into the P header. A solar panel can plug into J1 or J2, 3V @ 80mA (max) is provided on P1. If a 2nd solar panel is plugged into J3, 6V @ 80mA (max) is provided on P2. If a solar panel is plugged into J1 and a 2nd solar panel is plugged into J2, 3V @ 160mA (max) is provided on P1. Plugging 3 solar panels in, one each into J1, J2, and J3 is just silly.
Because the circuit does not have any components, just connectors and wire, I choose not to breadboard the project.
The materials use for this project are summarised in the following table:
| Qty | Item | Rapid Code |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3V Solar Panel | 42-0240 |
| 2 | 2way Molex header | 22-0838 |
| 3 | 1.3mm DC socket | 20-0995 |
| 1 | 25mm X 64mm stripboard | 34-0500 |
| 4 | 2way Molex housing | 22-0820 |
| 8 | Molex crimp | 22-0836 |
| 1 | 1 AAA holder | 18-3688 |
| 1 | 2 AAA holder | |
| 1 | 1 AA holder | 18-3689 |
| 1 | 2 AA holder | |
| Some 7/0.2 wire |
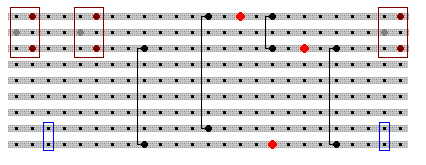
The stripboard layout for the charger is:
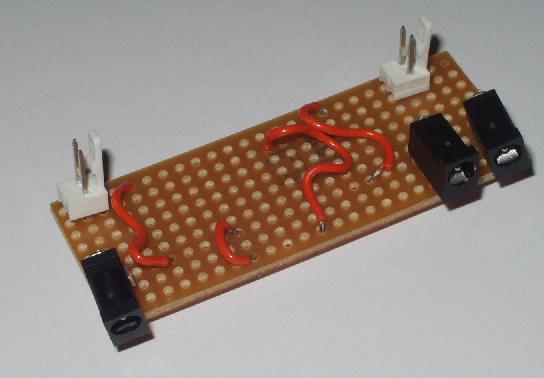
The final assembled project looked like this: