. . . . To close Advertisements, Click on Tab --->
|
"A faith that can not survive collision with the truth is not worth many regrets" - Arthur C. Clarke |
|
"A faith that can not survive collision with the truth is not worth many regrets" - Arthur C. Clarke |
- by R. Totten - (c)'99
If one particpates very much in discussions on biological evolution, then one finds out that the term "evolution" is used in various ways, which can be confusing at best and misleading at worst. The word "evolution" basically just means " gradual change," and so it is a very flexible word. Indeed, when evolution is used with regard to biology, its meaning is sometimes shifted to conveniently suit the point being made at the time, and shifted back to the original meaning for the next point.
For example, the concept of biological "evolution" (or Darwinism) is used to indicate the change in a population of generally light-colored moths being naturally selected by environmental pressures (dark tree trunks) to become a population of dark-colored moths; -- and then, pressured differently at a later time to return to the original light color. This "change" is called "evolution" by many people, even though it is only a manifestation of the variation in traits contained in the genetics of the wide-spread moth population (the "gene-pool") all along. There is no new genetic information in the overall moth population.
The same thing happens when a certain world-wide microbial population seems to "develop" resistance to the environmental "pressure" of certain drugs, --but this is actually also a manifestation of the resistance-capactiy found in the genetics somewhere in the microbial population around the world. There's no new information in the world-wide gene-pool of the microbe. It's just variation --traits already found in some small amount in the overall gene-pool.
There is no dispute regarding the facticity of this kind or degree of change. It happens all the time. Its source is mere variation. --However many people still claim it to be a small amount of Darwinian "evolution."
And then, at other times, the concept of biological "evolution" (or Darwinism) is used by people to indicate the changing of the simplest possible independently living cell (a proto-bacteria) to the point that its descendants develop and change into multi-celled organisms, and so forth until, ultimately, the most complicated multi-cellular life-forms have developed. -- Also "evolution."
---The problem is, these two instances of "evolution" are not only very different in degree, but they are not equivalent examples of the same biological process and mechanism. Thus, the concept of "Darwinian evolution," which is used with such broad flexibility of meaning, the discussion needs some qualifying terms injected into it for purposes of clarity.
Those terms are "micro"- and "macro"-evolution.
Many people wrongly suppose that there are no credible scientists, prominent in their fields, who have serious doubts as to the explanatory power and veracity of Neo-Darwinism. On the contrary, there are at present more than 700 scientists who either hold a Ph.D. in their discipline, or are an M.D. serving as a professor of medicine, who have been willing to sign a public statement declaring their scientific skepticism as to whether Neo-Darwinism seems adequate to explain the high amount of complexity found in natural life. To read their summary statement, as well as some of the justification for signing it, go to:
Micro and Macro
In order to more clearly communicate concerning biological evolution, two terms are now being widely used in scientific discourse: "Micro-evolution" and "Macro-evolution."
Micro
"Micro-evolution" means relatively little (micro) change in a plant or animal species, and that change is virtually totally due to the genetic "variation" already present in the "gene-pool" of the widespread overall population of that species.
Micro-evolution can --and sometimes does-- result in the formation of a new "species." -- (Note: A "species" is a population of living things which are genetically and structurally similar to each other, but different from other species in some respects [even if only in behavior], and the members of a species interbreed and produce fertile offspring among themselves. This doesn't mean that a species can't interbreed with a closely related species, but often it means that they simply won't, because the non-breeding is behavioral). --The formation of such new "species" may arise out of the wide amount of variation available in the gene-pool of the extended population (such as in hummingbirds or seagulls), and it isn't an instance of the origination of new bodily structure due to new genetic information in the overall gene-pool.
Micro-evolution can also come about through degenerative change (a loss of ability) due to environmental pressure and damage, or due to mutational degradation and loss of DNA information. Mutational change may be a significant factor in micro-evolution, but it is virtually always either neutral or damaging (and often lethal) in effect, and it often results in the loss of some functionality. This degenerative micro-evolution is often produced by the deterioration or loss of genetic information, (possibly resulting in a new species), where, for example, a species has a loss of structure and function (such as the loss of eyes or limbs).
Macro
On the other hand, "Macro-evolution" means relatively large (macro) change, wherein an original phylum or class of plant or animal eventually changes enough to result in newly descendant plant or animal phyla or classes, --which involves the evolution of new type(s) of structure (morphology) and function.
When the first tiny beginning of life is considered, such macro-changes had to have coded for the accumulation of new genetic DNA information (produced by natural random genetic mutations) being added to the overall genome of the population. This new DNA information specifies the assembly of new integrated structures which perform new functions which are selectively beneficial to the descendant organism (and not deleterious or destructive to its life-processes), --neither of which were present in the ancestral species (or class).
-- The problem with macroevolution is, primarily: No one has ever provided clear evidence to show that even one complex bio-mechanism (eg, a structure such as a flagellum or a cilium) --comprised of several different proteins which assemble together as well-matched and coordinated interacting bio-mechanical parts-- has ever evolved in nature from an ancestral class of life which totally did not have that structure. Such a development would necessarily have to be totally as a result of the gradual accumulation of genetic mutations, starting from no portion of that bio-mechanism in the ancestral gene pool of the species. --This sort of macro-evolution has never been evidenced, though this must have happened countless times if macro-evolution is a reality.
In the face of this kind of distinction (micro vs macro) in the theory of darwinist evolution, darwinists will sometimes object as follows: "This is not part of the theory of evolution. The theory only says that genes change, not that this change must be in a positive developmental direction, with an increase in the amount of DNA." --The problem is, for example, that if we grant (at the time of life's origin) the existence of only the simplest possible life-form (some sort of proto-bacteria), and there is not a subsequent increase in the amount of DNA in the genome (which specifies the building of new proteins and more advanced structures), then (obviously), all you would ever have is only that very simple life-form, but which never adds on a cilium or a flagellum, or a chloroplast, etc. --Clearly, Darwin's "general" theory of evolution (described below) requires increases in structural complexity, which must include increases in complex specified DNA information that must go with it. This is macro-evolution.
To focus on "simply change" alone (without such DNA informational increases), is simplistic and inadequate to explain the existence of higher life-forms. Sadly, in fact, in presenting evidence in favor of the neo-Darwinian schema of the general theory of evolution, a "bait-and-switch" type of logic is often employed: Start out establishing the veracity of natural selection's ability to produce impressive change in organismic varieties (micro-evolution), which everyone acknowledges as fact (this is the "bait"), and then jump immediately to the conclusion that natural selection (working with mutations) is also capable of producing significant new bio-genetic (DNA) information whereby the simplest possible form of life could (& did) change into the highest forms of life (macro-evolution) (this is the "switch"). This "bait-and-switch" argument, however common, is unproven and founded on faulty logic. The use of unbridled extrapolation often produces false results, for example, if you take the rate of growth of a human from conception until one year of age and extrapolate out until age 90, you'd get a person dozens of feet tall. --The accepted facticity of micro-evolution does not mean macro-evolution is true.
Darwin's Hypothesis (In Two Parts)
The above two terms, "Micro-evolution" and "Macro-evolution", may now help us to more clearly discuss darwinian evolution. Darwin set it out in two parts.
First of all, Darwin's "special" theory of evolution posits change in species due to environmental pressures, as natural selection "weeds out" less fit individuals from the population, and may cause new species to arise.
Secondly, Darwin didn't stop there, however, but went on to describe what is called the "general" theory of evolution: Going much further than the "special" part of his theory, the "general" theory asserts that all the life-forms on earth, right down to the most complex, are descendants of the first and simplest life-form.
In more recent years, darwinist scientists have added to Darwin's theory the factor of genetic mutations as the main source of genetic change, which is acted on by natural selection, and this is now known as "neo-darwinian" evolution.
So, as we consider the two sub-theories ("special" and "general") of neo-darwinian evolution, we see that they convey a very similar picture as what is described under "micro-evolution" and "macro-evolution."
The Partial Truth of Neo-Darwinian Evolution
As science has evaluated the changes that have occurred in plants and animals around the world, it has become apparent that micro-evolution (the "special" theory of darwinism) is well demonstrated as a fact of nature. ---Populations of moths have changed from light coloring to dark, and this was as a result of the tree-trunks in their environment changing from light to dark, allowing birds to see the light-colored moths better, so that more of them were eaten ...but when the tree trunks became lighter in color, so did the population of moths become lighter in color, because the birds saw the dark moths better to eat them more fequently. Natural selection in action.
A more dramatic example of micro-evolution even demonstrates that new species have descended from ancestral species. This is seen in "circular overlaps", where a chain of many subspecies (which do interbreed with one another along the chain) extends for a long geographical distance, but where the terminal links in the chain overlap, the two last species (that live side-by-side) will not interbreed with one another. They are effectively separate species because they will not interbreed with one another. The classic case of this is found in two species of European gull --the herring gull and the lesser black-backed gull-- which do not interbreed with one another, but they breed with a chain of interbreeding subspecies that extends around the globe. Speciation (the start of new species) clearly happens ...but this is still micro-evolution, because the change is due to selective pressures on the variation already available in the gene pool. --Darwin's Finches are an example of such variational change. More examples could be described, such as among other birds and insects (like fruit-flies), but this will suffice.
Clearly, then, Darwin's "special" theory of evolution, is largely correct, --and there are several factors which are clearly known to have an affect on micro-evolution, such as natural selection, recombination, gene flow (the introduction of genes from one population into another), genetic drift, founder effects (a small number of isolated organisms starting a new population ...possibly a new species), bottlenecks, and gene linkage (the occurrence of two genes on the same chromosome) ...among other factors.
Micro-evolution is well-demonstrated as basically a fact of nature, ...however, in the above examples or any that we might cite (along with the genetic factors that come into play), all micro-evolutional change is due to selection for or against genetic traits already present in the variation of the gene-pool, ...or sometimes selection for or against the loss or neutralization of DNA genetic information.
However, concerning macro-evolution, no one has ever been able to provide clear empirical evidence that a new plant or animal species has ever originated as a result of the gradual accumulation of DNA through mutations (acted on by natural selection), giving the new species new genetic information contained in a net increase in the amount of functional genetic material (DNA), which specifies and produces new beneficial type(s) of structure(s) and function(s) which are totally lacking in the ancestral species, and which are not deleterious to the life-functions of the new species. --Even in the case of something like bacteria which are able to develop resistance to antibiotics, or like viruses which are able to "mutate" their structures in order to evade immune-defenses, --those changes are made repeatedly by the bacteria and viruses when circumstances call for it, and thus, such "mutation" may not actually be mutation of any helpful significance, but a capacity already resident in the variation of those gene-pools.
The Unsubstantiated Part of Neo-Darwinian Evolution
So, Darwin "hit the bull's-eye" with his "special" theory, (which is essentially micro-evolution through variation) --however, the situation with the "general" theory (macro-evolution) is entirely a different story. There is no clear body of evidence to indicate that macro-evolution has ever occurred with any organism anywhere. No one has ever demonstrated an instance of macro-evolution --which we defined as a "relatively large (macro) change in a descendant plant or animal species which would be due to sizeable accumulations of new genetic information (arising from mutations) being added to the overall genome, where this new information specifies the assembly of new integrated structures which perform new functions which are beneficial to the descendant organism (and not deleterious or destructive to its life-processes), along with the carrying out of new beneficial biochemical processes, --neither of which were present in the ancestral species."
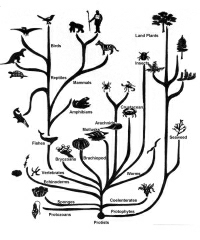
A darwinist might object to this stringent perspective on macro-evolution, but let's recall what is claimed to have happened through the process of the "general" theory of neo-darwinian evolution. We see that overall schema depicted here in the "Tree of Life," as Darwinism is basically portrayed:
It is claimed further that the simplest possible life-form then developed (added on) various structures which gave it an advantage (were "beneficial") in the task of survival, and natual forces selected in favor of this newly advantaged life-form. As these structures were added to the simplest life, the amount of information in the DNA necessarily increased to specify the building of those new structures.
It is also claimed, that this process continued on for many millions of years until all the complex classes of life evolved from that simplest life-form as the original ancestor.
Again, the necessary schema is that the genome of the simplest possible life (having perhaps 10,000 nucleotides in its DNA?) grew and evolved until we have the genome of very complex organisms, such as a mammals (with about 3 billion nucleotides).
---All the way up the "Tree of Life," along the macro-evolutionary trail, it is unavoidable that the genomes were generally growing in size, and the structures increasing in complexity, with advantage for survival being established as natural selection did its work.
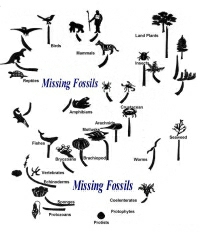
Paleontologists have discovered what we see in this illustration. There is no substantial fossil evidence to show that the general schema of darwinian evolution actually occurred.
There is no "Tree." The fossil record has not produced evidence of any part of the "trunk(s)" or the "limbs," but only the twigs at the ends. -- The tree is imaginary.
Instead of Darwin's conception of the descendantly relatedness of all life, the physical evidence actually shows that all the major classes of life appeared suddenly in the fossil record ---they appeared in an "instant" of geologic time, in the sedimentary rocks of the Cambrian period. And, in fact, these Cambrian life-forms are so complex, that it is conservatively estimated that it must have taken them about 1.5 billion years to have evolved (by the natural selection method of neo-darwinism) . . .and yet, no fossil record of their development was left in all that time... despite the fact that many of these life-forms are easily fossilized marine types.
The fossil evidence also shows that all the major classes (and phyla) of life appeared fully formed. There are no intermediate forms between the major classes of life. --Those fossils which must have existed by the billions, are completely missing.
NOTE: - If anyone can present significant evidence to make a bridge of intermediate fossils across any one of the "missing fossils" regions in the tree of life between two different animal phyla, classes or orders, there is a reward offer available from this website.
Evolutionary Hope of "Micro, Plus Time, Equals Macro"
Since micro-evolution is basically a fact, the neo-darwinist seizes upon it and argues that if there were enough time, then you would end up with macro-evolution. ---Well, so the darwinist hopes.
However, there is no solid body of evidence which indicates that anything of the sort has ever happened --or could happen (with any reasonable probability) using all the time and matter in the present universe. -- This situation is mainly true, because the more time is involved, the more mistakes are made in the passing down of genetic information, resulting in more genetic diseases and problems, rather than improvements.
It is at this point that the appeal to the fossil record is then routinely made, --with supposedly impressive lineups of bones which are said to provide evidence of macro-evolutionary progressions down through the millennia.
However, for the evolutionist, the big problem with the fossil record is: No one has demonstrated that we are actually looking at instances of macro-evolution --even though some degree of micro-evolution may be in evidence.
--Remember that almost all of micro-evolution results from the wide variability available in organisms ...for example, look at domesticated dogs. Even now, the wide variety of dogs is used as an example of evolution in action. And if dogs were extinct, and the bones of the tiniest chihuahua right on up through the mastiff were dug up, then you can bet that this series of bones would be a major show-case example of a "macro-evolutionary series" ---but, in reality, it would definitely not constitute such proof. Dog breeds are only the result of the variation already in the dog genome being manipulated by breeders. It is not macro-evolution at all, but only the wide amount of variation present in dogs.
Likewise, the fossil record gives some instances of small-dog-to-large-dog "evolution," which is really only variation in action. It is not macro-evolution. The famous "Eohippus" series of fossils is actually only an instance of "small-dog-to-large-dog" variation --along with a couple of outside species thrown in that are probably not even be in the same family as Eohippus. The darwinist's hope to demonstrate macro-evolution by looking at the fossil record, only appears to involve genetic changes which are actually only quite minor.
But fossil evidence of the large transitions between major classes of life required to demonstrate macro-evolution is basically totally absent, which is even admitted by some evoltionists, such as the late Stephen J. Gould, who admitted this lack of empirical support for his view, as he stated:
(Gould, S.J., "Is a new and general theory of evolution emerging?",
Paleobiology 6:119�130 (p.127), 1980.)
Fossils simply do not tell us much about the genetics of such fossilized forms (not directly) ---because, about 99% of the biology of any life-form is found in the soft anatomy, which is destroyed and lost in the process of fossilization.
Most importantly: The fossil record does not supply any uninterrupted series of transitional forms between phyla or classes or even families of animals or plants ---even though about 90% of the families of all animals are represented in the fossil record (excluding birds, which fossilize poorly).
G.G. Simpson "estimated the percentage of living species recovered as fossils in one region of North America and concluded that, at least for larger terrestrial forms, the record may be almost complete!" (ref: "Evolution: A Theory In Crisis" by Michael Denton, '86, p.189).
Whatever excuses darwinists make, one of the outstanding characteristics of the entire fossil record, is the systematic presence of non-transitioned gaps throughout.
--Micro-evolution has not been shown to add up to macro-evolution, no matter in which way or over how long a period the evidence is observed.
Darwin's Partial Success . . .A Starting Point
Although micro-evolution (and the "special" theory) is right, micro-evolution cannot necessarily be used and stretched to extrapolate out to a valid conclusion that macro-evolution is also correct. Dr. Michael Denton writes that there is "...a long list of leading authorities who have been inclined to the view that macroevolution cannot be explained in terms of microevolutionary processes, or any other currently known mechanisms" and "...it does not necessarily follow that, because a certain degree of evolution has been shown to occur, therefore any degree of evolution is possible" - (Denton, cited, p.86-87). Denton notes, by way of analogy, that Newtonian physics accounts perfectly well for the behavior of larger physical bodies, but that it is not applicable to sub-atomic physics and cosmological phenomena. A similar thing appears to be the case for darwinism: It applies to micro-evolutionary situations, but seems to have almost no explanatory power with regard to the larger macro-evolutionary picture.
That there is only a partial success for neo-darwinism is not a disaster, however, because a mid-course correction can be a good starting point. From here, the evidence indicates that intelligent design is the best option available to explain the initial origin of complex specified information (see link below) present in life-forms. Just as intelligent design is the only reasonably probable explanation for the ordered sequence of the letters in this sentence (and not random letter-choices), there are no known laws or forces of physics and chemistry which could initially dictate the sequential order of the nucleotides in living DNA/RNA, or the sequential order of amino acids in the functional & beneficial (& not detrimental) proteins which go together to make up a living thing. The random processes of mutations could not, in any reasonable probability, come up with those sequences. When you look logically at any sizeable amount of complex specified information, "it is abundantly clear that in every analogous system, pure unguided random events cannot achieve any sort of interesting or complex end. As the analogy deepens between organism and machine, as life at a molecular level takes on increasingly the appearance of a sophisticated technology and living organisms the appearance of advanced machines, then the failure to simulate Darwinian evolution in artificial systems increasingly approaches a formal disproof of Darwinian claims" (M. Denton, cited, p.348).
Although the small picture, or "micro-evolution," is successful and true, the larger picture of life is turning out to paint the picture of Intelligent Design.
A Side-Note:
--For example, the color-changes in moths, or polyploidy, or the ability of bacteria to become drug-resistant, are examples of such micro-evolutionary change. The changes in the beaks and behavior of Darwin's Finches would be an example of such a micro-change.
It is claimed, first of all, that life first developed from non-living chemicals in a supposed "primordial soup" (see our abiogenesis article) ---and this is actually the biggest single step of macro-evolution, where life first begins.
However, what does the fossil record actually show?
--There are no intermediates, for example, between the fishes and the amphibians ...even though there should be many millions of fossils to demonstrate this transition from the fish, since such water-dwellers were readily and abundantly fossilized down through the eons of their existence.
"The absence of fossil evidence for intermediary stages between major
transitions in organic design, indeed our inability, even in our
imagination, to construct functional intermediates in many cases, has
been a persistent and nagging problem for gradualistic accounts of
evolution."
NOTE: ...You, dear reader, are valuable and loved by God, . . .and that's why Jesus Christ came.
This page hosted by
![]() Get your own Free Homepage
Get your own Free Homepage