Data Transmission
Data communication is affected by several technical
matters:
Bandwidth
- Voiceband - speed of standard telephone line
- Medium band - speed of special leased lines
- 56,000 to 264,000,000 bps
- Broadband - speed of microwave, satellite,
coaxial cable, and fiber-optics channels.
- 56,000 to 30,000,000,000 bps
Type of Transmission

- Serial data transmission - bits flow in a
continuous stream
- Example: data sent over telephone lines.
- Parallel data transmission - bits flow through separate
lines simultaneously.
- Example: data sent from the system unit to the
printer.
Direction of Data Flow
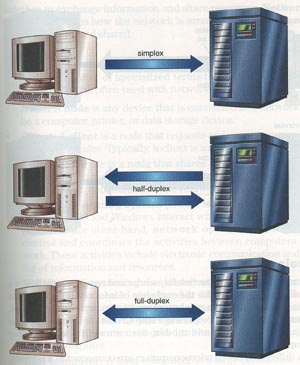
- Simplex communication
- Data travels in one direction only.
- Not used frequently in current communication systems
- Certain point-of-sales application may use this
method.
- Half-duplex communication
- Data flows in both directions, but not simultaneously.
- Frequently used to link microcomputers by telephone
lines to other computer systems such as Bulletin Board Services.
- Full-duplex communication
- Data can flow in both directions at the same time.
- Is the fastest method.
- Requires special equipments.
- Used primarily for mainframe communications.
Mode of Transmitting
Data
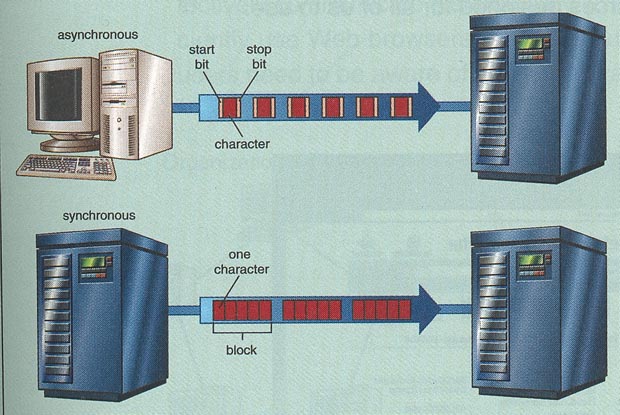
- Asynchronous transmission
- Data is sent and received one byte at a time
- Used frequently with microcomputers
- Often used for terminals with slow speeds
- Synchronous transmission
- Data is sent and received several bytes (or a block)
at a time.
- System requires a synchronized clock
- Sending and receiving of the blocks of bytes must
occur at carefully timed intervals.
Protocols
- A protocol is a set of communication rules for the
exchange of information.
- Defines the speeds and modes for connecting with another
computer.
- Network protocols can become very complex and
therefore must adhere to certain standards.
- The first sets of standards was IBM System Network
Architecture (SNA) which only works with IBM computers.
- The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) standard was developed
by the International Standard Organization to:
- Identify functions provided by any network
- Separate each network functions into seven layers of
communication rules.
< Previous Page
Next Page >



