Series
Wiring

What is the equivalent
series resistance Rs? |
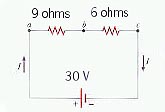
Rs = 9 + 6
= 15
W
|

I = 30 / 15
= 2 A |
Series Wiring Example

What is the power dissipated
in the 6 ohm resistor? |

|
I = 12 / 9
= 1.33 A
----------------
P = I2 R
= (1.33)2 (6)
= 10.6 W |
Resistors in Series: The
Extension Cord

Which resistor gets hotter?
|
 |
I = V / (R + r)
----------------------------
PR = I2
R
= [ V2 /
(R+r)2 ] R
----------------------------
Pr = I2 r
= [ V2
/(R+r)2 ] r |
Blowing a Fuse
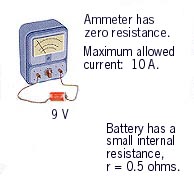
I =
9 / 0.5
=
18 A |

What is the least R which will
prevent the fuse from blowing? |
Parallel Wiring
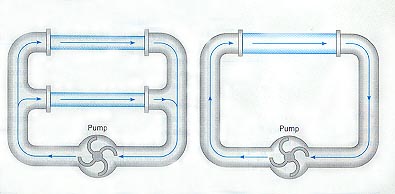
Two pipes in parallel can be replaced by one. The single
pipe
will have less resistance than the pipe with the least
resistance. |
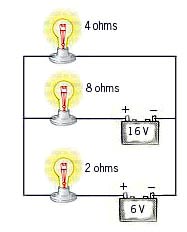
Light Bulbs in
Parallel
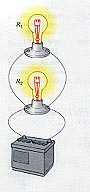
Light bulbs
connected
in parallel. |

Equivalent resistance of this
parallel combination found
through the relation
1 / Rp = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 |

Rp is the single resistance
which is equivalent to R1
and R2 in parallel. |
House Wiring is
Parallel
 |
Which connecting wire, A, B, C,
D, or E, will be the first to become
dangerously hot if too many
appliances are turned on?
How can overheating be
prevented, even if all the
appliances in the house are
turned on? |
Circuit
Breakers
 |
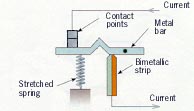
Brass expands more than steel
As temperature increases, the
bimetallic strip arcs to the left,
settles into groove, and the
spring pulls the metal bar down. |
Four Resistors in
Parallel
| Find the resistance between A and B:
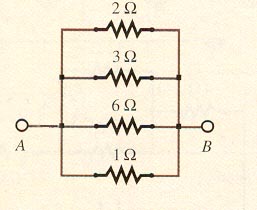 |
1 / Rp = 1 / 2 + 1 / 3 + 1 / 6 + 1 / 1
Rp = 0.50 W
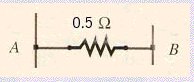
----------------------------------
VAB = 12 V
What is the current in each resistor?
What is the sum of all currents?
|
Three-Way Light

What is the resistance
of each filament? |
P = V2 / R
V = 120 volts for each filament
------------------------------------------
R1 = resistance of 75-W bulb:
75 = (120)2 / R1
R1 = (120)2 / 75
= 192
W
------------------------------------------
R2 = resistance of 100-W bulb:
100 = (120)2 / R2
R2 = (120)2 / 100
= 144
W |
Equivalent Resistance of Series and
Parallel Combination of
Resistors
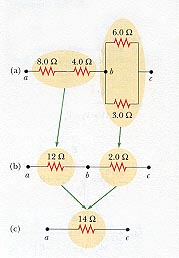 |
Parallel combination:
1 / Rp = 1 / 6 + 1 / 3
= 0.5
Rp = 1 / 0.5
= 2
W
---------------------
|
Series and Parallel
Circuits
| What is the total resistance between Points A and
B?
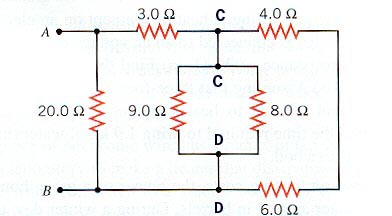 |
4 + 6 = 10
--------------------------------------
1 / Rp = 1 / 9 + 1 / 8 + 1 / 10
Rp = 2.98
W
-------------------------------------
2.98 + 3 = 5.98
-------------------------------------
1 / Rp = 1 / 5.98 + 1 / 20
Rp =
4.60 W |
A Series-Parallel Circuit Problem: Part
One

What is the potential difference between
Points A and B? |
1 / Rp = 1/3 + 1/6
Rp = 2
W
-------------------------
Total: 6
W
-------------------------
I = 12 V / 6
W
= 2 A
-------------------------
Ohm's Law:
VAB = (2 A) (2
W )
= 4 V |
A Series-Parallel Circuit Problem: Part Two

What is the current in the
5-W resistor? |
I = V / R (Ohm's Law)
-------------------------------
From Part One:
VAB = 4 V
-------------------------------
R = 6 W (lower
branch)
-------------------------------
I = 4 V / 6
W
= 2 / 3 A
This is also the current
in the 1 W
resistor. |
>
Series and Parallel
Connections

What happens when the wire
is connected? |
Kirchhoff's Junction Rule

Junctions are places where
wires are connected together. |

Kirchhoff's Junction Rule:
Total current into a junction
is equal to the total current
out of the junction. |

Gustav Robert Kirchhoff
(1824-1887) |
Kirchhoff's Loop Rule

A loop is a circuit, which is any
closed path with batteries and
resistors. |
The sum of the potential differences
encountered around a closed circuit
equals zero.
---------------------------------------------------
Traveling clockwise from A:
-12 I - 6 - 8 I + 24 = 0
or.............
Traveling counter-clockwise from A:
-24 + 8 I +6 + 12 I = 0
|
Kirchhoff's Rules
Problem Part One:
Kirchhoff's
Rules Problem Part Two:
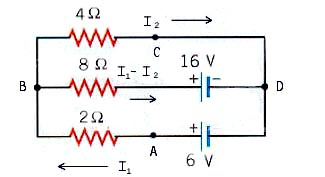
Loop BCDB:
-4 I2 + 16 + 8 (I1
- I2) = 0 (1)
-4 I2 + 16 +8 I1
- 8 I2 = 0
(2)
8 I1
-12 I2
= -16 (3) |
Loop ABDA:
-2 I1 -8 (I 1- I2) -
16 + 6 = 0 (4)
-2 I1 -8 I 1 + 8 I2 - 10
= 0 (5)
-10I1 + 8 I2
= 10
(6)
----------------------------------------------
Solve Equations 3 and 6:
I1 = 3 / 21 A
I2 = 30 / 21 A
|