2. 2,2-dimethylbutane
3. 1,1,3-trimethylcyclohexane
4. 2-heptanol, C7H16O
5. 1,6-hexanediol, C6H14O2
See the Chapter 3 handout.
Bottom of page; return links and contact information
| One topic in Ch 3 is combustion. You should know the basics of combustion from your general chem background -- but some students are rusty. So here are a few problems; the answers below give some explanation. Since this is a chapter on alkanes and cycloalkanes, I have asked you to figure out what the chemical is in some questions. | |
| In each case, write a balanced equation for the combustion of the given compound. Assume complete combustion. | |
|
1. heptane, C7H16
2. 2,2-dimethylbutane 3. 1,1,3-trimethylcyclohexane 4. 2-heptanol, C7H16O 5. 1,6-hexanediol, C6H14O2 |
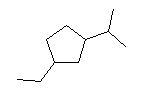
6.

|
1. C7H16 (l) + 11 O2 (g) --> 7 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (g)
This equation shows the essential features. Ordinary complete combustion refers to the complete oxidation by O2, producing the major oxides. For compounds of C and H (and O) those are CO2 and H2O. That is, the general reaction is
<compound of CHO> + O2 (g) --> CO2 (g) + H2O (g)
You should think about the phases. You may or may not know the phase of the organic reactant, but I bet you "know" more of them than you think; give them a try. It's reasonable to show the phase of water as either gas or liquid. It is a gas under the conditions of the combustion, but can be thought of as a liquid, back at "standard conditions".
As to balancing, there is a basic approach which generally works well for any CHO compound. Start with the organic compound. There is enough C to make how many CO2? There is enough H for how many H2O? Now, calculate how many O are on the right, and provide them on the left.
2. First, you need to figure out what the chemical is, from the name. You should be able to draw it. But all we need for balancing is the molecular formula. It has C6. It is an alkane, so has H2N+2 = H14 in this case. Thus the molecular formula is C6H14. Now, you write and balance the combustion equation as above:
C6H14 (l) + 19/2 O2 (g) --> 6 CO2 (g) + 7 H2O (g)
3. The compound is C9H18. Note that it has one ring, thus is short 2 H from having the 2N+2 maximum number of H.
C9H18 (l) + 27/2 O2 (g) --> 9 CO2 (g) + 9 H2O (g)
4. This is almost like #1. However, when you go to balance the O, remember that the organic reactant has 1 O. We still need 22 O, but 1 is in the C7H16O, so we only need 21 from O2.
C7H16O (l) + 21/2 O2 (g) --> 7 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (g)
5. C6H14O2 (l) + 17/2 O2 (g) --> 6 CO2 (g) + 7 H2O (g)
6. So what is the formula? It is C10H20. One way to find that is to write in all the H on the structure and then count everything. Another way is to count the C (there are 10), and then figure out the H. There might be 22 H for 10 C, but this structure is short 2 H, since it has one ring.
C10H20 (l) + 15 O2 (g) --> 10 CO2 (g) + 10 H2O (g)
Chapter 3 handout Organic/Biochem (X402) Chapter handouts Organic/Biochem (X402) home page
Contact information Site home page
Last update: January 4, 2009