1) The rate constant for the first-order dehydration of tert-butyl alcohol at 500oC is 1.20 x 10-4 s-1. The rate constant for this process at 600oC is 6.80 x 10-3 s-1. Calculate the activation energy for this reaction.
(a) -227 kJ/mol
(b) 227 kJ/mol
(c) 318 kJ/mol
(d) 100. kJ/mol
(e) -100. kJ/mol
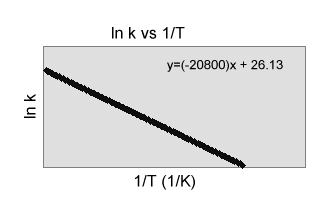
2) Use the graph to the right to calculate
the rate constant for the following reaction at 40.0şC. 
CH3CH2NO2(aq)
![]() C2H2(g) +
HNO2(aq)
C2H2(g) +
HNO2(aq)
(a) 3.1 x 10-18 sec-1
(b) 9.56 x 10-15 sec-1
(c) -8.3 x 105 sec-1
(d) -6.5 x 106 sec-1
3) The activation energy for the isomerization of cyclopropane to propene is 274 kJ/mol. By what factor does the rate of reaction increase as the temperature rises from 500oC to 550oC?
(a) 1.0
(b) 13
(c) 2.6
(d) 4.0 x 102
4) The rate constant for a certain first-order reaction at 27oC is 4.9 x 10-4 s -1 and is 0.18 s-1 at 227oC. Calculate the activation energy for this reaction.
(a) 8.55 x 104 kJ/mol
(b) 9.80 x 104 kJ/mol
(c) 3.68 x 104 kJ/mol
(d) -1.50 x 103 kJ/mol
(e) 1.50 x 103 kJ/mol
5) Use the graph to the right to
calculate the rate constant for the following reaction at 40.0şC. 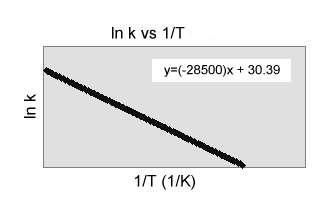
C2H5Cl(aq) ![]() C2H4(g) + HCl(aq)
C2H4(g) + HCl(aq)
(a) -9.29 x 106 sec-1
(b) -1.51 x 106 sec-1
(c) -57.0 sec-1
(d) 1.70 x 10-25 sec-1
6) The reaction rate triples when the temperature increases from 15 oC to 35 oC for a particular reaction. What is the activation energy for this reaction?
(a) 2.39 x 102 J/mol
(b) 2.06 x 10-3 J/mol
(c) 7.92 x 10-2 J/mol
(d) 4.05 x 104 J/mol