1400
|
The Bedlam Insane Asylum is founded in London starting a wave of new "modern" treatment for mentally ill patients.
|
The body of a frozen mammoth is found in Siberia.
|
|
1409
|
1409 - The Council of Pisa declares both Catholic popes to be deposed and elects a new one. However, the other two popes refuse to step down, so now the Catholic Church has three popes. |
| |
1421
|
The first patent for an invention is issued in Florence, Italy.
|
Prince Henry the Navigator of Portugal starts sending waves of Portugeese to map and explore the known world. They were able to map Western Africa all the way down to Sierra Leone.
|
1455
|
|
Gutenberg prints out his first copy of his famous Gutenberg Bible, the first book to be mass published on a movable-type printing press.
|
|
1452
|
Leonardo DaVinci is born. He immortalized the concept of the Renaissance Man, the jack of all trades.
|
|
|
1453
|
Constantinople finally falls to the Ottoman Turks, sealing the coffin on the last living vestige of ancient Greek and Roman civilization. The invaders rename it "Istanbul," which means "The City." Now the Roman Catholic Church has no competition
anywhere in the world in the Christianity business. On the plus side, the invading Ottomans did bring this esoteric cleansing
substance called "soap" with them.
|
|
1473
|
|
|
Michaelangelo paints the magnificent ceiling of the Sistine Chapel.
|
1478
|
The Trevisto Arithmetic, the first popular book of mathematics is printed and published.
|
|
|
1481
|
Tomas de Torquemada invents the Spanish Inquisition.
|
|
|
1484
|
|
German Inquisitors Sprenger and Kramer publish the Malleus Maleficorum, giving the budding Inquisition industry a new
target: witches. Pope Innocent VIII, giving new meaning to the term "papal bull", grants the authors broad powers to root out, try,
convict, torture, and incinerate anyone suspected of witchcraft.
|
1492
|
Cristoforo Colombo cajoles Spain, or maybe it was Portugal, to give him a miniscule fleet of ships so he can sail around the
world and plunder China. Fortunately, everyone who can read at the time knows that the world is round. Unfortunately, there is a
continent in the way between Spain and China, and when Columbus bangs into it he thinks he's missed China and landed on the
shores of India. Years later, after ransacking several small native villages and returning with a few
boatloads of slaves (all in the name of the Church, of course), he ends up broken and in prison because the land and people he's
plundered don't have any gold.
|
Ferdinand and Isabella, having united Spain, overthrow the Spanish moslems. Jews living in Spain, who have
been treated poorly under Moslem rule, are now treated poorly under Catholic rule. Spanish Jews are given 3 months to convert to
Catholicism or pack their bags and get the heck out.
|
1498
|
|
The first toothbrush is used by a Chinese man.
|
|
1530
|
|
Germany decides it's had enough with the Catholic Church, and starts up its own church. It's pretty much the same as the
Catholic church, witch trials and all, except they write their bibles in German (with 12 Old Testament books omitted) and don't take
orders from the Pope.
|
1542
|
|
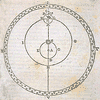
"On the Revolution of Heavenly Spheres"
by Nicholas Copernicus is published. He
changed the world by proposing that the
sun was the center of the universe and the
planets orbited around the sun.
|
|
1543
|
|
Andreas Vesalius, the father of Anatomy, publishes his work "On the Structure of the Human Body." The work set the standard for Anatomical works for many centuries.
|
1544
|
The French surgeon Amboise Pare, considered to be the founder of modern surgical treatments, publishes his reference of surgery that set the benchmark for centuries. He established the importance of tying off arteries to prevent hemorrhage, improved techniques of amputation, devised artificial limbs, improved the treatment of fractures, and developed several surgical and orthopedic devices.
|
|
1545
|
Gerolamo Cardano publishes "Ars Magna" (The Great Art,) the first work in Latin about Algebra.
|
|
|
1546
|
Gergius Agricola publishes "On the Nature of Fossils," one of his many famous works.
|
Girolamo Fracastoro first describes the transmission of disease by germs.
|
|
1554
|
|
|
South American tomatoes are cultivated in Europe.
|
1555
|
Nostradamus the French astrologer publishes The Centuries. The Centuries still today provides fodder for tabloids all over the world.
|
|
|
1556
|
A terrible earthquake in China kills 830,000 people and demolishes hundreds of towns and cities.
|
Agricola publishes his most famous work, "Re De Metallica." The work deals principally with the mining and smelting of ores. It is noted for its detail and clarity, enhanced by excellent woodcuts. The work was a standard reference for over a century and is a source of knowledge about mining practices of the time.
|
1557
|
|
|
The equals (=) sign is first used in mathematics.
|
1560
|
A solar eclipse is recorded in Europe.
|
Puritanism is first practiced in England.
|
|
1561
|
Ruy Lopes de Segura analyzes chess, his opening movies are still in use today.
|
|
|
1564
|
Ivan the Terrible begins his reign in Russia.
|
Horse drawn cariages come to England from Holland.
|
The manufacture of graphite pencils begins in Europe.
|
1569
|
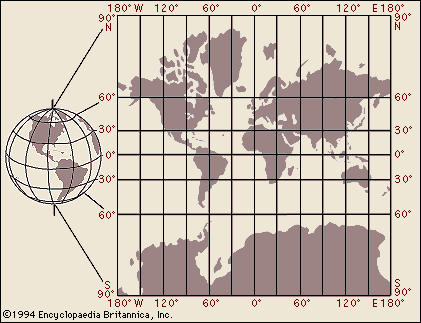
| Garadus Mercator, famous mapmaker, adds latitudes and longitudes to maps. He also started to overcome the problems of projecting a spherical earth onto a flat surface.
|
|
|
Jacques Besson develops a screw cutting lathe.
|
1572
|
|
A new star appears in the constellation Cassiopeia, causing many astronomers to throw out the "static universe" beliefs of Aristotle.
|
1573
|
The Momoyama period of Japan begins. The period is characterized by the many castles built at the time.
|
|
The potato is brought to Spain from the Americas and cultivated.
|
1576
|
Tycho Brahe builds his observatory on the island of Ven between Sweden and Denmark. He was able to catalogue and map the heavens very thoroughly and with great precision.
|
Henry III outlaws Protestantism in France.
|
1577
|
|
Frances Drake embarks on his voyage to circumnavigate the globe. He returned in 1580 with only one of the five ships he started the voyage with.
|
1578
|
The Christian catacombs are discovered in Rome.
|
|
|
1579
|
|
|
Frances Drake, at the halfway mark of his expedition, discovers San Fransisco Bay
|
1580
|
Michael de Montaigne publishes his work "Essays" (Attempts). This was the first time that a writer had focused only on one side of an issue and added his opinions. Before Montaigne, writers would try to explain every aspect of a subject, both the pros and cons, without letting his or her opinions intervene.
|
The western European witch hunts begin.
|
|
1582
|
|
Pope Gregory XIII takes credit for a new Calendar that omits the Leap Year on 3 out of every 4 years that end with 00. His monks also become obsessed with devoting each possible instant of their lives to correctly worshipping God, which causes them to
invent the second (1/60 of a minute, the way a minute was 1/60 of an hour).
|
1583
|
|
|
Edinburgh University is founded in Scotland.
|
1585
|
Roanoake Island is the first settlement in the Virginian Colony, now present-day North Carolina. More settlers returning there in 1591 found the enitre colony dissappeared without a trace.
|
|
1586
|
Pipe smoking, killer of many, is in fashion in England.
|
|
|
1588
|
|
The Spanish Armada, a huge fleet of fighting ships, is defeated by the unfavored English Navy.
|
|
1589
|
|
|
Galileo Galelii becomes a Professor or Mathematics in Piza University.
|
1590
|
Francois Viete writes Introduction to the Analytic Art.
|

|
Shakespeare, the Immortal Bard, begins to write his plays and poetry that will endure many centuries to come.
|
|
1592
|
Giordano Bruno, a philosopher and Dominican Priest, is Imprisoned for heresy by the church. He was burned at the stake in 1600 for his writings about his belief that that the Earth and human individuals are ultimately accidents of a single living world-substance.
|
1600
|
Hans and Zacharias Jannsen construct the first microscope.
|
|
William Gilbert publishes his work on magnetism, "De Magnete."
|
1602
|
|
Bodleian Library, the first public library in Europe opens in Oxford, England.
|
|
1603
|
Hamlet, one of the greatest works of Shakespeare is preformed for the first time.
|
|
|
1604
|
|
Hieronymus Fabricus publishes "De Forma Foctur" his study of embryology.
|
A supernova explosion is observed my astronomers all over the world.
|
1605
|
Frances Bacon publishes "The Advancement of Learning," a small part of his larger work, Instauratio Magna.
|
Cervantes publishes the first part of Don Quixote.
|
|
1607
|
|
|
John Smith settles Jamestown, the first English colony in the New World.
|
1608
|
.

|
Galileo assembles his first astronomical telescope.
|
|
A telescope is also assembled by Hans Lippershey.
|
|
1609
|
|
Johannes Kepler publishes his first law of planetary astronomy, stating that the planets move around the sun with elipitical orbits. Kepler was able to explain the apparent retrograde motion of Mars with his simple model of the universe.
|
1610
|
Galileo voices his stellar observations in "The Starry Messanger."
|
|
|
1611
|
|
The King James Bible is published in England. King James wanted to make the Bible accessable to all people in England, so he had the Latin Bible translated into English.
|
1614
|
John Napier, the developer of the logarithim, publishes his work Mirifici logarithmorum canonis descriptio (A Description of the Marvelous Canon of Logarithms). He developed the logarithm to help astronomers keep minor errors out of their calculations.
|
|
1615
|
|
|
Coffee is introduced to Italy from Turkey.
|
1616
|
Hundreds of New England Native Americans are killed by an epidemic of the small pox virus.
|
The Catholic Church issues a ban of Copernicism, a heliocentric belief.
|
|
1617
|
|
|
Tobacco becomes a lucrative market in the Southern Colonies of America.
|
1620
|
Cornelis Drebbel demonstrates a submarine in the Thames River.
|
Sir Francis Bacon publishes his Novum Organum, in which he comes out and says what's been "in the air" among the
scientific community for some time: that inductive reasoning by experiment is how you find out about stuff.
|
1621
|
Robert Burton, an English anatomist, publishes "Anatomy of Melancholy," a study of emotional illnesses as seen by people of the Renaissance. It relied heavily on Hippocrate's four humors theory to explain melancholy as a disorder of the black bile.
|
|
1623
|
|
Diego Valazquez is made court painter to Philip IV of Spain.
|
Philosopher Frances Bacon publishes "On the Dignity and Growth of Sciences."
|
1624
|
Flemish chemist Johannes Baptista van Helmont, analyzes gasses from vapors in chemical reactions.
|
|
|
1628
|
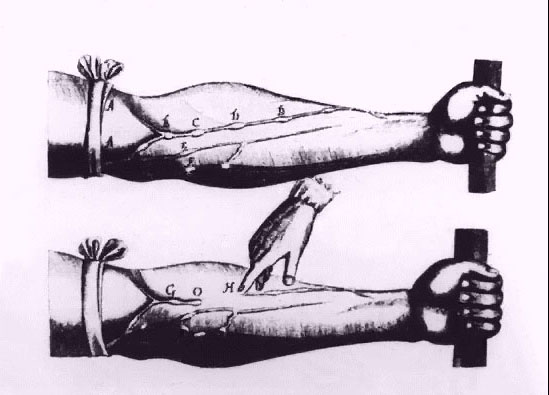
| English physician William Harvey publishes "On the Motions of the Heart and Blood."
|
|
|
Renee Descartes begins "Rules for the Direction of the Mind."
|
1631
|
The building of the Taj Mahal begins in Agra, India.
|
Le Gazette de France the first newspaper in Europe puts out the first edition.
|
|
1633
|
|
|
Galileo is imprisoned for "vehement suspicion of heresy."
|
1936
|
Harvard University is founded in Boston, Massachusetts.
|
|
|
1637
|
|
Descartes publishes "Discourse of the Method" on the concepts of analytic geometry.
|
|
1639
|
|
|
The first American printing press is established in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
|
1640
|
Russian explorers cross Siberia to the Pacific Ocean for the first time.
|
|
|
1643
|
|
Torricelli, an Italian, demonstrates the concepts of the barometer.
|
|
1644
|
|
|
Descartes proclaims, "Cogito, ergo sum," I think therefore I am.
|
1645
|
Blaise Pascal invents the first mechanical adding machine.
|
|
|
1648
|
|
Margaret Jones is exceuted as a witch, the first such execution in America.
|
|
1650
|
|
|
The first English coffeehouses open.
|
1654
|
|
Blaise Pascal and Pierre de Fermat colaberate in developing many different rules of probability.
|
|
1656
|
| Christiaan Huygens receives a patent for the first pendilum clock. He based his pendelum on the work of Galileo.
|

|
|
|
1657
|
|
|
Otto con Gericke demonstrates the possibility of the existence of a vacuum.
|
1658
|
Jan Swammerdam describes the presence of red blood cells.
|
|
|
1662
|
Charles the II grants money for the formation of the Royal Society of London for Natural Knowledge, one of the oldest scientific establishments in England.
|
Robert Boyle develops his gas laws, now called Boyle's laws. He stated that the pressure devided by the temperature of a gas is always equal to a constant.
|
1663
|
The first turnpike (toll road) is built in England.
|
|
|
1665
|
Another wave of plague hits London, this time Bubonic, killing many.
|
Robert Hooke publishes his observations of cells in the book, "Micographia." Hooke observed cork using his microscope and said that he saw many small compartments like monk's cells.
|
1666
|
| "The Great Fire" destroys large portions of London.
|
1667
|
|
The building of the Paris Observatory is begun.
|
|
1669
|
German Hennig Brandt makes phosphorus for the first time, from a residue of evaporated urine he obtained a white solid that glowed in the dark and ignited spontaneously in air.
|
|
Mount Etna erupts in Italy killing an estimated 20,000 people.
|
1672
|
|
Giobanni Cassini is elected to be the first director of the Paris Observatory.
|
|
1673
|
Leibniz begins this theories of integral and differential calculus.
|
The first mail system in America is established between New York and Boston.
|
|
1675
|
The Royal Observatory of England is established in Greenwich.
|
|
|
1676
|
|
German Ole Romer discovers the velocity of light.
|
|




