Numerous mining artifacts are now displayed in the museum
building, along with school and personal memorabilia, all dating
from the 1920s through the 1960s. The town itself flourished as
a company-owned and operated mining community from 1912
through 1951, at which time Consolidation Coal Company
sold all of their real estate. The model of the town on the third
floor of the museum depicts Van Lear during its heyday, the decades of the 1920s and 1930s. PLEASE REMEMBER if you plan to visit
the Museum, an "appointment" is important as all the museum
work is done by volunteers who have another life like you and I.
You may reach one of the volunteers at 606-789-9725,
via post at VLHS, Box 369, Van Lear KY 41265, or e-mail at
blevinstar@yahoo.com
1. Give nine rules for the use of capital letters. All sentences begin with capital letters; proper names of people, places, or things; titles of books, poems, movies, etc, other than prepositions and conjunctions; other important words in titles or headlines; the letter I when used as a personal pronoun; letters used as interjections as in O; the first letter in God, Bible, and words related to the Deity; the first word of a direct quotation; the title of a person; first letters of abbreviations of titles, states, etc.; words which one may wish to emphasize; months and days of the week.
2. Name the parts of speech and define those that have no modifiers. Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, article, conjunctions, prepositions, interjections; the latter four have no modifiers in normal usage.
3. Define verse, stanza, and paragraph. A verse is a sequence of words arranged metrically according to some system of design as in a single line of poetry. A stanza is a group of lines of verse forming one of the divisions of a poem or song, typically consisting of four or more lines of verse and a regular pattern as to the number of lines, meter and rhyme. A paragraph is distinct and separate section or subdivision of a chapter, letter, or written composition, always begun on a new line, often indented.
4. What are the principal parts of a verb? Give the principal parts of "lie," "play," and "run." The principal parts of the following (irregular verbs): do, does, did, doing; lie, lies, lied, lying; lay, lays, laid, laying; play, plays, played, playing, run, runs, ran, running. For regular verbs present tenses are formed by adding s to the infinitive or es following o, s, x, z, ch, and sh. Past tenses and past participles are formed by adding ed to the infinitive, as in halt and halted, start and started. Present participles are formed by adding ing to the infinitive as in halting and starting.
5. Define case; illustrate each case. Case refers to the subjective or nominative, the objective, and the possessive forms of pronouns, and the possessive form of nouns. I is the subjective or nominative case of the personal pronoun I, me is the objective case, and my or mine are the possessive case of the personal pronoun. John's is the possessive case of John showing ownership by John.
6. What is punctuation? Give rules for principal marks of punctuation. Punctuation is the use of standardized marks in writing and printing in separate sentences or sentence elements, or to make the meaning clearer when read. The period [.] is used at the end of declarative sentences, indirect questions and most imperative sentences, and after most abbreviations, as in U.S.A. The question mark [?] is used at the end of a direct question, and after each query in a series to emphasize each element. A question mark may also be used to express doubt. The exclamation mark [!} is used after an interjection or imperative sentence. The Semicolon [;] is used between two independent clauses when they are not joined by a conjunction. The Colon [:] is used before a long formal quotation, formal statement, or a list of items. The Dash [-] is used to indicate a break in the structure of a sentence or an unfinished statement, or to set off a summary or appositive. Parentheses [()] are used to enclose material that is explanatory or supplementary, or to enclose cross-references. Double quotation marks [" "] are used to enclose all direct quotations. Single quotation marks [' '] are used to enclose a quotation within another quotation. Quotation marks are used to enclose spoken words spoken and titles. The apostrophe ['] is used to indicate the possessive case of the noun or pronoun, to indicate the omission of letters or figures, and to indicate the plurals of figures, letters, and words. The hyphen [-] is used to divide a word at the end of a line and between parts of a compound modifier preceding a noun.
7-10. Write a composition of about 150 words and show therein that you understand the practical use of the rules of grammar.
Without language, we would have difficulty communicating with one another. Indeed, there once was a time when mankind had no written language, and only a crude form of spoken language. Gradually, various forms of both written and spoken languages evolved.
Modern languages are often made up of portions of many earlier languages. The English language contains elements of Latin, French, and German, and continues to change to meet the changing needs of society.
We use our language to express many things: Statements, questions, emotions, thoughts, prayers, and even our fondest hopes and aspirations. For example, have you ever wanted to share a dream that you have had with someone? You could either tell them about it orally, using spoken language, or you could take pen and paper and write a description of your dream; or, as may be more likely today, you could use your computer and word processor to compose your description. In any case, you would be using your knowledge of language and grammar in order to express what you wish to communicate.
11. Name and define the fundamental rules of arithmetic. The four fundamental rules of arithmetic are addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Addition is the summing of a set of numbers to obtain a total quantity of items to which the number set refers, and the process is indicated in arithmetic by + . Subtraction is the finding of the difference between two numbers or quantities, indicated in arithmetic by - . Multiplication is repeated addition. Multiplication is the finding of a number or quantity, referred to as the product, by repeating a number or quantity a, the multiplicand, a specified number of times, the multiplier, indicated in arithmetic by x . Division may be thought of as repeated subtraction. Division is the process of finding how many times a number, the divisor, is contained in another number, the dividend; the number of times is known as the quotient, and I indicated in arithmetic by ÷ .
12. A wagon box is 2 ft. deep, 10 feet long, and 3 ftt. wide. How many bushels of wheat will it hold? 2 x 10 x 3 = 60 cubic feet. A struck bushel equals 1 1/4 cubic feet. A heaped bushel in general equals 1 1/4 struck bushels. Therefore the wagon box if heaped contains 60 bushels and if struck, 1/5th less or 48 bushels.
13. If a load of wheat weighs 3942 lbs, what is it worth 50cts/bushel, deducting 1050 lbs for tare? 3942 – 1050 (wagon wt) = 2892 lbs divided by 58lbs/bushel = 49.86 bu x .50 = $24.93
14. District No. 33 has a valuation of $35,000. What is the necessary levy to carry on a school seven months at $50 per month, and have $104 for incidentals? The cost equals $50 X 7 + $104, or $454.The mil levy is $454 ÷ $35,000 = .013 levy or $1.30 per $100 valuation of the district’s property.
15. Find the cost of 6720 lbs of coal at $6.00 per ton. One ton equals 2000 lbs, therefore 6720 ÷ 2000 x $6 = $20.16
16. Find the interest of $512.60 for 8 months and 18 days at 7 per cent. 258 ÷ 360 X $512.60 or $25.72
17. What is the cost of 40 boards 12 inches wide and 16 ft. long at $20 per metre? 40 X 12 X $.20 = $96.00 ( 40 X 16 ÷ 1000 X $150 = $96.00 at $150/1000 board-feet)
18. Find bank discount on $300 for 90 days (no grace) at 10 per cent
.10 ÷ 4 X $300 = $7.50
19. What is the cost of a square farm at $15 per acre, the distance of which is 640 rods? One acre = 16 rods square or 256 square rods. The farm has160 rods square. 160x160=25600 square rods = 100 acres x $15/acre = $1500
20. Write a Bank Check, a Promissory Note, and a Receipt.
Bank Check:
Consumer Bank
My Town, America
July 4, 1776
Pay to the order of My Creditor
The sum of Five hundred fifty and 00/100 Dollars--------------$550.00
For services rendered __________________________
John Doe
Promissory Note:
I, John Doe, do hereby promise to pay to
Consumer Bank the amount of $550.00 in
10 equal payments of $5.50 on the first of each
month, starting August 1, 1776, ending May 1st, 1777,
plus simple interest on the principal amount of $550 at
6 per cent per annum, or $27.50 on May 1st, 1777
John Doe, July 4, 1776
Receipt:
Consumer Bank May 1, 1777
My Town, America
Received of John Doe, the sum of Five hundred seventy-seven and 50/100 Dollars --------------------------------------------------------------------------$577.50
Loan plus interest per note (attached)
Charles Official, Loan Officer
21. Give the epochs into which U. S. History is divided.
The period of discovery and settlement, 1492-1620; the period of expansion and colonization, 1620-1760; the period of revolution and independence, 1760-1780; the period of self-government, 1780-1840; the period of further expansion and testing of the union, 1840-1876; and the period of recovery as a nation, 1876 to the present (all as defined by historians in 1890).
22. Give an account of the discovery of America by Columbus.
A Norseman from Greenland named Leif Ericson established settlements along the northeastern coast of America at least 500 years before Christopher Columbus, and there may have been other Europeans who landed on the continent even earlier. However, Christopher Columbus, a Genoese Italian mariner, is generally credited with the modern discovery of America. In actual fact, Columbus may never have landed on the mainland of America. Instead, he landed on one of the islands in the Bahamas, believing that he had reached the East Indies by sailing west.
Columbus first studied drawing, geography and astronomy, and then became a sailor on the Mediterranean. He then went to Lisbon, Spain, where he became a mapmaker, under the tutelage of a mariner whose patron was Prince Henry the Navigator. Becoming convinced that the world was a sphere, he sought to prove that the shortest distance to the East Indies was by sailing westward. He had the map of Toscanelli, and believed it was correct. Around the year 1474 he began to seek funding to furnish a fleet, journeying from Genoa to Portugal, Venice, France, and England in 1484. Queen Isabella of Spain finally gave her approval and furnished half the money needed for his first voyage. The fleet consisted of three vessels, the largest, the Santa Maria, only sixty-three feet long and twenty feet in breadth, and two smaller vessels, the Pinta and the Nina. They sailed from Palos on August 3, 1492, and headed into unknown waters. Although the crews wanted to turn back, threatening mutiny, Columbus held them in check, and continued the voyage, finally sighting one of the Bahama Islands, October 12, 1492. We celebrate that day each year as a school holiday, Columbus Day. (The older 1890s “answer” to this question is more elaborate.)
23. Relate the causes and results of the Revolutionary War.
There were many causes of the War for Independence from Great Britain. By the year 1763, the colonies had begun to have serious differences with the mother country. That same year saw the creation of a New France in the province of Quebec, causing the British to fear that something similar may be afoot in the colonies. A line was drawn along the mountain sources of the rivers flowing into the Atlantic, and the colonies were
forbidden to plant settlements beyond that line.
George III, who became king in 1760, acted on the advice of his counselors, trying to enforce Cromwell's old Navigation Act of 1651 to stop smuggling, which had become the life-blood of the colonials. Writs of Assistance were adopted whereby any officer of the crown could write anybody's name in the blank line and then proceed to search private premises on the mere suspicion of there being smuggled goods in any home or store within the colonies. Boston merchants retained a lawyer named James Otis, who made an eloquent speech, but lost his case. This prompted John Adams and others to oppose the Writs and, ultimately, the Stamp Act of 1765, proclaiming, "Taxation without representation is tyranny!" The Stamp Act required every legal document, every newspaper, every bill of merchandise, and almost every form of paper to bear an official stamp. Benjamin Franklin was sent to London as agent for Pennsylvania to try to prevent the enactment of the law, but to no avail. The colonists organized a secret society, "The Sons of Liberty," and opposed the Stamp Act, which was repealed in 1766, but replaced by the even more onerous Townshend Acts of 1767. Samuel Adams, the "Father of the Revolution," drew up a circular letter, which was adopted by the Massachusetts legislature and sent to the other colonies. This action united the colonies, resulting in Great Britain sending General Gage and four armed regiments to Massachusetts to enforce the acts. On June 17, 1774, Samuel Adams introduced a resolution to the legislature calling for a Colonial Congress to combat these oppressive measures and acts. Gage heard about the resolution and hurriedly sent a messenger to deliver a proclamation dissolving the assembly. The messenger found the door locked, and was not opened until the resolution was adopted. The First Continental Congress met September 5, 1774. Independence was officially declared on July 4, 1776, and the American Revolutionary War went forward, terminating in the surrender of General Cornwallis to General Washington at Yorktown. Freedom had been won!
24. Show the territorial growth of the United States.
After the War for Independence, the acknowledged boundaries of the United States in 1783 were the St. Lawrence River and the Great Lakes to the north, the Mississippi River to the west, the northern border of the Floridas extending eastward from the mouth of the Mississippi to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east..
In 1803, President Thomas Jefferson acquired the ownership of the French province of Louisiana, a vast tract extending from the Gulf of Mexico at New Orleans west to the mountain sources of the Mississippi tributaries. This land was purchased from Napoleon for 15 million dollars, more than doubling the size of the United States. In 1819 the Floridas were purchased from Spain, after a treaty framed by John Quincy Adams, for $5,000,000, securing the southern border and the whole of the Atlantic seaboard. General Andrew Jackson was sent to stop Indian troubles along the Florida border with Georgia. By 1843 the northern border between Canada and the US west of the Great Lakes was fixed along the 49th parallel, and included all of the Oregon country below that line to the Pacific Ocean. In 1835 Texas seceded from Mexico, and at once asked for admission to the Union. President Van Buren refused, fearing war with Mexico. Texas then became the "Lone Star Republic." By 1845, Northern opposition to annexation weakened, and Texas was admitted as a slave state. On April 23, 1846, Mexicans crossed the Rio Grande and killed members of a small scouting party. War was declared with Mexico on May 13, 1846, and General Zachary Taylor was sent to prosecute the war. Much of Mexico was conquered, including Mexico City. With the treaty of peace of 1848, we annexed all of California and New Mexico, paying the Mexican government the sum of $15,000,000 "in consideration of the extension acquired by the boundaries of the United States." When another dispute arose in 1853 over the boundaries surrounding Arizona and Mexico, an additional $10,000,000 was paid to Mexico. (Both Alaska and Hawaii were subsequently added.)
25. Tell what you can of the history of the state of Kansas. (In other states, this question was amended to deal with the history of those states.)
Historians have reported that Native Americans were living in Kansas as early as 12,000 B.C. They were followed for centuries by many different tribes. Between 1541 and 1739 explorers from Spain and France came to the area in search of gold, knowledge, and trade with the Indians. In 1803, Kansas became a part of the United States as part of the Louisiana Purchase. Fifty-one years later, in 1854, it was organized as a territory, which included the eastern half of Colorado. Conflict over slavery led to bloody battles between free-staters (anti-slavery) and pro-slavery forces. This led to the attack on Lawrence by pro-slavery forces and the widespread public outcry associated with "Bleeding Kansas." Kansas became part of the United States as a free state in 1861.
After the War for Southern Independence, expansion of the rail system to Kansas and the increasing stream of immigrants lured to the state by offers of cheap land, Native Americans were forced into smaller and smaller reservations. Ultimately their removal to Indian Territory forced the final confrontation in the late 1870s that ended the independent life of the Native Americans. The establishment of military posts to protect the railroads and trails used by immigrants led to the creation of small towns. By 1870 the Kansas so-called cow towns, such as Dodge City, Abilene, Caldwell, Newton, Wichita and Salina had been settled. Kansas is now one of the leading wheat-producing states in the nation.
26. Describe three of the most prominent battles of the Rebellion.
The Battle of Chancellorsville, May 2 - 3, 1863 marked the turning point for the Confederates, even though it was a rebel victory. When General Thomas "Stonewall" Jackson was killed during this battle, General Lee said, he had lost his "right arm." The Confederates were elated with their victories at Fredricksburg and Chancellorsville and Lee was urged to carry the war into the North and compel the granting of a peace satisfactory to the South. With an army of 70,000 men, Lee crossed the Potomac, marched across Maryland and into Pennsylvania. There he was overtaken by the Army of the Potomac, 90,000 strong, under General Meade at the village of Gettysburg. On the first and second days the Confederates gained ground and control. On the third day the Union troops ceased firing to let the cannons cool. Lee thought that he had "silenced" the enemy's guns, and ordered Pickett's division of infantry to charge across the valley and pierce the Union lines. As 15,000 men marched out of the forest of oaks into the open valley, the Union cannons opened fire. Great holes were torn in the ranks. As they drew nearer the Union army closed ranks, charged the ridge, and the advance had reached a hand-to-hand fight when "retreat" was sounded, leaving the valley strewn with dead on both sides. The Battle of Gettysburg, July 1-3, 1863, was the greatest battle that the world had ever witnessed to that time. The Siege of Vicksburg, May 19 to July 4th, 1863, returned control of the entire Mississippi River and valley to the Union. Grant and Sherman had been repulsed in their first attempts to take that stronghold. Grant moved his army down the west bank of the river. He had his gunboats run past the forts, and marched his troops below Vicksburg, and re-crossed for an attack from the rear. He got between the Confederate armies of Generals Johnston and Pemberton, made Johnston retreat and drove Pemberton, after hard fighting, into Vicksburg. Grant then settled down (May 19) for a siege. Continually bombarding the city, he cut the city off from all supplies until the people were forced to eat the mules and rats. There was no relief and no escape. Pemberton surrendered with 32,000 prisoners (July 4), and the Union soldiers promptly shared their food with the starving men, women and children. Sherman’s march through Georgia and the Battle of Atlanta are also prominent actions of this war.
27. Who were the following: Morse, Whitney, Fulton, Bell, Lincoln, Penn, and Howe?
Samuel F.B. Morse invented the telegraph in 1840.
Eli Whitney invented the cotton gin in 1793, which made raising cotton profitable in the South.
Robert Fulton invented the first successful steam powered paddlewheel boat in 1807.
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1875.
Abraham Lincoln, a representative from Illinois, became our 16th President of the United States in 1860, and was reelected in 1864. Born in Hardin County, Ky., February 12, 1809, he moved with his parents to a tract of land on Little Pigeon Creek, Indiana in 1816 where he attended a log-cabin school at short intervals. Mostly self-instructed, he moved with his father’s family to Macon County, Illinois in 1830, and later to Coles County, Illinois. He read the principles of law and works on surveying. During the Black Hawk War he volunteered in a company of Sangamon County Rifles organized April 21, 1832 and was elected its captain and served until May 27, when the company was mustered out of service. He reenlisted as a private and served until mustered out June 16, 1832, returning to New Salem, Ill. He was unsuccessful as a candidate for the State house of representatives. He entered business as a general merchant in New Salem and was postmaster of New Salem from 1833-1836. He became deputy county surveyor from 1834-1836. Elected a member of the State house of representatives in 1834, 1836, 1838, and 1840, he declined to be a candidate for renomination. He was admitted to the bar in 1836, moved to Springfield, Ill. in 1837 and engaged in the practice of law. He was elected as a Whig to the Thirtieth Congress (March 4, 1847-March 3, 1849) but did not seek a renomination in 1848. He served as our president from March 4, 1861, until he was shot in the head by the actor John Wilkes Boothe as he attended a play in Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., April 14, 1865. He died the following day, April 15, 1865. He was our president and Commander-in-Chief during the War Between the States, determined that the Union should not perish, and he wrote and declared the Emancipation Proclamation, freeing all slaves.
The king of England owed William Penn a debt of fifteen thousand pounds. This debt was settled in 1682 by the granting of a tract of land, which became the colony of Pennsylvania. When the boundaries were finally set, the tract contained about 45,000 square miles. Penn was liberal to all white men and Indians, early deciding that in Pennsylvania there should be perfect freedom of conscience, and freedom of worship. In 1683 he laid out the plan of a city, which he called Philadelphia, meaning "brotherly love." All treaties and agreements that were made with the Indians and others were faithfully kept.
Elias Howe, the son of a Massachusetts farmer, invented the sewing machine in 1845, which earned for him more than two million dollars.
(Answers to this question on the Kansas exam were more elaborate.)
28. Name events connected with the following dates: 1607, 1620, 1800, 1849, and 1865
1607 - Establishment of Jamestown colony, May 1607, in what is now Virginia. Captain
John Smith had but one rule, "He that will not work shall not eat."
1620 - On December 21, 1620, the landing of the Pilgrims in Plymouth harbor began the
settlement of New England under William Bradford.
1800 - In the election of 1800, Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr received an equal number of votes. As the Constitution provided that the person having the greatest
number should be president, it became the duty of the House of Representatives to decide between the two. After thirty-five ballots the choice was Thomas Jefferson, our third president, author of the Declaration of Independence, and the mentor of James Madison, "Father of the Constitution". It was on Jefferson's insistence that Madison championed the first 10 articles of amendment to the Constitution, "The Bill of Rights."
1849 - The Gold Rush to California began after discovery of gold at Sutter's Mill on
the "American Fork" of the Sacramento River, February, 1848. The great discovery was
made just as California became American territory.
1865 - The end of the War Between The States, signified with the raising of the flag
again at Fort Sumpter, April 14, 1865, the assassination of President Lincoln at Ford's
Theater that day, and his death April 15, 1865. The war was over, a million troops of the Union armies marched through Washington in a last review, were mustered out, and returned to their homes.
29. What is meant by alphabet, phonetics, orthography, etymology, syllabication?
Alphabet - A system of characters, signs and symbols used to indicate letters or
speech sounds, the basis of all writing, as in our ABCs.
Phonetic orthography - The standardization of the sounds of the letters of the
alphabet in accordance with accepted usage. This varies from area to area within our
nation, but is becoming more and more uniform as communication and travel between the
sections increases.
Etymology - The study of the origin and development of a word, tracing it back to
its original language and to its sources in contemporary or earlier languages.
Syllabication - The process of dividing a word into syllables, to determine the
phonemic sound, the accent, and roots, to enable the reader to better grasp the meaning
and pronounce the word in speech and writing.
30. What are elementary sounds? How are they classified?
The elementary sounds are the consonants and vowels. A consonant is any speech sound
produced by stopping and releasing the air stream (p, t, k, b, d, g), by stopping it at one
point while it escapes at another (m, n, l, r), by forcing it through a loosely closed or
very narrow passage (f, v, s, z, sh, zh, th, H, kh, h, w, y) or a combination of these means.
A vowel (a, e, i, o, u and sometimes y) is a voiced speech sound characterized by
generalized friction of the air passing in a continuous stream through the pharynx and
open mouth, but with no constriction narrow enough to produce local friction. Phonemes include all significant differences of sound, including features of voicing,
place and manner of articulation, accent, and secondary features of nasalization,
glottalization, labialization, and the like. Labial sounds are mainly formed by the lips;
glottal speech sounds are formed mainly by closure of the glottis; nasal sounds are
formed primarily by resonance in the nasal passages.
31. What are the following, and give examples of each: trigraph, subvocals, diphthong, cognate letters, linguals?
A trigraph is a combination of three letters representing one sound. An example is eau as in bureau.
A subvocal is beneath the voice, a silent or nearly silent sound.
A diphthong is a complex vowel sound made by gliding continuously from the position
of one vowel to that for another within the same same syllable. An example is (ou) as in down.
Cognate letters are related in derivation, for instance, i and y.
Linguals are sounds articulated by using the tongue, for instance the sound th.
32. Give three substitutes for caret 'u.'
Substitutes for caret 'u' are oo as in tool, eau as in bureau, ew as in crew.
33. Give two rules for spelling words with final 'e.' Name two exceptions under each rule.
When spelling words having a final silent e, drop the e when adding a suffix beginning
with a vowel. Exceptions - knowledgeable, despiteous. If the suffix or verb ending begins with a consonant, keep the final e. Exceptions - truly, judgment
34. Give two uses of silent letters in spelling; illustrate each.
Sometimes words have silent letters. These follow patterns that can be memorized.
Examples:
gn, pn, kn = n as in gnome, pneumonia, knife
rh, wr = r as in rhyme, wrestle
pt, ght = t as in ptomaine, height
ps, sc = s as in psalm, science
wh = h as in whole
35. Define the following prefixes and use in connection with a word: bi, dis, mis, pre, semi, post, non, inter, mono, sup
a.) bi - having two elements or natures, i.e., biangular, bifurcated.
b.) dis - meaning away or apart from, i.e., disassemble, disregard.
c.) mis - meaning wrong, wrongly, bad, badly, i.e., misstep, misapply.
d.) pre - meaning before, ahead of, i.e., predate, prescience.
e.) semi - meaning not whole, partly, not fully, i.e., semicircle, semifinal.
f.) post - meaning after, behind, i.e., postscript, postpartum.
g.) non - meaning not, i.e., nonhuman, nonagressive.
h.) inter - meaning between, among, or reciprocal, i.e., intercede, interchangeable.
i.) mono - meaning one, single, alone, i.e., monocline, monotheism.
j.) super - meaning above, over, on top of, i.e., superabundant, superpose.
36. Mark diacritically and divide into syllables the following, and name the sign that indicates the sound: card, ball, mercy, sir, odd, cell, rise, blood, fare, and last
[ Note: Because of the limitations of html, the "macron" diacritical mark for vowels, a dash over the vowel, signifying the sound of the vowel name, is shown as ¯a, ¯e, ¯i, ¯o, ¯u ]
card = cärd, ball = bôl; mercy = mur'c¯e; sir = sur; odd = ãd; cell = sel; rise = r¯is;
blood = blud; fare = fer; last ~ last
37. Use the following correctly in sentences: cite', site, sight, fane, fain, feign, vane, vain, vei n, raze, raise, rays
a.) We cite references to indicate sources of information.
b.) The site was surveyed as the place where we would build.
c.) The sight of her caused him embarrassment.
d.) We celebrated the re-birth at fane.
f.) She would fain stay with her husband.
g.) Can you feign surprise even though you had prior knowledge?
h.) The vanes on the windmill cause it to move with the wind.
i.) It is vain to think you are better than another.
j.) Mother has a varicose vein in her leg.
k.) We will raze the old barn.
l.) Today they started to raise a new barn.
m.) The rays of the sun are warm.
38. Write 10 words frequently mispronounced and indicate pronuciation by use of diacritical marks and by syllabication.
a.) anonymity == an' o nym' i ty
b.) bestial == b¯es' tyal
c.) Capernaum == Ca pur' na um
d.) datum == d¯at' um
e.) either == ¯e' ther
f.) finaancier == fin' an sir'
g.) get == get
h.) homonym == häm' a nim
i.) inchoate == in k¯o' it
j.) I couldn't think of one starting with a "j", so, Salina == Sa l¯i' na , not Sa l¯e' na (The preceding were on the Kansas exam)
39. What is climate? Upon what does climate depend?
Climate is the prevailing or average weather of a place as determined by the temperature and meteorological changes over a period of years. The climate of a place depends largely on the latitude of the place, the features of the surrounding terrain, the nearness to an ocean, or a mountain range which channels and directs wind patterns. We have seasons in our weather pattern, and changes in the length of the warming day thoughout the year, due to the ecliptic of the earth's annual path around the sun. It is the daily warming and cooling of the land and oceans that is the prime generator of the world weather system. (The Kansas answer)
40. How do you account for the extremes of climate in Kansas?
The extremes of climate in Kansas are predicated on the fact that the state is in the middle of the continent and the Great Plains, not near any mountains or oceans, exposed in winter to cold winds from the north in Canada, and in summer to heavy moisture laden winds from the Gulf of Mexico. It is the meeting of these two wind sources in fall that creates the huge wind vortices and deep moist convections which become the tornadoes that are a yearly danger in Kansas. (Answers in other states reflected that state’s own weather characteristics, peculiar to its location.)
41. Of what use are rivers? Of what use is the ocean?
Rivers drain off excess water from the land surface; replenish the aquifers under their stream bead and underlying all of Kansas, from which we get most all of our water for irrigation and human consumption; the river is a highway of commerce, with the steamboats reaching far into the west; and rivers serve as places of recreation, fishing, boating and swimming. Oceans are the reservoir for the majority of heat received from the sun, for the runoff of all rivers and aquifers, the source of most all rain from the evaporation of the surface waters, and the engine which drives our weather patterns, and the moderator of coastal climates. The ocean fisheries are a major source of protein to many of the world's peoples. International commerce would not be possible except for the navigation of the oceans.
42. Name and describe the major mountains of North America.
The mountains of North America lay in four great chains, oriented generally north to south. They are in order from East to West, the Appalachian/Adirondack chain inland from the Atlantic coast which includes the Blue Ridge and Smokey mountains. They are an old range, worn down thru the eons. Across the Great Planes from them, midway to the Rocky Mountains, are the Black Hills of the Dakotas, somewhat isolated from the Rockies. The Rocky Mountains, consisting of many parallel ranges, are located at the western boundary of Montana, running southeasterly from the Yukon to Arizona and New Mexico. They form the Continental Divide, which determines the course of the rivers emptying into the Mississippi drainage, and those emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The high plateaus and basins of Utah and Nevada by and large intervene between the Rockies and the next great chain, the Sierra mountain range in California and the extension northward in Oregon and Washington State, where they are called the Cascade Range. Beyond the Sierra/Cascades across the interior valleys of California and Oregon is the Coastal Range, laying quite close to the Pacific Ocean. Westerly from the Cascades in Washington on the Pacific Coast is the Olympic range north of the Columbia River forming the Olympic peninsula. The Olympics have one of the important rainforests of the world and are a valuable source for timber, as are all the mountain ranges of North America. Most mining in North America is in the mountains, the eastern Appalachian Mountains are a source of coal and iron, the Rockies and Sierras are a source of gold, silver and other metals.
43. Name and describe the following: Monrovia, Odessa, Denver, Manitoba, Hecia, Yukon, St. Helena, Juan Fernandez, Aspinwall, and Orinoco
Monrovia City is the capital of the nation of Monrovia (Liberia), on the Atlantic Ocean, at the mouth of the Saint Paul River. Monrovia was founded in 1822 by the American Colonization Society as a refuge for freed slaves from North America, and was named in honor of United States president James Monroe
Odessa is capital of the Odessa region of the Ukraine, a port on Odessa Bay of the Black Sea. The third largest Ukrainian city after Kiev and Kharkiv, Odessa is an important rail junction and transportation hub. Odessa is also the name of an important city in Texas.
Denver, the capital of Colorado, is known as the Mile High City. Situated on the high plateau of the Rocky Mountains, it has a sunny, cool, dry climate, averaging 13 inches of precipitation a year. Denver was established by a party of prospectors on November 22, 1858, after a gold discovery at the confluence of Cherry Creek and the South Platte River. Town founders named the dusty crossroads for James W. Denver, editor of the Rocky Mountain News.
Manitoba, a province in south central Canada and the easternmost of Canada's three Prairie provinces, was part of the Hudson's Bay Company's holdings in North America
known as Prince Rupert's Land, founded in 1670.
Mount Hecla, one of the most active volcanic constructs in Iceland, is also the site of descent into the interior in Jules Verne's "Journey to the Center of the Earth."
The Yukon is Alaska's largest river. It originates in Canada in the Yukon Basin of the Northwest Territory and flows 2,000 miles west into the Bering Sea.
St. Helena is an island in the Atlantic about mid-way between South America and Africa. It was uninhabited when first discovered by the Portuguese in 1502.
The Juan Fernandez Islands, (33º 50'S, 80º 00'W) have developed in isolation, about 400 miles west of Santiago in Chile, on two small islands of volcanic origin, Robinson Crusoe Island and Santa Clara Island. The Spanish explorer Juan Fernandez discovered the islands in 1574.
Aspinwall, a town in Georgia, is in the area where the Seminole/Muskogee Indians lived.
The Orinoco River in Venezuela is one of South America's longest rivers, extending 1,590 miles from its source in the Guiana Highlands, on the slopes of the Sierra Parima, in extreme southeastern Venezuela, on the border of Brazil. It flows northwest to a point near La Esmeralda, where it divides. One arm, the Casiquiare River, goes south and after a course of 180 mi enters theRio Negro, a tributary of the Amazon River. The Orinoco is navigable for oceangoing ships for 260 miles, from the mouth to the city of Ciudad Bolivar. The Orinoco was sighted in 1498 by Christopher Columbus and was first explored by Europeans (1530-1531) to the confluence with the Meta River. The German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt explored the upper reaches in 1799.
44. Name and locate the principal trade centers of the U.S.
The principal trade centers of the United States are New York, New York, located at the mouth of the Hudson River; Boston, Massachusetts, located in Boston Harbor; Chicago, Illinois, located at the south end of Lake Michigan; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, located on the reaches of Delaware Bay; Baltimore, Maryland, located on the reaches of Chesapeake Bay; New Orleans, Louisiana, located between Lake Pontchartrain and the Mississippi River inland from the Gulf of Mexico; St. Louis, Missouri, located at the confluence of the Missouri River and the Misssissippi; Kansas City, Missouri, located on the Missouri River at the Kansas River confluencee, also being a great rail hub; Denver, Colorado, situated at the eastern slope of the Rockies as noted above; Los Angeles, California, in southern California at Los Angeles Harbor; San Francisco in the north of California at San Francisco Bay; and Seattle, Washington, located on east side of Puget Sound in Washington State, now becoming an important trade center in addition to its primary lumber industry and naval shipyards. (1890s)
45. Name five republics of Europe and their capital cities.
France with its capital at Paris, and Switzerland with its capital at Bern are the only
republics in Europe. There are no other republics in Europe as we know a republic to be, all the other nations are constitutional monarchies, or principalities. The major monarchies are Great Britain, London; Germany, Berlin; Russia, St. Petersburg; Ukraine, Kiev; Austria/Hungary, Vienna; Italy, Rome; Spain, Seville; Porugal, Lisbon; Belgium, Brussels; Holland, Amsterdam; Denmark, Copenhagen; Norway, Oslo; and Sweden, Stockholm. (An 1890s “trick question?”)
46. Why is the Atlantic Coast colder than the Pacific in the same latitudes?
The Atlantic coast is colder because the northward flow of the Japanese current prevents the majority of cold artic air from sinking south along the Pacific coast, until east of the Rocky Mountains, sweeping thence across the northern plains, sinking to lower latitudes bringing freezing weather south as far as Florida.
47. Describe the process by which the water of the ocean returns to the sources of rivers.
As the sun heats the ocean waters the evaporate rises into the prevailing wind currents which flow generally from west to east. On reaching mountainous areas the wind currents rise and are cooled, condensing the evaporate into rain, hail, or snow, which then returns to earth, the excess which is not absorbed becoming run-off and forming rivulets, streams, then rivers, returning to the sea to repeat the process over again. Eventually, even the water which is absorbed in the earth also returns to the see, as in our Colorado/Kansan aquifer, although that may take many thousands of years.
48. Describe the movements of the earth. Give the inclination of the earth in degrees.
Today we know that the earth is involved in five motions, Rotation, Revolution, Precession, Motion around the galactic nucleus, and Motion of the galaxy. The rotation or spinning motion of a planet about an axis is the most basic of the five planetary motions. The earth rotates about its axis once every 24 hours, producing changes in what portion of the Earth is illuminated by the Sun, creating our day and night. The tern "revolution" refers to the orbital motion of the earth as it travels an elliptical path around the sun. The earth's period of revolution, i.e., the time to complete a revolution, is 365.25 days. As the earth's axis is inclined 23.4 degrees relative to the orbital plane, this produces our seasons. The Earth's axis is "wobbling", meaning that the axis changes its orientation with respect to celestial objects. This wobbling motion is referred to as "precession". Precession is similar to the wobbling motion of a top as it spins. The earth's period of precession is about 26,000 years. As we look out into the nighttime sky we cannot help but ponder the vastness of space and the innumerable stars that fill it. Our Sun is one of 100 billion stars that are gravitationally bound and make up the Milky Way Galaxy. Because we are a part of the galaxy, it is difficult for us to determine its shape and size and our location in it. However, based on the best available information, the Milk Way is a spiral galaxy similar in structure to its nearest neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy. Our Sun is located in the flattened disk approximately two-thirds of the way from the central bulge in a spiral arm. Just as the planets orbit the Sun, the Sun orbits around the galactic nucleus. The velocity of the Sun and the planets around the galactic nucleus is consistent with the laws of Kepler and Newton. Astronomers calculate that this period of revolution around the galaxy center is 240,000,000 years. The suspected motion of the galaxy through space has not yet been determined. (As of 1890 and beyond)
The preceding constituted the “exam” in a number of states. The exam in Kansas included the following health-related questions:
49. Where are the saliva, gastric juice, and bile secreted? What is the use of each in
digestion?
Saliva is secreted in the mouth by the salivary glands. Saliva is a somewhat alkaline fluid that moistens the mouth, softens food, and aids in digestion. The submaxillary glands are located around the mouth under the lower jaw, the sublingual glands are located beneath the tongue, and the parotid glands are found in front of each ear. The buccal glands, in the cheeks near the front of the mouth, also secrete saliva.
Gastric juice is a thin, strongly acidic (pH varying from 1 to 3), almost colorless liquid secreted by the glands in the lining of the stomach. Its essential constituents are the digestive enzymes pepsin and rennin, hydrochloric acid, and mucus. Pepsin converts proteins into simpler, more easily absorbed substances; it is aided in this by hydrochloric acid, which provides the acid environment in which pepsin is most effective. Rennin aids the digestion of milk proteins. Mucus secreted by the gastric glands helps protect the stomach lining from the action of gastric juice. Gastric secretion is stimulated by a number of hormones and chemical substances, by the presence of food in the stomach, and by a number of psychological factors, such as the smell of a favorite food.
Bile is a yellowish-brown or green fluid secreted by the liver in the bile duct. This liquid carries away waste from the processes of the liver and helps in the digestive process.
50. How does nutrition reach the circulation?
Nutrients reach the circulation by absorbtion thru the intestinal walls. The main purpose of the intestines it to take the partially digested food from the stomach and convert it into energy. The small intestine is about 20 feet long. The small intestine is divided into three sections, the duodenum, the jejunum and ileum. The small intestinal glands secrete intestinal juices that helps with the digestive process. The liver dumps bile into the small intestine through the bile duct. The pancreas secretes pancreatic enzymes into the small intestine. Bile and the pancreatic enzymes break down fats, proteins and carbohydrates. This partially digested mixture empties into the large intestine through an opening the ileocecal valve. The main purpose of the large intestine is to further digest the food, releasing nutrients into the blood and to absorb fluids.
51. What is the function of the liver? Of the kidneys?
The liver is the center for the storage of vitamins and nutrients which are dissolved and digested in the intestines. The nutrients are carried to the liver by two large veins. Blood passes through the liver at a rate of about 1 1/2 quarts per minute. At any given time the liver contains about 10% of all the blood in your body. The liver is divided into two main parts called lobes. The liver is protected by the bottom part of the ribs on the right side of your chest and the liver weighs between 3 and 4 pounds. The liver also works to make bile. Bile is used to break down fats in the small intestine. The bile is stored in the gall bladder until it is needed to help digest the food you eat. If you eat a real fatty food your body will need more bile to help digest those fats than it would need in comparison to a salad or some fruit.
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located near the middle of the lower back, just below the rib cage. The kidneys are sophisticated trash collectors. Every day, the kidneys process about 200 quarts of blood to sift out about 2 quarts of waste products and extra water. The waste and extra water become urine, which flows to the bladder through tubes called ureters. The bladder stores urine until you go to the bathroom. The wastes in the blood come from the normal breakdown of active muscle and from the food we eat. Our body uses the food for energy and self-repair. After our body has taken what it needs from the food, waste is sent to the blood. If our kidneys did not remove these wastes, the wastes would build up in the blood and damage our body.
52. How would you stop the flow of blood from an artery in the case of laceration?
If the laceration is in an arm or a leg, I would apply a tourniquet around the limb between the laceration and the heart, tightening it until the flow was stopped, loosening the tourniquet every 10 minutes to let blood pass to nourish the cells beyond the tourniquet, at the same time applying pressure over the laceration with a cloth pad to staunch the loss of blood. A laceration of the arteries of the neck obviously cannot be controlled by a tourniquet, in which case pressure should be applied with a cloth pad. Loss of blood and oxygen to the brain can quickly lead to death.
53. Give some general directions that you think would be beneficial to preserve the human body in a state of health.
Regular meals should include a variety of foods, both animal and vegetable. Regular exercise is needed to keep the muscles, heart and lungs in good tone. Regular rest of from 7 to 8 hours sleep a night is important. Regular personal hygiene, brushing teeth, washing skin and hair with good soap should be practiced everyday. Regular times of ease, prayer and meditation are important.
(Personal answers to these latter questions varied. Don't worry too much if you had difficulty answering these quesstions correctly, and no, we didn't have to take this exam at Van Lear. However, we DID have an excellent school sysytem (thanks to people like C. V. Snapp and Verne P. Horne). This exam may be a cause for some concern over the present state of our public schools, and their use of the time allotted to them for classroom instruction. Or not.
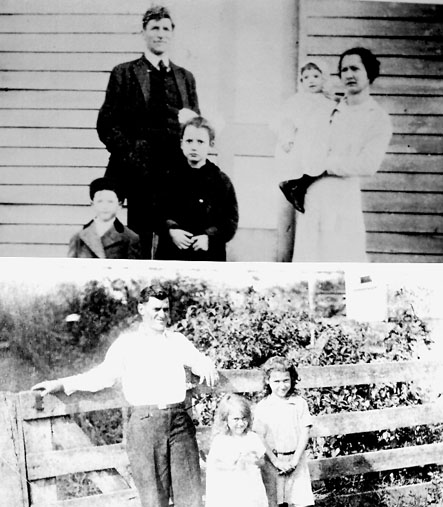



We are indebted to numerous donors of old photos, particularly
the late Silva Lyon, son of Van Lear's second physician, Doctor
John Lyon (Dr. Sparks was the first). If you have a photo that
you would like to see in this space, send a copy to us. If you
choose to view any of the photos via the hypertext links that follow, be sure to come back to our Website via the BACK< button on your browser screen.



