^“THE
CONTINENCE OF SCIPIO”,
Le
Moyne's depiction and many others, and Livy's text which inspired them.
— The
Continence of Scipio by Le Moyne
— The episode
depicted, narrated by Livy and Valerius Maximus, tells of how after the
taking of New Carthage in 209 BC Scipio had treated with respect a beautiful
virgin princess, one of the hostages who had been consigned to him, and
had sent her back to her intended husband and parents with the sole recommendation
that her suitor strive for peace between Rome and Carthage.
From the Renaissance onwards The Continence
of Scipio was an extremely popular subject in European art. During the Second
Punic War (218-201 BC), the Roman military commander Publius Cornelius Scipio
(c. 235-183 BC) took the city of New Carthage in Spain. The Romans gained
vast booty and the historian Livy tells how Scipio could have taken as his
concubine the most beautiful and noble girl of the city, captured along
with many others, but did not make use of his right, returning her to her
beloved.
Once Carthago
Nova (Kartagenea: modern Cartagena) was captured, commanding general Publius
Cornelius Scipio acted with great humanity toward the people thus put in
his power. The Carthaginian citizens he set free and restored to their property;
of two thousand artisans (it was the main armory of Spain), he promised
freedom if they would work in the Roman service. Others he enrolled as rowers
for the ships he had captured in the harbor. The large number of Spanish
hostages that had been kept in the city, he sent home, a calculated diplomatic
move. During the capture, some young Roman soldiers came across an exceptionally
beautiful girl. Knowing that Scipio had an eye for beautiful women, they
brought her to their commander as a present. Scipio was astonished at her
beauty, but mindful of his position of Commander expressed his gratitude
to his men, he showed his own moderation and self-restraint by refusing
the gift. Learning that the girl was betrothed to a young Spanish chief
named Allucius, Scipio sent for the young man and presented her to him.
When the girl's parents came to thank him and presented him with gifts,
Scipio turned the gifts over to Allucius as a dowry from himself. Thus Scipio's
reputation for kindness and generosity was spread far and wide among the
Spanish tribes. This gallant act may well have been politically inspired
- Allucius himself soon after joined Scipio with 1,400 Spanish warriors
of his tribe. But it has been the inspiration of dozens of works of art.
— Livy, Roman
History, XXVI, 50 (Original Latin: Ab
Vrbe Condita)
Captiva
deinde a militibus adducitur ad eum adulta virgo, adeo eximia forma
ut quacumque incedebat converteret omnium oculos. Scipio percontatus
patriam parentesque, inter cetera accepit desponsam eam principi Celtiberorum:
adulescenti Allucio nomen erat. Extemplo igitur parentibus sponsoque
ab domo accitis, cum interim audiret deperire eum sponsae amore, ubi
primum venit, accuratiore eum sermone quam parentes adloquitur. "Iuvenis",
inquit, "iuvenem appello, quo minor sit inter nos huius sermonis verecundia.
Ego cum sponsa tua capta a militibus nostris ad me ducta esset audiremque
tibi eam cordi esse, et forma faceret fidem, quia ipse, si frui liceret
ludo aetatis, praesertim in recto et legitimo amore, et non res publica
animum nostrum occupasset, veniam mihi dari sponsam impensius amanti
vellem, tuo cuius possum amori faveo. Fuit sponsa tua apud me eadem
qua apud soceros tuos parentesque suos verecundia; servata tibi est,
ut inviolatum et dignum me teque dari tibi donum posset. Hanc mercedem
unam pro eo munere paciscor: amicus populo Romano sis et, si me virum
bonum credis esse quales patrem patruumque meum iam ante hae gentes
norant, scias multos nostri similes in civitate Romana esse, nec ullum
in terris hodie populum dici posse quem minus tibi hostem tuisque
esse velis aut amicum malis."
Cum adulescens, simul pudore et gaudio
perfusus, dextram Scipionis tenens deos omnes invocaret ad gratiam
illi pro se referendam, quoniam sibi nequaquam satis facultatis pro
suo animo atque illius erga se merito esset, parentes inde cognatique
virgines appellati; qui, quoniam gratis sibi redderetur, virgo ad
quam redimendam satis magnum attulissent auri pondus, orare Scipionem
ut id ab se donum acciperet coeperunt, haud minorem eius rei apud
se gratiam futuram esse adfirmantes quam redditae inviolatae foret
virginis. Scipio quando tanto opere peterent accepturum se pollicitus,
poni ante pedes iussit vocatoque ad se Allucio. "Super dotem" inquit
"quam accepturus a socero es, haec tibi a me dotalia dona accedent";
aurumque tollere ac sibi habere iussit. His laetus donis honoribusque
dimissus domum, implevit populares laudibus meritis Scipionis: venisse
dis simillimum iuvenem, vincentem omnia cum armis, tum benignitate
ac beneficiis. Itaque dilectu clientium habito cum delectis mille
et quadringentis equitibus intra paucos dies ad Scipionem revertit.
|
Soon afterwards an adult maiden who had been captured was brought
to him by the soldiers, a girl of such exceptional beauty that she
attracted the eyes of all wherever she went. On inquiring as to her
country and parentage, Scipio learnt, amongst other things, that she
had been betrothed to a young Celtiberian noble named Aluccius. He
at once sent for her parents and also for her betrothed, who, he learnt,
was pining to death through love of her. On the arrival of the latter
Scipio addressed him in more studied terms than a father would use.
"A young man myself," he said, "I am addressing myself to a young
man, so we may lay aside all reserve. When your betrothed had been
taken by my soldiers and brought to me, I was informed that she was
very dear to you, and her beauty made me believe it. Were I allowed
the pleasures suitable to my age, especially those of chaste and lawful
love, instead of being preoccupied with affairs of state, I should
wish that I might be forgiven for loving too ardently. Now I have
the power to indulge another's love, namely yours. Your betrothed
has received the same respectful treatment since she has been in my
power that she would have met with from her own parents. She has been
reserved for you, in order that she might be given to you as a gift
inviolate and worthy of us both. In return for that boon I stipulate
for this one reward-that you will be a friend to Rome. If you believe
me to be an upright and honorable man such as the nations here found
my father and uncle to be, you may rest assured that there are many
in Rome like us, and you may be perfectly certain that nowhere in
the world can any people be named whom you would less wish to have
as a foe to you and yours, or whom you would more desire as a friend."
The young man was overcome with bashfulness
and joy. He grasped Scipio's hand, and besought all the gods to recompense
him, for it was quite impossible for him to make any return adequate
to his own feelings, or the kindness Scipio had shown him. Then the
girl's parents and relatives were called. They had brought a large
amount of gold for her ransom, and when she was freely given back
to them, they begged Scipio to accept it as a gift from them; his
doing so, they declared, would evoke as much gratitude as the restoration
of the maiden unhurt. As they urged their request with great importunity,
Scipio said that he would accept it, and ordered it to be laid at
his feet. Calling Aluccius, he said to him: "In addition to the dowry
which you are to receive from your future father-in-law you will now
receive this from me as a wedding present." He then told him to take
up the gold and keep it. Delighted with the present and the honorable
treatment he had received, the young man resumed home, and filled
the ears of his countrymen with justly-earned praises of Scipio. A
young man had come among them, he declared, in all ways like the gods,
winning his way everywhere by his generosity and goodness of heart
as much as by the might of his arms. He began to enlist a body of
his retainers, and in a few days returned to Scipio with a picked
force of 1400 mounted men. |
_ Compare:
Batoni's
The
Continence of Scipio (1772, 226x297cm) _ This painting of Batoni [25
Jan 25 1708 – 04
Feb 1787] canvas forms a pair with Thetis
Takes Achilles from the Centaur Chiron, likewise commissioned
by Catherine the Great (who selected the theme, probably finding it in De
Genealogia Deorum Gentilium of Giovanni
Boccaccio [Jun/Jul 1313 – 21 Dec 1375]). The two works are similar
both in composition and in coloring. Scipio wears a deep pink cloak - this
is the color of the victorious hero - as he returns the girl to her kneeling
beloved, while the white dress of the prisoner symbolizes her innocence.
There are various marvelously painted vases in the foreground: Batoni was
a jeweler in his youth and he loved to make small, detailed, elegant still
lifes through the introduction of extraneous items.
dell'Abbate
's The
Continence of Scipio
Eeckhout's
The
Continence of Scipio (1652) [giant size reproduction]
van
Mander's The
Continence of Scipio (1600) [giant size reproduction]
Pellegrini's The
Continence of Scipio
Reynolds's
The
Continence of Scipio (1789, 240x166cm) _ In 1785 the British diploma
Lord Carysfort was entrusted with a commission to Reynolds for two paintings,
one for Catherine the Great of Russia, and the other for her favorite friend
and adviser, Prince Grigory Potemkin. The artist himself was to choose the
subject. For Potemkin's painting, Reynolds settled on a subject from Livy's
"History
of Rome". Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (235 – 183 BC), military
commander and hero of the Second Punic War, showing virtue and great restraint
(or "continence"), returns a beautiful captive Carthaginian woman to her
fiancée. This was a very obvious hint at the virtue of Potemkin himself
- a renowned general, he led the Russian army in numerous campaigns against
Turkey. The composition is based on a contrast between the powerful figure
of the hero, calm and unshaking, and the tender captive, almost fainting
at the horror of what she thinks lies before her. The painting was exhibited
at the Royal Academy of Arts in 1789 and met with a mixed reaction. Some
criticized the overloaded composition as a major defect, others noticed
the beautiful coloring, "equal to the finest works of the Flemish School".
Steen's
The
Continence of Scipio (1665)
Bellini's
Continence
of Scipio (left half), _ (right
half) (1508) _ detail
Poussin's
The Noble Deed
of Scipio (1640)
Van
Dyck's The
Continence of Scipio _ One of Van Dyck's most important "history paintings",
it was probably commissioned in 1620-21 by George Villiers, 1st Duke of
Buckingham and favorite of James I. Although it ostensibly represents a
classical subject it is thought to be an allegory of the difficult circumstances
surrounding the marriage of Buckingham to Lady Katherine Manners, and the
figures holding hands are likely to be portraits of the couple. Like his
master Rubens, Van Dyck had a keen interest in antiquity, and he invokes
the world of ancient Carthage with the inclusion of a Roman frieze copied
from a piece known to have been in the Earl of Arundel's celebrated collection
of antiquities.
|
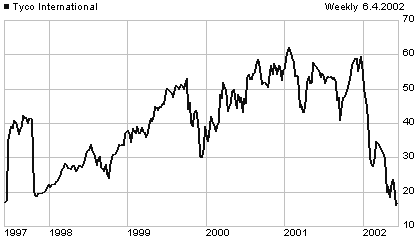 On 03 June Tyco's board forced the resignation of Kozlowski. If it had fired
him, Tyco would have probably had to pay Kozlowski a severance package of
at least $120 million. Kozlowski also resigned on 03 June as a director
of the Raytheon Company.
On 03 June Tyco's board forced the resignation of Kozlowski. If it had fired
him, Tyco would have probably had to pay Kozlowski a severance package of
at least $120 million. Kozlowski also resigned on 03 June as a director
of the Raytheon Company.