Pleural Effusion
The Image
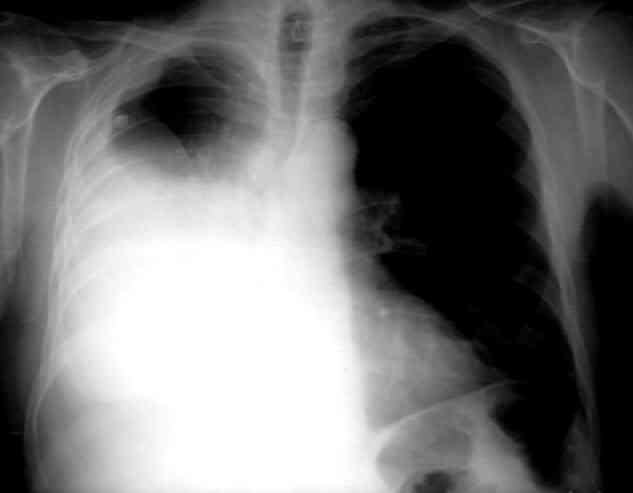
General Features in Pleural Effusion
Effusions may include exudates, transudates or malignancies. The costophrenic sulcus is frequently blunted, and this is often first seen on lateral X-rays. A decubitus film is helpful. The effusion often forms a meniscus at its interface with the chest wall and shows a homogeneous density. Large effusions shift the mediastinum and may cause some underlying lung collapse. Infectious or neoplastic effusions may become loculated.
Diagnosis
Lung Carcinoma with Pleural Effusion.
Back to Case 3: Atelectasis
Forward to Case 5: C.O.P.D.
Return to Radiology for Medical Students Index
This page hosted by
 Get your own Free Homepage
Get your own Free Homepage
