 |
| |
|
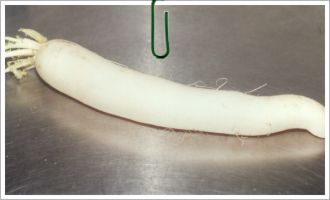
Diakon |
 |
- Aliases
- Oriental Radish, Japanese Radish, and Giant White Radish
- Description
- Diakon is a root vegetable believed to have originated in the eastern Mediterranean. It is a smooth-fleshed white skin winter radish
It's color can range from white to pink to black to green. The variety most commonly available is about 1 foot long and 1 to 4 inches in diameter.
They can weigh up to 50 pounds if they are left to grow, but are rarely seen this size in the market.
- Preparation and Serving
- Scrub or peel removing only a thin layer of the outside. It can be grated, or cut into cubes, sticks, or thin slices. It can be eaten raw or
cooked. Cooked diakon is used much like a turnip in soups and stews. Raw diakon can be used to add some crunch and spice to salads and
relishes.
- Recipe Links
- Miso Soup Varieties
- Diakon and Tuna Salad
- Kim Chee
- Seared Ahi Salad with Shoyu Daikon, Wasabi and Ginger Vinaigrette
- Fried Oyster Hot Pot
- Shake to daikon no gyunyu nabe -- Salmon and long white radish milk dish
- Jellyfish, Daikon and Chicken Breasty Salad
- Chirizu (Spicy Dipping Sauce for Sashimi)
- Watercress, Bell Pepper, and Daikon Radish Salad
- Links
- Melissa's Mini Merchandiser
- PLANTanswers--Texas A&M
- Epicurious Food Dictionary
- Nutritional Information
Nutritional Value per 100g Edible Portion
| Diakon |
Raw |
Cooked |
| Calories |
18 |
17 |
| Water |
94.5% |
n/a |
| Carbohydrates |
3.7 g |
n/a |
| Protein |
0.60 g |
0.67 g |
| Fat |
0.10 g |
0.24 g |
| Fiber |
0.64 g |
0.49 g |
| Calcium |
27 mg |
17 mg |
| Iron |
0.40 mg |
0.15 mg |
| Magnesium |
16 mg |
9 mg |
| Phosphorous |
23 mg |
24 mg |
| Potassium |
227 mg |
285 mg |
| Sodium |
21 mg |
13 mg |
| Thiamine (B1) |
0.020 mg |
0 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
0.020 mg |
0.023 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
0.200 mg |
0.150 mg |
| Ascorbic Acid (C) |
22.0 mg |
15.1 mg |
Report filed 04.23.98
Last updated 08.16.98
| |
|
|
![]()
![]()