Research Center
Islam
Games
Links
Chat Room
World Time
Autobiography
Email Me
Net Search
This Site Contains No Frames!
Webmaster: Anees Udyawar
Copyright ©1998, 1997 by Geocities
Corp.
This site is restrictedly for educational,
entertainment and leisure purposes.
If you do copy some
of my articles or pictures please email me and tell me where they have been placed. |
By:Anees Udyawar
This is a brief research report I had
performed in my English class, and wished to put on the
internet that other people may achieve some informations
on this extraordinary comet!
Comet's do not follow the rules of
heavenly bodies like stars, sun, moon and planets.
A comet can appear in the sky without warning, they
become brighter and brighter for a while then grow
dimmer and dimmer and will finally disappear. Comet
coming like that unexpectedly, seemed to be a warning
of something unusual. To most
people "something
unusual" was frightening in the beginning! One way to
prove that the sight of a comet was disaster is that
people would record the year of an appearance of a comet
and then would describe the terrible events and things
that took place soon afterwards. Of course, terrible
things happen every year, whether comets appear or not.
Take for instance a comet was sighted in 11 BC which was
then connected with the assassination of Julius Caesar
in the very same year. Or when a comet was spotted in
66 AD and four years later in 70 AD Jerusalem fell into
Roman hands. Also when the fall of Constantinople to
the Turks in 1453 was blamed on a comet that appeared
in 1456. Can this be true that comet's are viewed as a
heavenly comment on the destruction of mankind? Comets
often become scapegoats for historical events around
the world, because there is nothing else to take the
blame for! To most
people "something
unusual" was frightening in the beginning! One way to
prove that the sight of a comet was disaster is that
people would record the year of an appearance of a comet
and then would describe the terrible events and things
that took place soon afterwards. Of course, terrible
things happen every year, whether comets appear or not.
Take for instance a comet was sighted in 11 BC which was
then connected with the assassination of Julius Caesar
in the very same year. Or when a comet was spotted in
66 AD and four years later in 70 AD Jerusalem fell into
Roman hands. Also when the fall of Constantinople to
the Turks in 1453 was blamed on a comet that appeared
in 1456. Can this be true that comet's are viewed as a
heavenly comment on the destruction of mankind? Comets
often become scapegoats for historical events around
the world, because there is nothing else to take the
blame for!
Finally in 1682, and English
astronomer,
named Edmund Halley observed a bright comet in the sky,
and began his attempts to calculate its orbit. It was
not an easy task at first, but Halley worked on it for
many years. He was soon surprised to notice that the
comets sighted in 1066, 1145, 1222, 1301, 1378, 1456,
1531, 1607, and 1682, had traveled across the same
portion of the sky, and so he deducted the comets to be
Halley's comet. After Halley calculated that it took
75-76 years between each comet sighting, he predicted
that the same comet will again appear in 1758, but he
never got a chance to see his comet again because he
died in 1742! Sighting of comets that are most
spectacular are ones with very long orbits that approach
the sun only once in many thousand years. These types
of comets have few occasions when they come close to
our sun. When this happens they only lose some of their
particles and survive much longer.

Comets that appear once in a thousand years are called
"new comets"
because when they do appear it will be the first time
they will ever be observed scientifically. A good time
to look for a new comet is to look for it at night or in
early morning with a powerful telescope. Of course if
you do sight a comet you should make sure that the comet
has not already been discovered before by somebody else.
So how many comets are there? Kepler, when asked this
question four centuries ago answered, "As many as there
are fish in the sea". Nowadays we see many more comets
than people did in Kepler's time, for now we have the
telescope, so that a new comet is spotted on the average
on two to three weeks. So the next question is, how
are comets formed? Well there is not enough evidence
for scientists to make a clear assumption.
The general thought among astronomers now
that the entire solar system originated about 4,600
billion years ago, from a vast slowly whirling cloud of
dust and gas that gradually contracted under the pull
of its own gravitation. On the very rim of this cloud
was material that did not share in the contracting
process. It was too far away from the center to be
sufficiently effected by the gravitational pull, and it
tended to remain where it was. Turbulence made it
coalesce into small icy bodies and so forming comets.
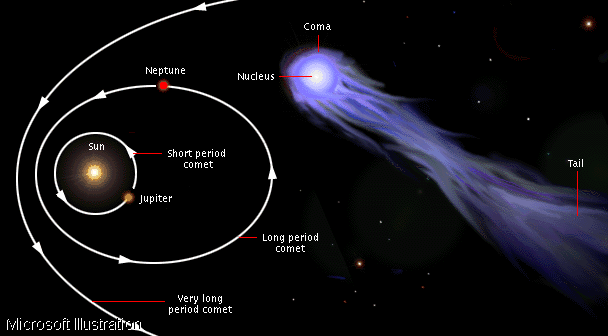
A good idea of how faraway comets might recede came
in 1973, when a Czech astronomer, Lubos Kohoutek
detected an approaching comet while it was still beyond
the orbit of Jupiter. Because it could be seen from so
far away, it seemed to be a large comet, and therefore
a new comet coming from far out in the depths of space.
When the path of the comet was plotted, its orbit turned
out to be the most enormous ever calculated for any
body in the solar system. It is 102 times as far away
from the sun as Halley's comet ever gets. This takes
Comet Kohoutek over 200,000 years to go once about its
orbit around the sun. What now concerns people is
the possibility of collision with a comet. The chance
of collision with ant one comet is virtually zero, but
if there are a great many comets, the chance of
collision with any one of them, sooner or later is very
great. Comets that have short orbits around the sun
(short-orbit comets) vaporize quicker than the
(long-orbit comets). This is because each time a comet
comes close to the sun some of its particle evaporates,
because the comet is composed of frozen gas and so
becomes dimmer each time it gets close to the sun and
will finally vaporize. Comets are only visible when
near the sun because the intense solar radiation
vaporizes parts of icy nucleus from the comet's coma and
tail.
Return to Main page
|
 To most
people "something
unusual" was frightening in the beginning! One way to
prove that the sight of a comet was disaster is that
people would record the year of an appearance of a comet
and then would describe the terrible events and things
that took place soon afterwards. Of course, terrible
things happen every year, whether comets appear or not.
Take for instance a comet was sighted in 11 BC which was
then connected with the assassination of Julius Caesar
in the very same year. Or when a comet was spotted in
66 AD and four years later in 70 AD Jerusalem fell into
Roman hands. Also when the fall of Constantinople to
the Turks in 1453 was blamed on a comet that appeared
in 1456. Can this be true that comet's are viewed as a
heavenly comment on the destruction of mankind? Comets
often become scapegoats for historical events around
the world, because there is nothing else to take the
blame for!
To most
people "something
unusual" was frightening in the beginning! One way to
prove that the sight of a comet was disaster is that
people would record the year of an appearance of a comet
and then would describe the terrible events and things
that took place soon afterwards. Of course, terrible
things happen every year, whether comets appear or not.
Take for instance a comet was sighted in 11 BC which was
then connected with the assassination of Julius Caesar
in the very same year. Or when a comet was spotted in
66 AD and four years later in 70 AD Jerusalem fell into
Roman hands. Also when the fall of Constantinople to
the Turks in 1453 was blamed on a comet that appeared
in 1456. Can this be true that comet's are viewed as a
heavenly comment on the destruction of mankind? Comets
often become scapegoats for historical events around
the world, because there is nothing else to take the
blame for!

