Universidad de Costa Rica
Sede Rodrigo Facio
Facultad de
Ingeniería
Escuela en Ciencias
de la Computación e Informática
Curso: Redes de
Computadoras
Profesor: Luis Loría

REPORTE DE LABORATORIO
LABORATORIO # 5
Realizado por:
Karol Salazar Garro A03849
Yesenia Gonzalez
Villalobos 971540
Diana Gonzalez Vargas 971537
Esteban Brenes
Chavarría 940596
2 Semestre
2004
Índice
Descripción de cada una de las actividades
del laboratorio
Teoría que apoye los conocimientos del
laboratorio.
Ejemplos y resultados obtenidos en el
laboratorio
Introducción
En este laboratorio se dan los conceptos básicos de la configuración del
router en cisco, y se trabaja son la necesidad de tener un router real conectado,
basta con una simulación del mismo. Presentamos cada uno de los pasos que seguimos para hacer esta
configuración de la manera correcta.
Descripción del Laboratorio
Problema
Se presenta una topología de red, en la cual hay que configurar los distintos
router que se necesitan para el correcto funcionamiento de la red, esto se hace
de manera simulada, no existe ningún router real.
Objetivo
Aprender a configurar routers (en este caso Cisco) y entender todos los
conceptos teóricos y prácticos para lograrlo.
Desarrollo del laboratorio
Descripción de cada una de las actividades del laboratorio
En un principio se
nos da la topologia de la red:
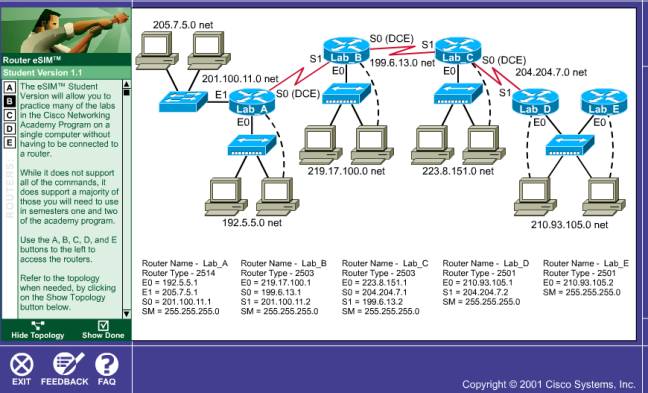
Y se nos da un test
de configuración el cual debemos ir haciendo, al inicio este test aparecen
todas las actividades marcadas como no realizas, cada vez que se completaba una
actividad esta se iba marcando como realizada.
Test de configuración al inicio
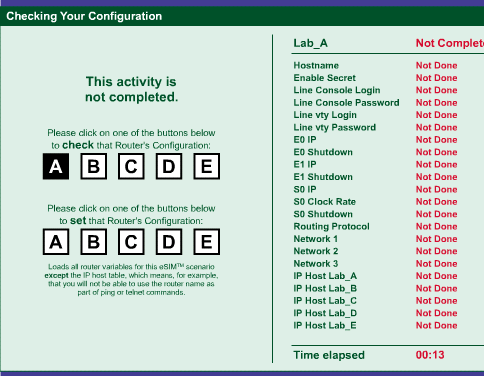
Seguidamente
empezamos a completar esa tabla, y asi
configurar el router, el orden que escogimos es indiferente, nosotros empezamos
por las cosas más fáciles y rapidas como asignar las ip o poner el login y el
password.
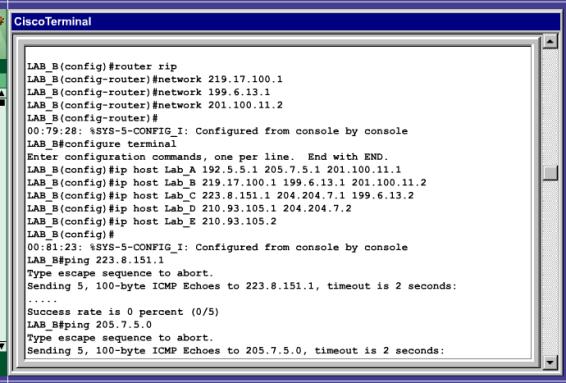
En las siguientes imágenes, se presenta la forma en que fuimos configurando el router, y los pasos que seguimos.
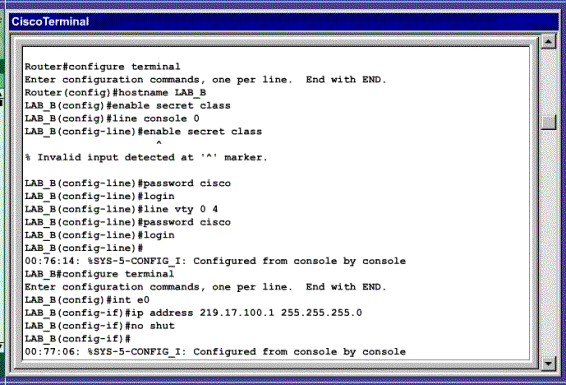
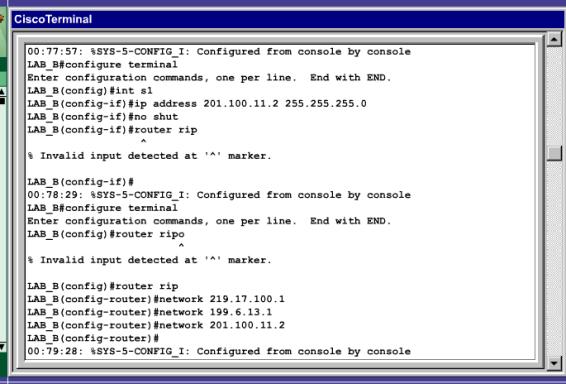

Teoría que apoye los conocimientos del laboratorio.
Estas son algunas de
los comando que utilizamos para la configuración, esta es una lista de comandos
proporcionados por la pagina oficial de cisco.
Basic
Cisco Router Commands
( Not All
Commands May Be Available Without Enable Access Or Router Version )
|
Router
Name> |
User executable mode, view but can’t make changes |
|
Router
Name> enable |
Gets you to Privilege mode allowing you to make
changes to the router |
|
Router
Name
#
|
Privilege mode, changes can now be made to router |
|
Router
Name # disable |
To get back to user mode |
|
Router
Name # exit |
To
exit router |
|
Router
Name # shft+ctrl+6 |
Break
Key |
|
Router
Name # write erase |
To clear all previous configurations |
|
Router
Name # reload |
Reboot
the router |
|
Router
Name # setup |
Setup command brings up the configuration dialog
box. |
Some Router Show Commands
|
Router
Name # sh ? |
shows parameters supported by the router |
|
Router
Name # sh int
|
shows status of all interfaces |
|
Router Name # sh int
s0
|
shows status of interface you selected, ie: s0, s1,
e0, e1, ... |
|
Router Name # sh ip
int
|
view
ip parameters |
|
Router Name # sh ip int brief |
brief summary of all interfaces and status |
|
Router Name # sh ip
route |
shows networks available to interface and routing
table |
|
Router Name # sh proc cpu |
shows CPU utilization on router |
|
Router
Name # sh mem |
shows
memory utilization |
|
Router Name # sh mem big |
to see the largest blocks of memory |
|
Router
Name # sh log |
to check recent history of router |
|
Router
Name # sh version |
shows summary of hardware and reason for last reload |
|
Router
Name # sh diag |
shows more detailed hardware information |
|
Router
Name # sh flash |
shows
IOS file |
|
Router
Name # sh run |
shows running configurations on router ( version
10.3 and above ) |
|
Router
Name # wr t |
shows running configurations on router (version 10.3
below/above) |
|
Router Name # sh env all |
shows current router temps, power supply and general
health of router |
|
Router Name # sh env table |
shows warning levels for shutdown to take place |
|
Router Name # sh startup-config |
shows saved config in NVRAM |
|
Router Name # sh controllers(int) |
shows serial line configurations. Make sure a space
is used for int. ie: s 0 |
|
Router Name # sh cdp neighbor |
shows
directly connected neighbors |
|
Router Name # sh cdp neighbors detail |
shows detail of directly connected devices: (router,
bridge, switch) |
|
Router Name # sh cdp int |
shows which interfaces are running CDP |
|
Router
Name # sh
arp
|
shows lan devices and mac address' ( arp table ) |
|
Router Name # sh ip
arp |
shows the arp table in the router |
|
Router
Name # sh protocol |
shows which protocols are configured |
|
Router Name # sh ip
protocol |
shows routing protocol configured and parameters |
|
Router Name # sh ip route isis |
displays all routes in the route table that
originated in ISIS |
|
Router Name # sh isis spf-log |
displays information on the duration/cause of recent
SPF runs |
|
Router Name # sh isis database |
displays all information known by ISIS |
|
Router Name # sh isis database detail … |
displays contents of entire LSP (add router info,
hr1.lga2.00-00) |
|
Router Name # sh isis topology |
summary of best path from router to every other
router |
|
Router Name # sh ip bgp |
lists all routes learned from bgp |
|
Router Name # sh ip bgp <route> |
shows BGP information for that particular route, use
w/ sh ip rou |
|
Router Name #sh ip bgp community-list |
add list # to end of string. Bgp routes that match a
given list |
|
Router Name # sh ip bgp filter-list |
bgp routes that match a given AS path filter list |
|
Router Name # sh ip bgp neigh(address) |
shows the details on a route in the route table |
|
Router Name # sh ip bgp sum |
used to view the status of a BGP session |
|
Router Name # sh route-map (name) |
show the details of a specific route-map |
|
Router Name # sh adjacency detail |
adjacency table used by CEF. Verify router/device is
discovered |
|
Router Name # sh ip cef |
to view the CEF cache or FIB (forwarding information
base) table |
|
Router Name # sh ip cef summary |
gives an overview of the cef entries |
|
Router Name # sh cef not-cef-switched |
if CEF is enabled, this will show packets not being
CEF switched |
|
Router
Name # sh standby |
displays the information on the operation of HSRP |
|
Router Name # sh standby brief |
displays a summary of interfaces running HSRP |
|
Router Name # sh standby (interface) |
displays state of the port, hello intervals, MAC
address, config |
|
R#
sh mpls traffic-eng tunnels tunnel # |
displays tunnels between hops in a route masked by
MPLS |
Some
Basic Switch Commands
( Not All
Commands May Be Available Without Enable Access )
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
|
Switch1>
? |
responds with main help menu |
|
Switch1>
hist |
to view a listing of previous commands used |
|
Switch1>
show ? |
responds with various show commands |
|
Switch1>
show ver |
information about IOS and hardware components |
|
Switch1>
show module |
quick view of status on all modules |
|
Switch1>
show port |
provides general summary of all ports: errors,
collisions, speed, duplex |
|
Switch1>
show port (#) |
specific information for a individual port |
|
Switch1>
show port status |
provides single line general summary of all ports |
|
Switch1>
show mac (port#) |
summary information on what has been sent and
received on a given port |
|
Switch1>
show test (module#) |
if a module is in failed status, show test will show
specifics |
|
Switch1>
show log |
shows history of switch on a per module basis |
|
Switch1>
show config |
shows
configurations on switch |
|
Switch1>
show system |
shows uptime and levels of utilization |
|
Switch1>
show vlan |
lists the VLAN's that are resident on the switch |
|
Switch1>
show cam |
lists the LAN switch transparent bridging table |
|
Switch1> sh cam (mac address) |
to locate a single MAC address |
|
Switch1>
show cam dynamic |
lists all dynamically learned MAC addresses |
|
Switch1>
show span |
lists info on a port listening/diagnostics feature
(switched port analyzer) |
|
Switch1>
show spantree (port#) |
allows you to see the spantree status of a specific
port |
|
Switch1>
show trunk |
provides a summary of the ports in trunking mode |
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
Some
Router Enable Commands
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Enable A Port
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# int (+ interface you are designating, token ring must
put in ring speed 16 or 4)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ip address _._._._ (mask)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# no shut
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Disable A Port
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# int (interface or port)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# shut
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Enable A Protocol
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
Different protocols will have different instructions
below is a generic example:
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# router (protocol type + any
extensions needed in instructions)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# network (+ IP address)
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Disable A Protocol
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# no router (+ protocol type)
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Change Router Name
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# hostname Jim (global command)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ctrl z
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
From Config T settings:
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ctrl z (to save settings and execute the command)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ctrl c (starts over, abort)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# write mem (saves everything to NV Ram)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# write t (shows running configurations, also can use show run)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# telnet (to telnet into another router)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ip host name (name & address - To Build Host Table - Global
Command)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# no host (to remove a host name)
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
* On a 4000 series router you must specify what type
of media is being used:
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# int (+ interface you plan to configure, ie: e0, s0, ... screen
changes, major command)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# media-type 10baseT (or whichever media is being used, sub command)
<!--[if !supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Enable RIP
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# router rip
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# network (+ network address, ie: 150.111.0.0 )
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# int (+ interface you plan to configure, ie: e0, s0, ... screen
changes)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Config-if#
ip address 150.11.1.1 255.255.255.0 (full statement with subnet mask,
sub command)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Config-if#
no shut (this logically activates the interface, required at every
interface configuration)
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Enable SNMP
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# snmp server community public (RO, RW)
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Enable IPX (Novell)
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ipx routing
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# int (+ interface you plan to configure, ie: e0, s0, ... screen
changes)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# ipx network (ipx address)
|
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]--> Router
Name # sh ipx servers |
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]--> shows ipx servers on the network |
|
Router Name # sh ipx
route |
shows ipx networks seen by the routers |
|
Router Name # sh ipx traffic |
shows
ipx related protocols |
Router Name # sh ipx
int
view ipx address on an interface
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
To Enable VTY
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# config t enable password cisco enter (global
command)
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# line vty 0 4
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# login
<!--[if !supportLists]-->·
<!--[endif]-->Router
Name# password cisco
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
<!--[if
!supportEmptyParas]--> <!--[endif]-->
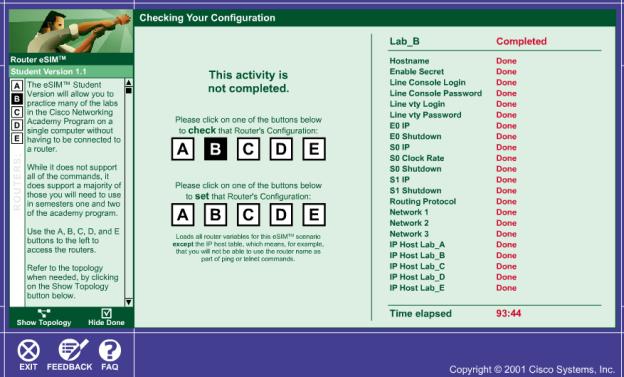
Ejemplos y resultados obtenidos en el laboratorio
Resultado final del test de
Configuración
Bibliografía
http://shadowfax.ecci.ucr.ac.cr/material/Enrutamiento/