Human
Cloning and Life Extension
The idea of clonal growth of one's own body double and a brain transplantation
into it so as to live longer has  two parts or procedures which came from physician scientists Landrum Shettles,
Ph.D., M.D. and Robert White, Ph.D., M.D. respectively Both procedures
have a conceptual simplicity but there effects are far ranging. Both the
technical, scientific and the bioethical, societal questions are addressed
in turn in the following outline. Feel free to leave any compliments or
contradictions in my e-mail at the end of the outline. I will try to answer
all e-mail.
two parts or procedures which came from physician scientists Landrum Shettles,
Ph.D., M.D. and Robert White, Ph.D., M.D. respectively Both procedures
have a conceptual simplicity but there effects are far ranging. Both the
technical, scientific and the bioethical, societal questions are addressed
in turn in the following outline. Feel free to leave any compliments or
contradictions in my e-mail at the end of the outline. I will try to answer
all e-mail.
Body Transplantation (Brain Surgery)
I Human Cloning, Embryonic and Adult Techniques
Currently a company called Valiant
Ventures, Inc. promises to offer adult human cloning (for infertile
but wealthy couples primarily) for "as low as" $200, 000.00. It is sponsored
by the International Raelian Movement
which is a quasi-religious sect that teaches human origins are extraterrestrial.
There views are akin to Eric Von Daikein's Chariots
of the Gods book and the Ancient
Astronaut Theory in general.
Also, some excellent books on human cloning have come out recently.
The most important is Remaking
Eden, Cloning and Beyond in a Brave New World by Dr. Lee M. Silver
from Princeton's Departments of Molecular Biology, Ecology, and Evolutionary
Biology and the Program in Neuroscience. I am reading this book as of December
23, 1997 and find it fascinating. It tells about the scientific techniques
primarily and their potential future impact. A book by Dr. Pence covers
philosophical considerations only in a pro-cloning argument with his book
Who's
Afraid of Human Cloning? I presently (12-23-97) have this book on order.
A third book takes various religious viewpoints into consideration called
Human
Cloning, Religious Responses. I have not looked at or ordered this
book but probably will eventually.
|
 |
Here Robert White, MD, Ph.D. shows his plans for human body transplantation.
He did this research at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
in Cleveland, Ohio. |
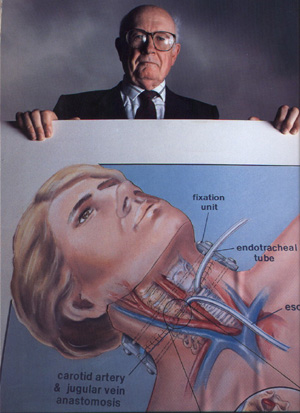 |
(top
of page)
A Embryonic human cloning has been developed by Jerry Hall and Dr. Robert
Stillman
1 First a two cell embryo is separated into two cells after removing the
zone pellucinda, an outer coating essential for development which I think
functions both as physical protection for the delicate embryo as well as
initial nutrition before implantation.
2 The removed zone pellucinda is replaced with a seaweed derived gel Jerry
Hall had developed.
3 The researcher repeated the procedure several times and was able to generate
three to four cloned embryos from a single original.
B Adult cloning
1 John Gurdon and Marie Di Beradino did early work here.
2 Landrum B. Shettles, M.D.,Ph.D..- cloned a human spermatogonium cell
to the gastrula stage at which time it is ready for uterine implantation.
This procedure, photographically recorded in his article, proves that adult
humans can be cloned
3 Cloning is necessary to prevent tissue rejection -Paul
Segall, Ph.D.
II Body transplantation has been relatively
successful in monkeys -Robert White, M.D., Ph.D.
Robert White did his original research in the late 70s and early
80s but was harassed by animal rights activists and censored by ethics
committees regarding his body (brain) transplantation work. Members of
the Ukrainian science community invited him to continue his research there.
He has stated recently that he is ready to try body transplantation in
humans. See various news articles
about his work.
(top
of page)
( Early work has been done by V.P. Demikov and K. Terao.)
A It involves the connection of one carotid artery and jugular vein at
a time [there are two of each] from body to body to prevent loss of blood
to the brain and provide an uninterrupted supply of oxygenated blood.
B Mechanical control of respiration circulation and arterial pressure is
crucial.
C Microsurgical suturing of the entire vasculature is a major issue. [This
will require prolonged periods of surgery with the use of particularly
advanced magnification imaging and profound hypothermic arrest to allow
for the time needed.]
D Neurological reconnection of the spinal column is important.
Spinal neuronal transmission is almost entirely axonal spinal chord transmission
may only require bridging "gap junctions" to allow the electrical signal
to Jump across the separation at the site of spinal dissection.
Links to both adult
human cloning and neuroscience can be reached here.
Regeneration
of the central nervous system's spinal column may be impossible with the
current state of knowledge and technology. A better chance of neural regeneration
may be at the peripheral nervous system's 32 nerves. This would require
a highly involved operation in which both the original brain and its spinal
column are transplanted together. Earlier Russian work on brain transplantation
(in dogs, not monkeys) involved this entire central nervous system approach
which may more easily preserved more upper body
motor functioning.
1 Evidence with Parkinson's patients and other neurodegenerative disease
reversals].
2 Nerve growth factors may also help re-heal the severed spinal column.
3 Liquid collagen combined with omentum from the stomach with fetal cells
surrounding the omentum has proven useful for neurological regeneration
as well.
4 differentiation into nerve cells for neuroregeneration A simple experiment
could confirm or refute this possibility by growing adult embryological
clonal cells in large numbers via the techniques of Landrum Shettles and
Hall, Stillman.
5 Cytoplasmic similarity is also important for a better cloning result.
a) The transformation of embryonic cells to their neighbors itself illustrates
the profound effect of signal transduction i.e. intercellular messages
(by G proteins) can direct undifferentiated cells in their direction of
development.
b) All cytoplasm embryonically is maternal. Postadolescent women can harvest
their own unfertilized eggs by laproscopy. Even after menopause some eggs
can be surgically removed by laproscopy because not all eggs are used during
a woman's ovulating phase of life. Men can receive their cytoplasmic heritage
through their mother. If the mother is dead or uncooperative, men may be
without a cytoplasmic source unless a sister is available. One's own daughter's
cytoplasm comes from the man's mate. Only a biological female sibling (sister)
will work.
6 The study of neural plasticity from embryological to neurological development
at fetal, juvenile and adult stages holds the most promise in solving the
riddle of differentiation.
a) The endocrinology above is of primary importance
b) Secondarily, the signal transduction potential of mitochondria should
be investigated (if it hasn't been yet)
c) Various invertebrate substances allow for their own complete neuroregeneration:
The isolation, purification, understanding and application of these metabolic
regulatory factors may help neuroregenerative ability in the future. Such
work could start with echinoderms such as starfish and the Western blot
protein characterization as well as its DNA exon coding sequence. A zoo
blot and in situ hybridization of this DNA can be matched to human genomic
positions. The potential variation of neuroregenerative nerve growth factors
can also be tested for above at various stages of embryology.
E To prepare the human body clone for reception of one's current brain,
one would need to remove the telencephalon [the fetal beginnings of the
higher brain functions] at 6 weeks of gestation (Paul
Segall, Ph.D.)
1 The rapid growth of a body clone beyond ordinary annual growth would
require the use of growth factors, supernutrient feeding and hormones
2 Electrical stimulation of the muscles would be necessary to prevent atrophy
through lack of use.
F These body clones could then be stored in liquid nitrogen until they
are needed.
1 Vitrification and other cryoprotectants such as glycerol or freezing
under 2000 ATMs to produce "shrunken ice (known as Ice III) which does
not cause damage due to crystallization can be used in the safe storage
of such body clones
2 Hypothermia and blood replacement leading to cryogenic suspension of
a dying individual who has not had a body clone prepared yet can be done
to allow for the time needed to grow such a body clone
3 The relevant spermatogonium or oogonium sample needed to start the cloning
process would need to be extracted before the cryogenic suspension of the
patient
4 During the cloning process it is important to separate a good supply
of undifferentiated embryonic cells before further development to use as
a critical element of reattaching the spinal column (or more importantly
the peripheral nerves which would require many more embryonic or fetal
cells) when the body transplantation has been otherwise completed
G Long term technical consideration to indefinitely extend human life:
1 Periodic neuroregeneration of the transplanted spinal chord and one's
brain will be necessary to compensate for neural cell death, Both the spinal
column and brain are irreplaceable based on current technology. The brain
which contains one's entire personality will always be irreplaceable.
2 Replicant fading of clonal cells needs to be averted by
i) Cloning from original fetal cells as much and as long as possible.
ii) Eventually nanotechnological micromachines may be able to check genetic
codes for accuracy. The codes for each person would need to be sequenced
for these nanometric machines to check against. Every individual's genome
would then need to be sequenced by a highly advanced pulsed field gel electrophoresis
of entire chromosomes. Duplicate sequencing would be necessary to check
for automated mistakes
III Bioethics
'Let me suggest a conceptual approach that might
be adopted. In the light of medical proposals to redefine death in
terms of irreversible coma of a loss of higher brain function, ... if such
a noncerebral or decorticate patient is no longer in any human sense or
any personal sense, would it not follow that a pre-cerebral embryo or fetus
is not yet alive in any human or personal sense? This would, of course,
obviate any further use of such question-begging rhetoric as "killing unborn
babies"
- Joseph Fletcher |
Many of these bioethical questions are considered in a philosopher's
book called Who's Afraid of Human Cloning by Dr. Pence who argues in favor
of it. The counter arguments against human cloning (of any kind) are easily
accessible and are expounded on especially by Jeremy Rifkin. Again, the
book Human Cloning; Religious Responses covers a variety of opinions according
to the book review I have read.
(top
of page)
A Legal issues
Web Surfer's Note on Legal Resources: I found an excellent legal
search engine at LawGuru.com.
Lots of legal questions that you may have can be answered free with this
engine that does a parallel search of over 340 different legal databases.
Most of these databases the engine accesses for you have a high monthly
subscription charge so use these databases for free (indirectly) while
it's still legal! (Seems like such a good deal that it may not last forever).
[For a general parallel search engine I recommend MetaCrawler.]
1 Status of clonus versus conceptus- Is the cloned tissue a part of the
original person [property] or a separate entity?
2 Legality-
i) Regardless of the former issue, it seems that if a person's rights begin
at birth or at least viability as determined by Roe v. Wade and subsequent
cases, a six week old cloned fetus can be operated on to remove its telencephalon
because it is not viable yet.
ii) Since death is measured by the lack of electroencephalogram [EEG] activity
or brain death, it would seem that a legal definition of life should conform
to the same standard. Life would then require the beginning of EEG activity
which would be prevented by the telencephalon removal.
a) Ultimately the legality in the United States of body clones as advocated
by Dr. Paul Segall and body transplantation as researched by Dr. Robert
White will be determined by a majority vote.
b) Legal precedents on fetal tissue transplantation have already been favorable
in Mexico and Sweden. Supportive rulings on anencephalic babies have already
been made in Germany, Canada and to some extent the U.S.
B Philosophical issue- When does human personhood and rights begin?
Many bioethicists argue similar to the above rationale that personhood
is determined not by the genetic code but by an analysis of the spectrum
or continuum of life and various watershed events within it such as EEG,
EKG [heartbeat], etc. This developmental approach is predominant in philosophical
discussions today.-
The banking of self in body clones can be likened to the banking
of one's own blood which is becoming fairly common practice today.
C Religious perspective- Many ministers and priests welcome life extension
if it does not purpose answers to absolute truth and infinity
IV Society
(top
of page)
A The knowledge base of society dwindles with the death of its most experienced
and educated citizens. Long term projects such as discoveries of genetic
cures, a grand unified theory or a controlled fusion reaction could be
more easily solved if researchers who cannot fully transmit their insights
to the next generation no longer can make progress.
B Affordability and access- with massive demand that should result, the
procedure should quickly become mainstream and fall in price.
1 Biotech company competition for cloning [which is already a fairly simple
process] and surgical competition for patients should keep the price low
as long as the government does not try to regulate the law of supply and
demand {which is one law that can not be legislated}.
2 Commercial agricultural applications in mass production of the best livestock
will add to the streamlining of the technology
3 It is cheaper to supply people's bodies with guaranteed matches then
to use dialysis or other bionic parts or play the roulette of donated organs
in terms of availability and compatibility.
C May enhance people's prospects for hope in the future- Those who fell
"there is no way out" of their apparently dismal situation in life may
feel less hopeless if there is more time to correct things.- the protection
of one's current life by partial body transplants of organs increases one's
quality of life.
D May promote a commitment to long term projects- as people see they may
themselves directly benefit from the project mentioned above, their commitment
to these projects will likely increase their funding through Congress,
other countries, corporations and private foundations.-
Self interest is a strong motivation. Those who will see the future themselves
will want to improve the future. Extending human use to ocean floors and
the routine use of deserts, tundra and mountains as well as asteroids,
moons, Mars, space stations and eventually interstellar trips will become
more likely.
V The next stage - human genetic engineering
(top
of page)
A The genetic altering of the human DNA code to improve on the species'
weaknesses was called "algeny" or genetic alchemy by Nobel laureate Joshua
Lederberg, an early proponent of the idea. Today, as it is slowly
incorporated into medical practice it is referred to as "gene therapy".
B With more elaborate knowledge from the results of the Human Genome Project
of NIH and HuGO, we may be able to genetically increase the capacity for
embryological development especially of the brain by altering the protooncogenes
that restrain this development (once these protooncogenes are determined
and located).
1 Such engineering should be undertaken with caution and serious reflection
if done.
2 Animal experimentation with related mammals such as Rhesus monkeys
or, even better, chimpanzees would be desirable.
3 The amazing discovery of the basic body plan genes that are held in common
apparently by all members of the animal kingdom (that have been genetically
tested so far) is a breathtaking first step in getting the basic outline
of genetic relationships between species. In the distant future the genomes
of many different mammals, reptiles, birds, etc. may have been sequenced
and comparative genetic analysis performed. At this point the possibility
of transgenic improvements in Homo sapiens are possible. Various
sensory apparati such as the eye of an Eagle, the ear of a Tiger and the
nose of a Cougar could be possible. Some Transhumanists suggest such
a species, our successor, be called Homo excelsior.
-
A developmental biology Professor hosts a very
informative web site about these body plan genes that all animals have
in common.
C Currently alive humans could also benefit from some biological improvements
such as increased brain capacity without the benefit (or need or possibility)
for genetic engineering.
1 Artificial skulls probably made out of a protein based plastic compound
could000 be constructed to increase the cranial cubic centimeters for brain
development and the "extra space" can be bathed in a viscous fluid similar
to the neurotransmitter liquid it resides in.
2 increased brain size is caused by injections of embryonic tissue from
one's clonal copy.
a) The clonal recipient body is enlarged in size compared to the original
you by growth hormone therapy.
b) This increased clonal recipient size, then, allows for a naturally increased
cranium to accommodate the artificially induced neurodevelopment of one's
original (and only) brain.
E "Artificial Life" , what is life?
1 a complex adaptive system: information rich, recombines/replicates/evolves,
derives order from chaoes (open thermodynamics)
a) distinction between biological minds and our reality with nonbiological
minds and the "simulated" "artificial" or "virtual" realities ofcomplex
adaptive programs that fit the above definition of life.
-
Focus on biological minds as primary -
Nanotechnology (advocated by Drexler)
can be used to improve human life as is, unaltered. It could be used
as NanoMedicine which could extend well beyond the genetic
engineering/ gene therapy schema of today's clinical research into atomic
engineering/ molecular reconstruction of damaged tissue. Tissue regeneration
by cloning and trophic factors would be potentially superceded. The
nanotechnologist could remove frostbite (cellular damage due to crystalization
especially of liquids like blood and water) from cryonic suspendees so
that whatever other ailments could then be fixed by the assemblers or other
medical advances then available.
-
Focus on nonbiological minds as primary -
Mind uploading (advocated
by Moravec) is a far more theoretical and speculative possibility in which
the information content of the brain (and its associated consciousness)
is transferred from the neural-organic substrate of the brain to a "neural
network" computer microchip design. The microchip may be organic
(carbon-based) instead of silicon-based.
b) the differance between the two is one of the type of information storage
c) study of the two types of information storage are geneticis and cybernetics
d) Compromise: Use both approaches. Enhance the biological with
neural implants or interfaces that convert between the two information
storage systems much like a modem does between the signal of the computer
and that of telephone wires (which are obviated by fiber optics or satelite
transmission incidentally)
-
Neural implants
could augment memory and computing capacity while allowing for the parallel
processing and intuitive cognition of the brain.
F Cryonics
(originated by Ettinger) primarily needs to work on the neurocryopresrvation
of the brain's informational structure since this is the essence of individual
identity. The rest of the body can be cloned from a body double from his
own skin cells or other stored cells from his body. Fully reversable
cryonics or cryostasis is also very useful in interstellar migrations that
may be likely in the late 21st century.
G The Omega Point
Hypothesis is that life will spread across the universe until all matter
participates in conscious self awareness. The interstellar migrations
will be a new start for this cosmic process.
bibliography (including articles
referenced elsewhere on the FTT home page)
(top
of page)
Backlund, Erik-Olof et al. "Towards a Transplantation Therapy in Parkinson's
Disease, A Progress Report from Continuing Clinical Experiments" Cell
and Tissue Transplantation into the Adult Brain New York Academy of
Sciences 1987 Vol. 495 pp. 658-686
Bahr, Robert "A New Ethical Question- Head Transplants?" Science
Digest May, 1977 page 76
Beauchamp, Tom L. and LeRoy Walters "Anencephalic Donors: Separate the
Dead from the Dying" Contemporary Issues in Bioethics Wadsworth
Publishing Company, Belmont, CA 1989 page 542
Chee, Mark et al. "Accessing Genetic Information
with High-Density DNA Arrays" Science Vol. 274 October 25, 1996
Couturer, Larry A. and Dan T. Stinchcomb
"Anti-gene therapy: the use of ribozymes to inhibit gene function" TIG
Vol. 12 No. 12 December 1996
Ducat, Craig R. and Harold W. Chase "Substantive Due Process" in Constitutional
Interpretation, Rights of the Individual West Publishing Company New
York 1974 & 1992 pp. 556-588
Elmer-Dewitt, Philip "Cloning: Where Do We Draw the Line?" Time,
Time, Inc. New York Vol. 142 No. 19 November 8, 1993
Elmer-Dewitt, Philip "The Genetic Revolution: New technology enables
us to improve on nature. How far should we go?" Time Time, Inc.,
New York Vol. 143, No.3 January 17, 1994 pp. 46-56
Fletcher, Joseph "Ethical Aspects of Genetic
Controls" New England Journal of Medicine Vol. 285 September 30,
1971
Fletcher, Joseph "The Cognitive Criterion of
Humanhood" Hastings Center Report Vol. 4 December, 1975
Green, R. "Tinkering with the Secrets of Life" Health January
1990 Vol. 22
Harrington, John J. et al. "Formation of de
novo centromeres and construction of first-generation human artificial
microchromosomes" Nature Genetics Vol. 15 April, 1997
Kahn, Carol "Doubletakes" Omni Omni Publications
International, Ltd. New York Vol. 11 No. 1 October, 1988 page 58
Lederberg, Joshua, Ph.D. "Experimental Genetics and Human Evolution"
Bulletin
of the Atomic Scientists October 1966 Vol. 23
Lederberg, Seymour "Law and Cloning" in Genetics and the Law
page 377
Rorvik, David Michael As Man Becomes Machine,
The Evolution of the Cyborg Doubleday & Company, Inc. Garden City,
New York 1971
Rorvik, David Michael In His Image, the Cloning of a Man Hamish
Hamilton, London 1978
Thomas, L. "On Cloning a Human Being" New England Journal of Medicine
Vol. 291 page 1296
Segall, Paul, Ph.D. and Carol Kahn Living Longer,
Growing Younger Random House New York 1989
Shettles, Landrum B. "Diploid Nuclear Replacement
in Mature Human Ova with Cleavage" American Journal of Obstetrics and
Gynecology 1979
Smolan, Rick, Phillip Moffitt and Matthew Naythons, M.D. The Power
to Heal Prentice Hall Press New York 1990 page 174
White, Robert J., M.D., Ph.D. "Brain Transplantation"
Surgical
Neurology Vol. 23 1985 page 449
White, Robert J., M.D., Ph.D. "Cephalic exchange
transplantation in the monkey" Surgery July, 1971 Vol. 70 pp. 135-139
White, Robert J., M.D., Ph.D. "Modifications in
primate cerebral and electrical activity with profound hypothermia" Cryobiology
October 1972 Vol. 9 pp. 383-392
White, Robert J., M.D., Ph.D. "Primate cephalic
transplantation: neurogenic separation, vascular association" Transplantation
Proceedings March 1971 Vol. 3 pp. 602-604
Return to table of contents.
E-mail me.
 two parts or procedures which came from physician scientists Landrum Shettles,
Ph.D., M.D. and Robert White, Ph.D., M.D. respectively Both procedures
have a conceptual simplicity but there effects are far ranging. Both the
technical, scientific and the bioethical, societal questions are addressed
in turn in the following outline. Feel free to leave any compliments or
contradictions in my e-mail at the end of the outline. I will try to answer
all e-mail.
two parts or procedures which came from physician scientists Landrum Shettles,
Ph.D., M.D. and Robert White, Ph.D., M.D. respectively Both procedures
have a conceptual simplicity but there effects are far ranging. Both the
technical, scientific and the bioethical, societal questions are addressed
in turn in the following outline. Feel free to leave any compliments or
contradictions in my e-mail at the end of the outline. I will try to answer
all e-mail.
