DEPARTMENT OF
BIOSTATISTICS AND MEDICAL INFORMATICS
 ACTIVITIES
ACTIVITIES
![]() Biostatistics
teaching to undergraduates and postgraduates
Biostatistics
teaching to undergraduates and postgraduates
![]() Guidance and
consultancy on research methods and statistical analysis
Guidance and
consultancy on research methods and statistical analysis
![]() Biostatistical computing
Biostatistical computing
![]() Graphics
Graphics
![]() Research on
health measurements
Research on
health measurements
![]() Wi-Fi internet facility to all the academic and non-academic
departments
Wi-Fi internet facility to all the academic and non-academic
departments
![]() Building up
national database on health
Building up
national database on health
![]() Disease specific
databases
Disease specific
databases
![]() Programmes for computer aided teaching
Programmes for computer aided teaching
![]() Annual
report and souvenir for the college
Annual
report and souvenir for the college
![]() International
consulting such as to the World Health Organization, the World Bank and UNAIDS
International
consulting such as to the World Health Organization, the World Bank and UNAIDS
![]() Writing books on
biostatistics and medical research methods
Writing books on
biostatistics and medical research methods
- Teaching
to medical undergraduates
§ Sources of data (health information system, patient records, government reports)
§ Measures of morbidity and mortality (infant mortality rate, maternal mortality ratio, age specific death rate, age standardized death rate) and incidence and prevalence rates.
§ Demography and fertility (various fertility rates, demographic cycle, population pyramid)
§ Graph and diagram (bar diagram, pie diagram, line diagram, other charts)
§ Statistical distributions (histogram, polygon, normal distribution, skewed distribution)
§ Regression and correlations (linear regression, product moment correlation coefficient, causal relationship)
§ Tests of significance (Chi-square, student’s t test and elements of ANOVA F test)
§ Confidence intervals for means, proportion, difference in means and difference in proportions
- Teaching to medical postgraduates
· Medical uncertainities (epistemic and aleatory)
· Designs to control the impact of uncertainities (observational studies, experiments and clinical trials)
· Adequacy of samples (method of sampling and size of samples)
· Collation of data
· Assessment of health and disease (normal/abnormal levels, morbidity, mortality and duration of survival)
· Degree of uncertainities (sensitivity/specificity, predictivities and relative risk)
· Statistical significance (P-value, power, Chi-square, t, F, repeated measures, nonparametrics—medical significance)
· Medical relationships (Correlation and cause-effect, linear regression—simple, multiple)
- PhD
· Index of need for health resources
· Index of child mortality
· Analysis of paired ordinal data
- In
service Medical Technology
· Statistics in medical laboratory techniques
·
Gaussian shape, Mean±2SD limits,
· Quality control, chart, accuracy and replicability
![]() RESEARCH
GUIDANCE AND CONSULTANCY
RESEARCH
GUIDANCE AND CONSULTANCY
- TO
MD/MS students
· Designing of studies—writing of protocol
· Sample size and power
· Analysis of all kinds of data
· Interpretation of results
· Evaluation of thesis protocols in PG Cell
- To
the Faculty of all departments
· Designing of studies—writing of protocol
· Sample size and power
· Analysis of all kinds of data
· Interpretation of results
A.
Data analysis of PG students and
faculty
· Simple, multiple, linear, nonlinear and logistic regressions
· Repeated measures ANOVA
· Exact tests for small samples
· Cluster, factor and survival analysis
B.
Development of computer programmes
· Tukey and Dunnets tests for two-way and higher-way ANOVA
· Exact test for multinomial data
· Flow diagram for choosing statistical method
A.
Three dimensional graphs
B.
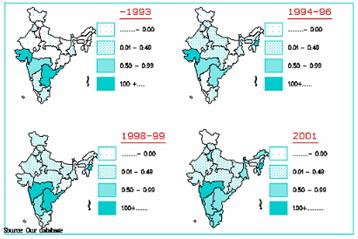
Maps
Prevalence of
HIV among non-professional blood donors
- Health
Indicators for South-East Asian Countries (for WHO)
- Index
of need for health resources
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=2066229&dopt=Abstract
- Index
of child mortality
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=8635808&dopt=Abstract
- Social
classification
|
Income
category* |
Education |
Occupation
(examples) |
Score |
|
|
|
Below poverty line |
Illiterate |
Burden on society such as begging, unemployed |
0 |
|
|
|
In bottom 20% population (0 to 20%) but above poverty line |
Less than primary |
Unskilled labour |
1 |
|
|
|
In next 20% population (20% to 40%) |
Primary to less than high school |
Skilled labour, small shop, soldier, small farmer |
2 |
|
|
|
In next 20% population (40% to 60%) |
High school to less than bachelors (exclude professional diploma) |
Clerk, medium business sales person, technician, medium farmer |
3 |
|
|
|
In next 20% population (60% to 80%) |
Non-professional bachelors or professional diploma |
Officer, teacher, big business, big farmer |
4 |
|
|
|
In top 20% population (80% to 100%) |
Professional graduates MA/MSc/PhD |
Executive, industrialist, lawyer, consultant, engineer, doctor |
5 |
|
|
|
Category |
Per capita (Rs.) |
Add scores for income, education and occupation: If the total score is ≤3 4-6 7-9 10-12 13-15 |
Social class is V IV III II I |
|
|
|
Below poverty line -20% -40% -60% -80% -100% |
<Rs.300 300-1000 1000-2000 2000-3000 3000-5000 5000+ |
||||
Both the college and the hospital buildings have wi-fi facility for internet access
NATIONAL
DATABASE ON HEALTH INDICATORS
Statewise values of various indicators (SRS-based)
- Mortality (1970 onwards)
- Crude death rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Under five mortality rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- 1-4 yr mortality rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Infant mortality rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Neonatal mortality rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Post neonatal mortality rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Perinatal mortality rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Stillbirth rate (Rural/Urban/Combined for each major state)
- Age-specific death rate (Male/Female/Person, Rural/Urban/Combined)
- Causes of death (1978 onwards) (Rural only)
- Expectation
of life (1970 onwards Quinqinniel)
· At birth (Male/Female/Person, Rural/Urban/Combined)
· At age one year (Male/Female/Person, Rural/Urban/Combined)
- Socio-demographic
(1970 onwards)
- Percent of population by age, 0-4, 5-9,………, 70+ (Male/Female/Person, Rural/Urban/Combined)
- Literacy rate (Male/Female/Person, Rural/Urban/Combined)
- Sex ratio
1971—(Persons, Combined)
1981—(Persons, Rural, Urban, Combined)
1991—(Persons, Rural, Urban, Combined)
- Percent
urban population (1971, 81 & 1991)
- Per
capita net domestic product (1970 onwards)
· At constant prices (Combined)
· At current prices (Combined)
HIV (Prepared for UNAIDS)
- Computer
assisted learning package for frequency distribution of physiological
variables
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=9055102&dopt=Abstract
- Flow
diagram for choosing statistical method
A.
College annual reports
Since 2000
Latest available at: www.ucms.ac.in
B.
Annual Day souvenir
Since 1997
Latest available at www.ucms.ac.in
A.
World health organization
· Analysis of child survival data (SEARO)
· Teaching Health Statistics: 20 Lessons & Seminars (HQ)
· Allocation of resources (SEARO)
· Maternal mortality (SEARO)
· Health system performance analysis (HQ)
· Burden of disease studies (SEARO)
·
Health Indicators (
· Health information system (SEARO)
· Chapters for biregional report (SEARO-WPRO)
· Integration of chapters to the biregional report (SEARO-WPRO)
B.
The World Bank
· Epidemiology of HIV and AIDS
·
Sensitivity analysis of the estimates of HIV
cases in
· Models for allocation of resources for controlling HIV
C.
UNAIDS
· HIV Database
· Synchronization of databases
· Comprehensive HIV/AIDS databases
A.
Medical Biostatistics
A.Indrayan, SB Sarmukaddam
CRC
Press,
B.
Simple Biostatistics (II Ed.)
A.Indrayan, L. Satyanarayana
Academa
Publishers,
C.
Basic Methods of Medical Research
A. Indrayan
AITBS
Publishers,
 BOOKS
BOOKS