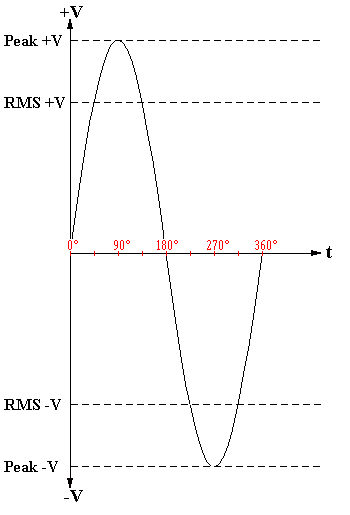
The sine or sinusoidal wave is the most common periodic wave in analog electronic circuits. If peak amplitudes are +1 and -1 then:
Angle (a) | Amplitude (sina) 0 0.500 0.707 1 0.707 0 -0.707 -1 -0.707 0 |
Average Voltage:
Average AC voltage = 0.637 × Peak
Average AC voltage = 0.9 × RMS
Peak Voltage: Maximum positive and negative excursions of an alternating current.
Peak AC voltage = 1.414 × RMS
Peak AC voltage = 1.57 × Average
RMS Voltage: (Root Mean Square Voltage) That AC voltage that equals a DC voltage that does the same work. For a sine wave, 0.707 times the peak voltage.
RMS AC voltage = 0.707 × Peak
RMS AC voltage = 1.11 × Average
Frequency: The frequency of a sine wave is the number of cycles per second. Hertz (Hz) is the unit of frequency. One Hertz (1Hz) is one cycle per second (1C/S). The reciprocal of frequency f is the period T.
Note: f equals frequency in Hertz (Hz), C equals the speed of light 3×108m/s, and λ equals wavelength.
f = 1/T
f=C/λ
Period: The period of a sine wave is the time for one complete cycle to occur. The reciprocal of period T is the frequency f.
T = 1/f