High Performance Cement
for High Strength and Extreme Durability
Introduction
Considered for a long time as ordinary material for concrete production, cements have undergone significant progress in the past years. New complex admixture improved their performance.
Intergrinding the complex admixture with clinker, gypsum, and selected mineral admixtures allows to rise the strength and durability of the cement and provides the industry with wide range of new custom- made cements.
Strength increasing is the demand for engineering of cement with high volume of mineral admixtures or utilising of industrial by-products and waste in the cement composition. This phenomenon allows to use a required amount of mineral admixtures like granulated blast furnace slag (35- 50%) in the composition to increase chemical and thermal resistance.
According to the present experience, high performance (HP) cement and mortars with compressive strength up to 95 and 145 MPa, respectively can be produced. High performance cement based mortars possess low permeability, high resistance to chemical attack, thermal resistance, and excellent freezing and thawing resistance.
Basic Idea of HP Cement
The HP cement technology is based on:
The main idea of the HP cement technology is based on mechanical-and-chemical activation of the cement grinding process for increasing dispersion and reaction ability, as well as modifying of material surface by chemical admixtures.
The three main processes are take place at HP cement production. They are:
Chemical Composition
Chemical composition for HP (HPC) and normal portland cement (NPC) are the following:
SiO2 |
Al2O3 |
Fe2O3 |
CaO |
MgO |
K2O |
Na2O |
SO3 |
L.O.I. |
|
| Normal Portland Cement (NPC) | 19.4 |
4. 8 |
3.6 |
63.7 |
1.9 |
0.8 |
0.2 |
2.7 |
2.4 |
| High Performance Cement (HPC) | 34.3 |
7.8 |
2.5 |
43.4 |
5.7 |
1.0 |
0.2 |
2.4 |
1.5 |

Physical Properties
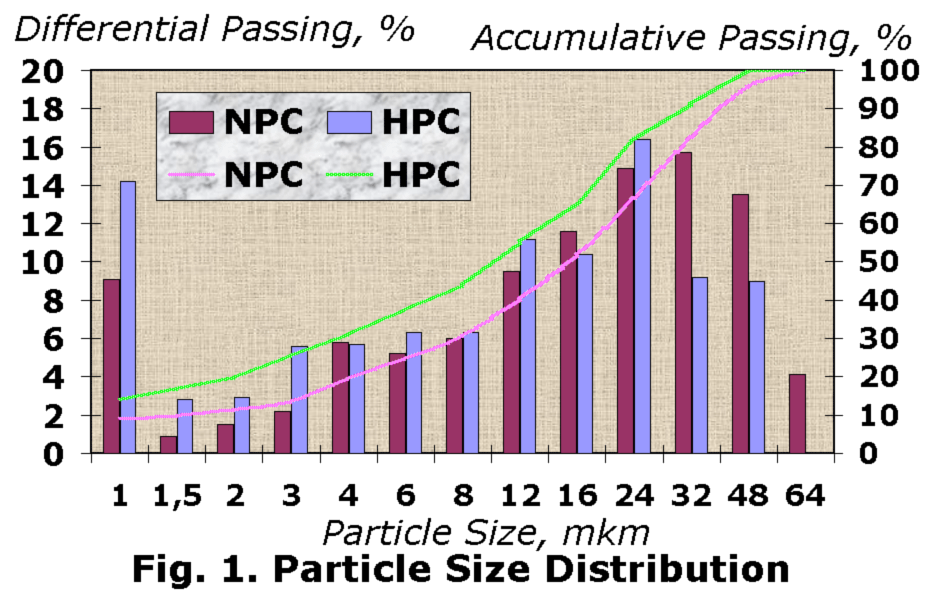
The particle size distribution of HP cement and normal cement are presented in Fig. 1.
The results of comparison test of HP cement and normal cement (in accordance with corresponding ASTM procedure) are the following:
Fineness |
Setting Time h:min |
NC % |
Compressive Strength, MPa (psi) @ age, days |
|||||||||||||
Blaine cm2/g |
45mkm % |
|||||||||||||||
Initial |
Final |
1 |
2 |
3 |
7 |
28 |
90 |
|||||||||
NPC |
3120 |
8.50 |
2:45 |
3:25 |
27.1 |
26.2 (3800) |
36.4 (5279) |
42.4 (6149) |
48.5 (7034) |
57.1 (8281) |
64.7 (9384) |
|||||
HPC |
5790 |
5.20 |
2:55 |
3:45 |
17.5 |
35.2 (5105) |
44.8 (6497) |
54.2 (7861) |
65.6 (9514) |
92.7 (13445) |
105.5 (15301) |
|||||
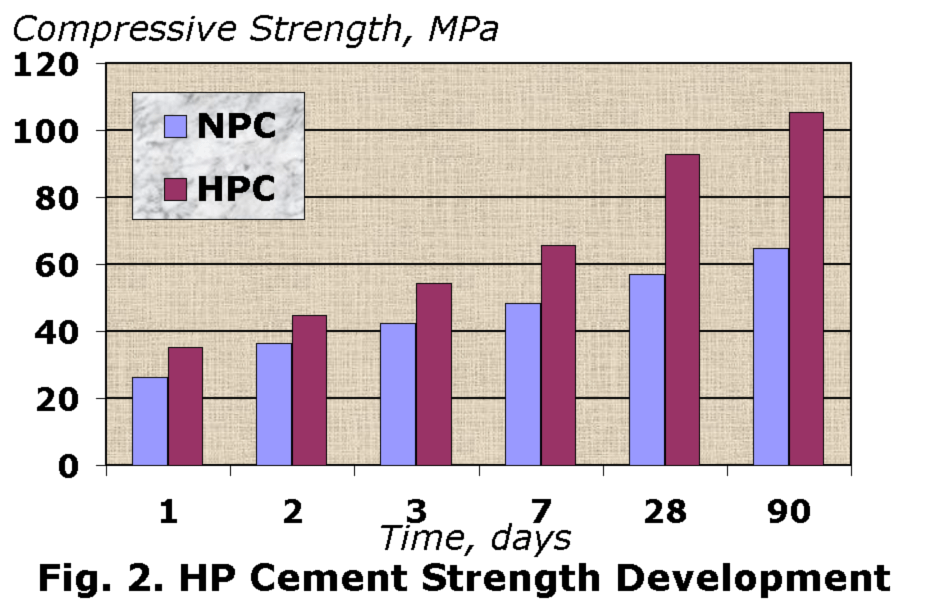 HP cement possesses 28-
day compressive strength, which is at least 65% higher then
normal cement. Early age strength development of the HP cement
allows classifying one as super rapid hardening cement. In
addition, HP cement demonstrates ability to growth a long-term
strength (Fig. 2).
HP cement possesses 28-
day compressive strength, which is at least 65% higher then
normal cement. Early age strength development of the HP cement
allows classifying one as super rapid hardening cement. In
addition, HP cement demonstrates ability to growth a long-term
strength (Fig. 2).
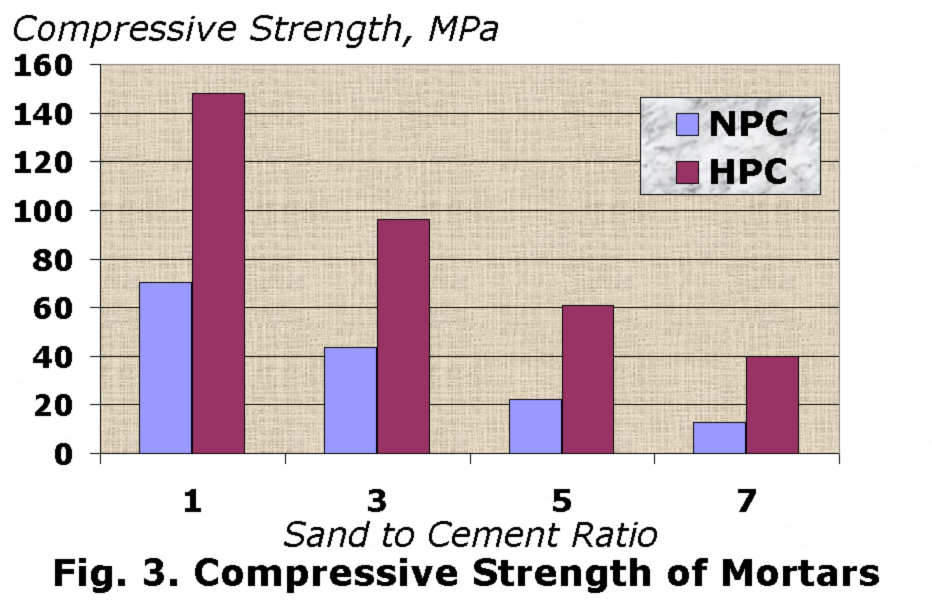
Mortar Strength
High strength phenomenon allows to apply the HP cement for production of the wide range of mortars with 28-day compressive strength in the range of 40 to 145 MPa (5,800 – 21,000 pci) at the different sand to cement ratio (S/C). The test results of strength behaviour of HP cement based and reference mortars are summarised in Fig. 3.
Impermeability
Due to low W/C of HP cement based mortar and concrete, the capillarity is very low at water absorption value around 0.3-0.8%. The usage of granulated blast furnace slag provides additional reduction of pore size. These factors provide impermeability of HP cement stone at low diffusion coefficient of 1.2-0.8*10-10 cm/s.
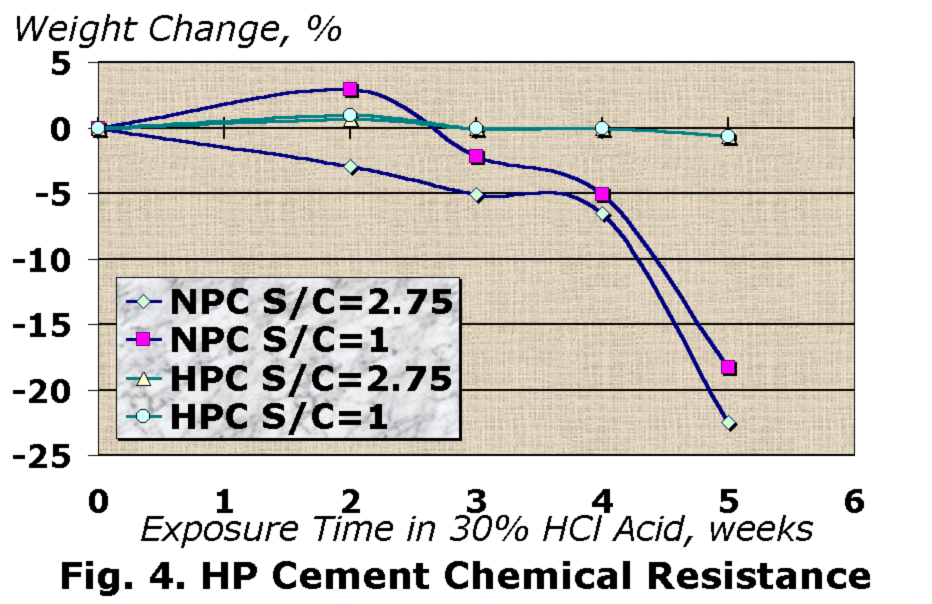
Chemical Resistance
Very low permeability of HP cement systems provides high resistance to chemical attack. The chloride permeability of HP cement systems is extremely low. Sulfate resistance of HP cement is better than existing requirements for sulfate resistance cement and concrete due to super low permeability and more resistant chemical structure. Investigations of HP cement acid resistance demonstrate the opportunity to apply such systems in HCl solutions for a long time then normal cement samples were destroyed after two weeks (Fig. 4).
Freezing
and Thawing Resistance 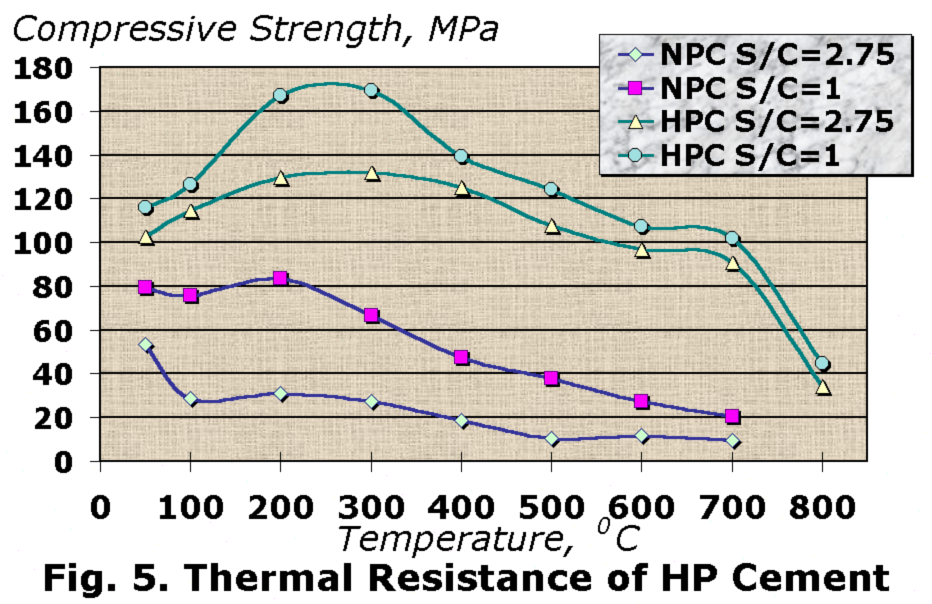
HP cement system possesses excellent freezing and thawing resistance. There was no visible destruction of HP cement samples after 140 cycles of freezing and thawing at –50 0C. Bar expansion was 0.02%, than normal portland cement length change was indicated at 0.1% after 45 and 35 cycles, respectively.
Thermal Resistance
The HP cement mortars demonstrated high compressive strength at temperature range from 100 to 500 0C and only 10- 20% reduction of strength takes place than temperature rises from 500 to 700 0C (Fig. 5).
Applications
The HP cement based concrete can be applied in unique projects such as high-rise buildings, airport runway structures, bridges, marine and offshore structures, tunnels, parking desks, shotcrete and repairing of structures, underwater concrete, special floors.
Concrete Properties
The HP cement based concretes are characterised by:
Advantages
The production and application of HP cement and concrete allow reducing of the expenses in construction. Taking in consideration high level of HP materials properties, the most important economical benefits are the following: