Explanation of Phase Change
Phase change refers to a physical change in the state of a pure material at constant temperature.
In our normal day to day lives, we see this process occur when liquid water changes to a solid
(freezing) or when liquid water changes to a vapor (boiling or evaporation). The energy being
absorbed during evaporation or released during condensation is called the latent heat of
vaporization. The energy associated with the solidification or melting process is term the heat of
formation.
The following figure illustrates the "saturation dome" for a pure substance such as water.
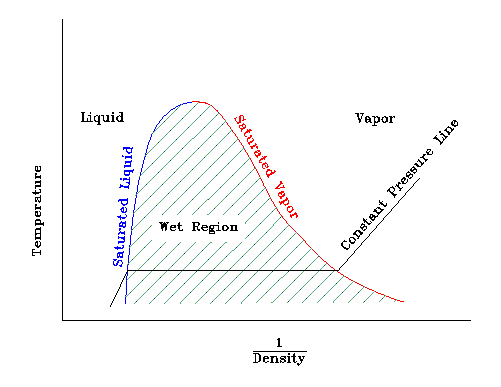
The "saturated liquid" line represents the combination of two state properties (like pressure and
temperature) at which a liquid just begins to evaporate.
The "saturated vapor" line represents the combination of two state properties at which vapor just
begins to condense.
The "wet region" refers to the condition where liquid and vapor exist at the same conditions.
It is within the wet region that phase change devices operate. Thus, a solid understanding of thermodynamic processes is key to conducting research in this area.
This page hosted by
 Get your own Free Homepage
Get your own Free Homepage

