 |
| Br asil |
Resistors
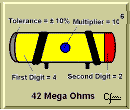
First Digit Second Digit Multiplyer Tolerance
Adapted from Java Script Bible written by Danny GoodmanIllustration by Carlos Eduardo Lazarini da Fonseca
Resistors Theory
A resistor is a component that opposes or impedes the flow of electrons through it. Thus, it limits the current flow in a circuit. A resistor can also be used to reduce the voltage. All resistors have two basic ratings, their electrical value, expressed in ohms, and their power rating, expressed in watts. The wattage rating of a resistor is a measure of how much power it can handle without being damaged by heat and it has no bearing on the resistance value. The electrical value of a resistor is a measure of its voltage drop divided by the current flowing through it (R = E/I). There are many kinds of resistors and they appear in any mumber of shapes and sizes. Three examples of the most common types of fixed carbon resistors are shown in the figure below.
Fixed Carbon Resistors Types
| A. Axial Leads | B. Radial Lead Dot | C. Radial Lead Band |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
The most widely used method of resistor identification is designating the value by means of a color code.
Resistor Color Code Table
| Color | Color | Digits | Multiplier | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | 1 | ||
| Brown | 1 | 10 | ||
| Red | 2 | 100 | ||
| Orange | 3 | 1,000 | ||
| Yellow | 4 | 10,000 | ||
| Green | 5 | 100,000 | ||
| Blue | 6 | 1,000,000 | ||
| Violet | 7 | 10,000,000 | ||
| Gray | 8 | 100,000,000 | ||
| White | 9 | 1,000,000,000 | ||
| Gold | 0.1 | 5% | ||
| Silver | 0.01 | 10% | ||
| No color | 20% |
| Home
| Radios Index | Portuguese |
| Slides Show
| Dial Lamps
| Ballast Tubes
| Links |
Copyright 1996-2003©
Carlos Eduardo Lazarini da Fonseca
Comments, questions, fill in gaps, etc, please e-mail clf7@terra.com.br
Created: Mar, 1997
Last update: Thursday, Sep 18, 2003