
| Sapwood is a living and conducting organ which is located in the most recent ring (or rings) of wood growth. |  |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
| Hardwood anatomy is more complex than that of conifers. They have vessels which are analogous to tracheids, but are more complex. Vessels have sieve plates on the ends for longitudinal transport; and pits in the sides for radial transport. |  |

| Material moves from vessel to vessel through sieve plates or from one cell type to another through opposing pits. |  |
| Diffuse-porous - little or no variation in size of vessels during the growing season. Several year's growth can carry water. | Ring-porous - large vessels are formed in the early wood. Most transport occurrs in current-year's vessels. As a result, these are very susceptible to wilt diseases. |
 |
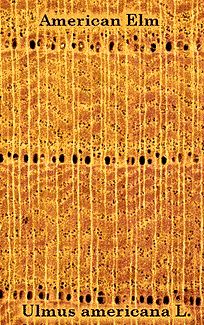 |
| Tyloses form when membrane-bound cytoplasm from neighboring parenchyma cells protrude through a pit pair and expand into the vessel element. Cell wall material is then laid down |
|
|
 |
