Last update:00-04-25

The sun radiates energy as a black body having a surface temperature of about 6000oC
over a spectrum of wavelengths from 300-470 nm. The intensity of solar radiation on a
surface normal to the sun's rays beyond the earth's atmosphere at the mean earth-sun
distance (about 150 million kilometers) is defined as the solar constant I. The currently
accepted value is 1370 W/m2.
The spectral energy distribution varies with altitude, due to the filtering effect of the
atmosphere, especially of ozone and water vapour. Some of the shorter wavelengths are
absorbed in the atmosphere and re-radiated at much longer wavelength, e.g. long infra-red
up to 100nm.
When the sun's rays passing
through the earth's atmosphere,
a) a portion of solar radiation is
scattered when striking on molecules of air, water vapour and dust particles. That portion
scattering downward from the atmosphere arrives at the earth surface in the form of diffuse
radiation (scattered radiation).
b) another portion of solar radiation is absorbed, and
c) the remaining portion of solar radiation transverses through the atmosphere and reaches
the earth surface in the form of direct radiation (beam radiation).
Incident solar radiation.For the five windows, monthly and yearly averages of incident
solar radiation are given in terms of global radiation, clear-day global radiation, and
diffuse radiation.
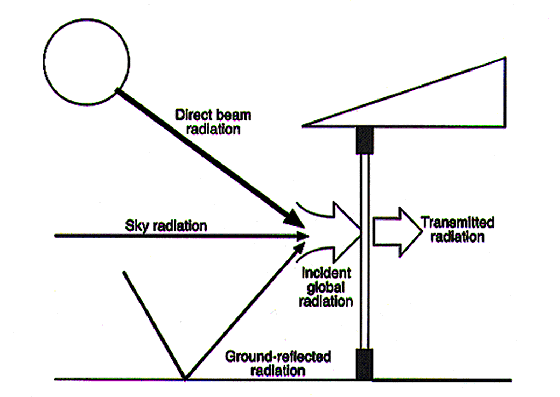
Global radiation is the total radiation received by the window and is the sum of the
direct beam radiation component, sky radiation, and radiation reflected from ground in
front of the surface. Clear-day global radiation represents the global radiation
obtainable under clear skies.
Diffuse radiation is the sum of sky radiation and radiation reflected from the ground in
front of the surface.
Global solar radiation. The incident global solar radiation (I) received by a surface,
such as a window, is a combination of direct beam radiation (Ib), sky radiation
(Id), and radiation reflected from the ground in front of the surface (Ir).
The following equation can be used to calculate incident global solar radiation:
I = Ib cosq + Id + Ir
where q is the incident angle of the sun's rays to
the surface.
The incident angle is a function of the sun's position in the sky and the orientation of
the surface.