Last update:00-04-24
The conditions of the sky of daylighting evaluation
are classified as either overcast, clear
or partly cloudy. Each classification has characteristics
that influence daylighting design.
Overcast sky--

The overcast sky is defined as one in which the position of the sun cannot be determined because of the dense cloud
cover; the light is diffuse and relatively even over the sky dome. The overcast sky is
approximately three times brighter at the zenith than at the horizon, and the illumination
is evenly distributed around the zenith.
Therefore, the top of the sky dome is the main source of illumination. The overcast sky is
frequently used as the minimum design condition, through the actual amount of illumination
in fact varies with the altitude of the sun and the density of the cloud cover.
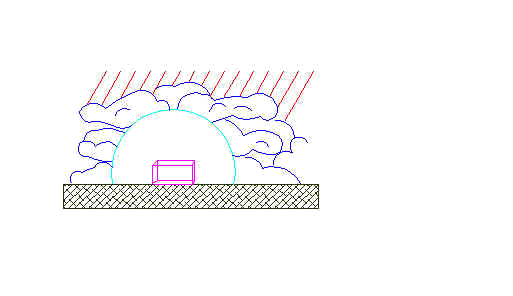
Overcast sky
back to top
Clear sky--
Illumination from the sun's direct rays is extremely intense
compared with those diffused through the sky dome; because direct sunlight is so powerful, it is a potential source of glare.
Excluding the sun, the clear sky is less bright than the overcast sky. The distribution of
light from a clear sky, (except the area immediately around the sun), is just opposite to
that of the overcast sky, i.e. three times brighter at the horizon than at the zenith.
Therefore, without direct or reflected sun rays, building openings that face the top of
the sky dome, receive less light on clear days than on overcast days.
The illumination from a clear sky varies with the position
of the sun, as well as the amount of water vapour in the atmosphere. Therefore, the amount
of illumination available to any surface changes throughout the day and the year.
Sunlight reflected from the ground usually represents 10 to
15% of the total illumination reaching a vertical window. It can even account for more
than 50% when the window is shaded from direct radiation. Reflected light from the ground
can be a valuable source of daylighting during clear sky conditions because it reflects
off the ceiling (usually in light colours) and penetrates deep into the room.
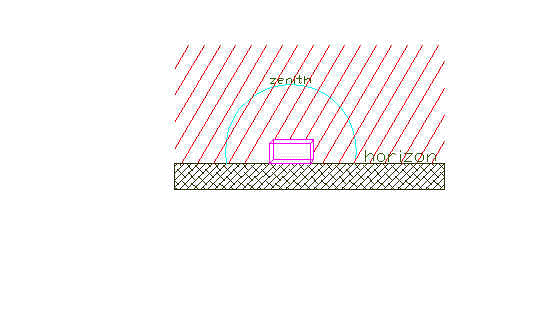
Clear
sky
back to top
Partly cloudy sky--

Partly cloudy sky is the situation most commonly occurred.
It falls somewhere between the extremes of overcast sky (that has a few clear spots) and
mostly clear sky (that has a few clouds). Partly cloudy sky frequently exhibits very
different amounts of illumination across the sky dome as the cloud cover changes over
time.
The assessment of daylighting is different
because the light source (the sun) is subject to continuous variation. Both the
illuminance in a room and the character of lighting undergo extensive changes as the
external conditions vary. Some European countries, like Germany and the UK, have
considerably more daylight hours with an overcast sky than with a clear one. Hong Kong,
however, has more clear sky daylight hours than an overcast sky will be discussed here
because the approach is comparatively simple and it represents the minimum design
condition.
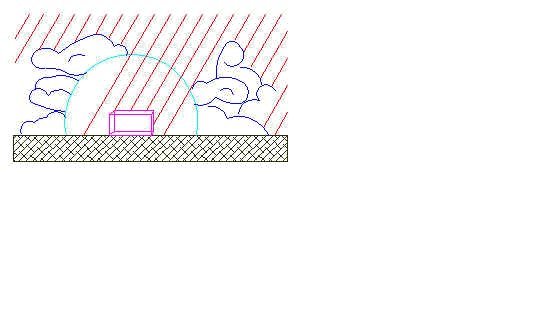
Partly
Cloudy Sky
back to top

