 The Balanced Scorecard framework
The Balanced Scorecard framework BSC Indicators
BSC Indicators ICT Balanced Scorecards
ICT Balanced Scorecards New BSC topics faced
New BSC topics faced Publications / Related Publications
Publications / Related Publications The Balanced Scorecard framework
The Balanced Scorecard framework BSC Indicators
BSC Indicators ICT Balanced Scorecards
ICT Balanced Scorecards New BSC topics faced
New BSC topics faced Publications / Related Publications
Publications / Related Publications -
-

The evaluation of the IT function has been and still remains one of the main topics of many academic and business discussions. But well-known financial measures such as the “return on investment” (ROI), “internal rate of return” (IRR), “net present value” (NPV) and the “payback” time (PB) has been demonstrated to be not sufficient to adequately explain IT investments decisions nor for their assessment. For assessing IT investments, it is crucial to understand how organisational and strategic goals are achieved. First step was to introduce more dimensions (or perspectives) of analysis, since the financial one was not sufficient, representing just the tip of the iceberg, hiding all the relations among processes.
So, in 1993 Robert S.Kaplan of the Harvard School of Business and consultant David Norton developed the Balanced Scorecard (BSC), an evolution of the concepts included in the Tableau de Bord which emerged in France at the turn of the 20th century. The aim of the Tableau was to translate each company's unit vision and mission into a set of objectives, passing through the identification of Key Success Factors and Key Performance Indicators. About the differences between the French original idea and its American "translation", there is an interesting report from Bourguignon & Malleret.
Kaplan and Norton have defined the BSC as a multi-dimensional framework for describing, implementing and managing strategy at all levels of an enterprise by linking objectives, initiatives and measures to an organisation's strategy. The scorecard then provides an enterprise view of an organisation's overall performance by integrating financial measures with other key performance indicators around customer perspectives and internal business processes, and around organisational growth, learning and innovation. It must be noted that the BSC is not a static list of measures, but rather a framework for implementing and aligning complex programs of change, and, indeed, for managing strategy-focused organisations. In summary, a scorecard is to be used to facilitate the translation of strategy into action.
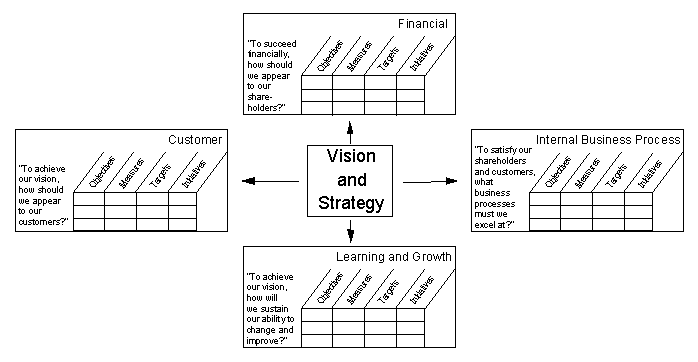
The BSc provides a framework for studying a causal link analysis based on internal performance measurement through a set of goals, drivers and indicators (lag and lead types) grouped into four different perspectives:
According to Renaissance, a good BSc should tell the story of the organisation's strategy. Three criteria help in determining whether or not this objective has been achieved:
The relevance and effectiveness of the BSc in the business world has been recognised by the Harvard Business Review (HBR) which identifies it as one of the most important management practices of the past 75 years.
Metrics represent the control mechanism within BSCs for checking if the strategy map has been properly designed through the linkage among the organizational processes. They must be splitted across the four (or more) perspectives and have to be process-oriented, trying to express the goodness of such process. It is really important to "create" metrics for your own processes and not to apply "as-is" what found out from other BSC experiences (there is an interesting paper from Arthur Schneiderman about it), even if some indicators can cover common exigences.
Now it is reported a list of metrics applied by domain/theme (with a subdivision by BSC perspective), in order to provide some examples:
 The first source for case studies (and therefore where finding also indicators adopted in such case) is the "Netconference" archive on the BSCOL website;
The first source for case studies (and therefore where finding also indicators adopted in such case) is the "Netconference" archive on the BSCOL website;
 This paper by Allistar Shaw proposes some thoughts about financial vs non-financial indicators and a possible list of metrics for the second group;
This paper by Allistar Shaw proposes some thoughts about financial vs non-financial indicators and a possible list of metrics for the second group;
 This paper proposes an analysis of how to use them in a BSC logic, associating those indicators to the usual five perspectives of an ICT BSC;
This paper proposes an analysis of how to use them in a BSC logic, associating those indicators to the usual five perspectives of an ICT BSC;
 This brief paper by Shree Phadnis focuses the attention on the way for selecting metrics for a Six Sigma project, plus an example of strategy map applied;
This brief paper by Shree Phadnis focuses the attention on the way for selecting metrics for a Six Sigma project, plus an example of strategy map applied;
 Here it is possible to look at the metrics for the library of the University of Virginia (starting from the academical year 2001-02);
Here it is possible to look at the metrics for the library of the University of Virginia (starting from the academical year 2001-02);
 The University of Edinburgh devotes a page to the its BSC, gathering and presenting all the info and metrics from 1999, with related analysis;
The University of Edinburgh devotes a page to the its BSC, gathering and presenting all the info and metrics from 1999, with related analysis;
 The Henry County School BSC;
The Henry County School BSC;
 A proposal of indicators for higher education entities (see on p.5);
A proposal of indicators for higher education entities (see on p.5);
 The BSC for the Syracuse University;
The BSC for the Syracuse University;
 A report about the experience of the University and Regional Library of Munster (Germany), where the four perspectives are: Users, Finances, Internal Processes and Innovation (Potentials);
A report about the experience of the University and Regional Library of Munster (Germany), where the four perspectives are: Users, Finances, Internal Processes and Innovation (Potentials);
 The Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission has recently produced a report on its 2003/Q3 BSC indicators;
The Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission has recently produced a report on its 2003/Q3 BSC indicators;
 The UK CHI (Commission for Health Improvement) has set up a series of performance indicators (see the left frame with four sub-areas and related links);
The UK CHI (Commission for Health Improvement) has set up a series of performance indicators (see the left frame with four sub-areas and related links);
 The DOE BSC page, with a huge amount of info, including indicators (see part 5);
The DOE BSC page, with a huge amount of info, including indicators (see part 5);
 The Washington State Dept. of Printing FY2001-02 BSC;
The Washington State Dept. of Printing FY2001-02 BSC;
 An assessment of performance of Impatient Mental Health Care;
An assessment of performance of Impatient Mental Health Care;
 The INSEAD CMER (Centre for the Management of Environmental and Social Responsibility) is studying these aspects and proposes an example of Sustainability BSC as well as a list of possible KPIs for it;
The INSEAD CMER (Centre for the Management of Environmental and Social Responsibility) is studying these aspects and proposes an example of Sustainability BSC as well as a list of possible KPIs for it;
 A 2001 paper by T.Bieker & C.U.Gminder about the Sustainability BSC;
A 2001 paper by T.Bieker & C.U.Gminder about the Sustainability BSC;
 This paper from the METIS project (IST-2000-25175) discussed possible KPIs for Knowledge Management in a Community of Practice (CoP), looking at the four Intellectual Capital (IC) categories identified (Socialization; Externalization; Combination; Internalization);
This paper from the METIS project (IST-2000-25175) discussed possible KPIs for Knowledge Management in a Community of Practice (CoP), looking at the four Intellectual Capital (IC) categories identified (Socialization; Externalization; Combination; Internalization);
The software world has recently tried to use BSC for achieving better results in Software Intensive Organisations (SIO), since Software Process Improvement (SPI) and SPI models are not a goal in itself, but just an element in the overall strategy of the company. Thus, few attempts to build an ICT scorecard have been done. The two most interesting ones are:
Therefore, the five distinct perspectives, derived from the original scorecard, are:
Starting from the analysis of ICT BSC proposed in the technical literature, some interesting topics have been faced during last years. In particular:
 the 2000 revised paper by Lamotte & Carter;
the 2000 revised paper by Lamotte & Carter;
 some thoughts (in Italian);
some thoughts (in Italian);
 a mapping between the two, trying to match the 9 EFQM factors within the 4 BSC perspectives;
a mapping between the two, trying to match the 9 EFQM factors within the 4 BSC perspectives;
 the integration proposed by Strategy&Focus (in Spanish);
the integration proposed by Strategy&Focus (in Spanish);
 a comparison of the two by 2GC
a comparison of the two by 2GC
 the Deaking University (Information Resources, Clients, Financial resources, Internal Processes and Learning & Growth)
the Deaking University (Information Resources, Clients, Financial resources, Internal Processes and Learning & Growth)
 Stan Brignall (social and environmental aspects),
Stan Brignall (social and environmental aspects),
 RMIT University (Investment in the Future),
RMIT University (Investment in the Future),
 DON eBusiness Balanced Scorecard (Stakeholder perspective),
DON eBusiness Balanced Scorecard (Stakeholder perspective),
 the QPR Scorecard (Community perspective),
the QPR Scorecard (Community perspective),
 Paul Arveson (Ethics perspective),
Paul Arveson (Ethics perspective),
 Rosemann & Wiese (Project perspective)
Rosemann & Wiese (Project perspective)
 CSC Balanced Scorecard Process (Committments, Quality, Productivity, Future Value, Customer Satisfaction)
CSC Balanced Scorecard Process (Committments, Quality, Productivity, Future Value, Customer Satisfaction)
 This paper wrote with Prof.Abran discussed this question, trying to explain and justify the rationale behind such assumption.
This paper wrote with Prof.Abran discussed this question, trying to explain and justify the rationale behind such assumption.
 A recent SEI Technical Note proposed a way for using the GQ(I)M methodology in order to derive measures and indicators for a BSC
A recent SEI Technical Note proposed a way for using the GQ(I)M methodology in order to derive measures and indicators for a BSC
 L.Buglione, N.Quintano & D.Reo, Balanced IT Scorecard and EFQM: A Balanced Approach to Performance Measurement for Software Intensive Organisations,
Proceedings of the 2nd European Software Measurement Conference - FESMA 1999, October 4-8, 1999, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ISBN 90-76019-07-X, pp. 415-426
L.Buglione, N.Quintano & D.Reo, Balanced IT Scorecard and EFQM: A Balanced Approach to Performance Measurement for Software Intensive Organisations,
Proceedings of the 2nd European Software Measurement Conference - FESMA 1999, October 4-8, 1999, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ISBN 90-76019-07-X, pp. 415-426
 Reo D. (trad.it. Buglione L. & Satriani G.), La Balanced IT Scorecard per organizzazioni software-intensive. Un possibile scenario, Qualità, Rivista dell'AICQ, Anno XXX, No. 7, Agosto 2000, pp. 45-47
Reo D. (trad.it. Buglione L. & Satriani G.), La Balanced IT Scorecard per organizzazioni software-intensive. Un possibile scenario, Qualità, Rivista dell'AICQ, Anno XXX, No. 7, Agosto 2000, pp. 45-47
 D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, Measuring Software Development - There is more than just measuring software!,
Proceedings of the 2nd European Software Measurement Conference - FESMA 1999, October 4-8, 1999, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ISBN 90-76019-07-X, pp. 391-402
D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, Measuring Software Development - There is more than just measuring software!,
Proceedings of the 2nd European Software Measurement Conference - FESMA 1999, October 4-8, 1999, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ISBN 90-76019-07-X, pp. 391-402
 D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, Quantitatively Managing the EFQM Excellence Model, ESI-1999-TR-042, December 1999
D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, Quantitatively Managing the EFQM Excellence Model, ESI-1999-TR-042, December 1999
 D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, ESI Balanced IT Scorecard Infrastructure & Innovation Perspective, ESI-1999-TR-043, December 1999
D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, ESI Balanced IT Scorecard Infrastructure & Innovation Perspective, ESI-1999-TR-043, December 1999
 D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, Measures That Make an IMPACT, ESI-1999-TR-058, December 1999
D.Reo, N.Quintano & L.Buglione, Measures That Make an IMPACT, ESI-1999-TR-058, December 1999
 L.Buglione & A.Abran, Balanced Scorecards and GQM: what are the differences?,
FESMA/AEMES 2000 Conference, October, 18-20, 2000, Madrid, Spain
L.Buglione & A.Abran, Balanced Scorecards and GQM: what are the differences?,
FESMA/AEMES 2000 Conference, October, 18-20, 2000, Madrid, Spain
 L.Buglione, A.Abran & R.Meli, How Functional Size Measurement supports the Balanced Scorecard framework for ICT, FESMA-DASMA 2001 (4th European Conference on Software Measurement and ICT Control), Heidelberg, Germany, May 8-11, 2001, pp. 259-272
L.Buglione, A.Abran & R.Meli, How Functional Size Measurement supports the Balanced Scorecard framework for ICT, FESMA-DASMA 2001 (4th European Conference on Software Measurement and ICT Control), Heidelberg, Germany, May 8-11, 2001, pp. 259-272
 A.Abran & L.Buglione, A Multidimensional Performance Model for Consolidating Balanced Scorecards, International Journal of Advances in Engineering Software, Elsevier Science Publisher, Vol. 34, No. 6, June 2003, pp.339-349
A.Abran & L.Buglione, A Multidimensional Performance Model for Consolidating Balanced Scorecards, International Journal of Advances in Engineering Software, Elsevier Science Publisher, Vol. 34, No. 6, June 2003, pp.339-349
 L.Buglione & A.Abran, Improving Measurement Plans from multiple dimensions: Exercising with Balancing Multiple Dimensions - BMP, 1st Workshop on "Methods for Learning Metrics", METRICS 2005, 11th IEEE International Software Metrics Symposium, 19-22 September 2005, Como(Italy)
L.Buglione & A.Abran, Improving Measurement Plans from multiple dimensions: Exercising with Balancing Multiple Dimensions - BMP, 1st Workshop on "Methods for Learning Metrics", METRICS 2005, 11th IEEE International Software Metrics Symposium, 19-22 September 2005, Como(Italy)
 L.Buglione & A.Abran, A Model for Performance Management & Estimation, Proceedings of METRICS 2005, 11th IEEE International Software Metrics Symposium, 19-22 September 2005, Como(Italy), ISBN 0-7695-2371-4
L.Buglione & A.Abran, A Model for Performance Management & Estimation, Proceedings of METRICS 2005, 11th IEEE International Software Metrics Symposium, 19-22 September 2005, Como(Italy), ISBN 0-7695-2371-4
 L.Buglione, Sistemi Informativi & modelli di Software Process Improvement: relazioni e impatti, Proceedings of itAIS2005, 2nd Conference of the Italian Chapter of AIS, 1-2 December 2005, Verona (Italy)
L.Buglione, Sistemi Informativi & modelli di Software Process Improvement: relazioni e impatti, Proceedings of itAIS2005, 2nd Conference of the Italian Chapter of AIS, 1-2 December 2005, Verona (Italy)
 L.Buglione, BSC e metodi di misurazione multi-dimensionale delle performance organizzative: un percorso evolutivo, Il Change Management nelle imprese e nelle pubbliche amministrazioni, Workshop Nazionale di "Studi Organizzativi", 5-6 June 2006, Castellanza (Italy)
L.Buglione, BSC e metodi di misurazione multi-dimensionale delle performance organizzative: un percorso evolutivo, Il Change Management nelle imprese e nelle pubbliche amministrazioni, Workshop Nazionale di "Studi Organizzativi", 5-6 June 2006, Castellanza (Italy)
 Abrahamsson P., Measuring the Success of Software Process Improvement: The Dimensions, EuroSPI 2000 Conference, Copenhagen (Denmark), November 7-9 2000
Abrahamsson P., Measuring the Success of Software Process Improvement: The Dimensions, EuroSPI 2000 Conference, Copenhagen (Denmark), November 7-9 2000
 Sweeney A. & Bustard D., Strategic Alignment of Information Technology, Information Systems and Organisational Change: Practice and Performance, FEAST 2000 Conference, London (UK), July 10-12, 2000
Sweeney A. & Bustard D., Strategic Alignment of Information Technology, Information Systems and Organisational Change: Practice and Performance, FEAST 2000 Conference, London (UK), July 10-12, 2000
 Schmid K., Integrated Cost-and Investment models for Product Family Development, Fraunhofer Institute, Café Project, Eureka Programm, ITEA ip00004, 2003
Schmid K., Integrated Cost-and Investment models for Product Family Development, Fraunhofer Institute, Café Project, Eureka Programm, ITEA ip00004, 2003
 Gouscos, D., Kalikakis M., Maria Legal M., Papadopoulou S. & Verginadis G. , A Performance and Quality Assessment Model for One-Stop Government-to-Business E-Services, Proceedings of Business Excellence '03 Conference, Guimaraes (Portugal), June 10-13 2003
Gouscos, D., Kalikakis M., Maria Legal M., Papadopoulou S. & Verginadis G. , A Performance and Quality Assessment Model for One-Stop Government-to-Business E-Services, Proceedings of Business Excellence '03 Conference, Guimaraes (Portugal), June 10-13 2003
 Aversano L., Bodhuin T., Canfora G. & Tortorella M., A Framework for Measuring Business Processes based on GQM, HICSS'04, Proceedings of the 37th Hawaii International Conference of System Sciences, January 2004
Aversano L., Bodhuin T., Canfora G. & Tortorella M., A Framework for Measuring Business Processes based on GQM, HICSS'04, Proceedings of the 37th Hawaii International Conference of System Sciences, January 2004
 Béland S. & Abran A., Utilisation d'un balanced scoreboard pour l'intégration des mesures associées à un programme d'assurance qualité, CUSEC 2004, Montreal (Canada), January 15-17 2004
Béland S. & Abran A., Utilisation d'un balanced scoreboard pour l'intégration des mesures associées à un programme d'assurance qualité, CUSEC 2004, Montreal (Canada), January 15-17 2004
 e-Italy.com, List of webpages on Scorecards, 2004
e-Italy.com, List of webpages on Scorecards, 2004
 MAAW - Management and Accounting Web, Articles & Books Related to the Balanced Scorecard
MAAW - Management and Accounting Web, Articles & Books Related to the Balanced Scorecard
 M. Golfarelli, S. Rizzi, I. Cella, Beyond data warehousing: What's next in business intelligence?, Proceedings 7th International Workshop on Data Warehousing and OLAP (DOLAP 2004), Washington DC, 2004.
M. Golfarelli, S. Rizzi, I. Cella, Beyond data warehousing: What's next in business intelligence?, Proceedings 7th International Workshop on Data Warehousing and OLAP (DOLAP 2004), Washington DC, 2004.
 L.Proietti La Balanced Scorecard. Presupposti concettuali, implicazioni applicative ed inquadramento nell'A.S.V., Dipartimento di Scienze della Gestione d'Impresa, Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Ottobre 2002.
L.Proietti La Balanced Scorecard. Presupposti concettuali, implicazioni applicative ed inquadramento nell'A.S.V., Dipartimento di Scienze della Gestione d'Impresa, Università di Roma "La Sapienza", Ottobre 2002.
 A.Dos Passos, Balanced Scorecards e Mapas Estratégicos: Proposta de Implantação no TCU, Monografia de conclusão do curso de graduação
em Sistemas de Informação, ULBRA, Brazil, 2004
A.Dos Passos, Balanced Scorecards e Mapas Estratégicos: Proposta de Implantação no TCU, Monografia de conclusão do curso de graduação
em Sistemas de Informação, ULBRA, Brazil, 2004
 D.Lekkas & D.Spinellis, Handling and Reporting Security Advisores: A Scorecard Approach, IEEE Security & Privacy, July 2005, pp.32-41
D.Lekkas & D.Spinellis, Handling and Reporting Security Advisores: A Scorecard Approach, IEEE Security & Privacy, July 2005, pp.32-41
 Nick M. & Althoff K.D., Engineering Experience Base Maintenance Knowledge, IESE Technical Report 018.01/E, March 2001
Nick M. & Althoff K.D., Engineering Experience Base Maintenance Knowledge, IESE Technical Report 018.01/E, March 2001
 Hong J., Suh E. & Em N., A Strategic Model for Consolidating BSC Measures Based on the Desirability Function: A Case Study of a Web-based Company, PACIS 2005 Conference, 9 July 2005
Hong J., Suh E. & Em N., A Strategic Model for Consolidating BSC Measures Based on the Desirability Function: A Case Study of a Web-based Company, PACIS 2005 Conference, 9 July 2005
 Hong J. A Performance System Based on the BSC Approach for Measuring Performance in a Business Environment
, POSTECH 2005 Spring Seminar
Hong J. A Performance System Based on the BSC Approach for Measuring Performance in a Business Environment
, POSTECH 2005 Spring Seminar
 L. Aversano, T. Bodhuin, G. Canfora, and M. Tortorella, Technology-Driven Business Evolution, The Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 79, no. 3, 2006, pp. 314-338
L. Aversano, T. Bodhuin, G. Canfora, and M. Tortorella, Technology-Driven Business Evolution, The Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 79, no. 3, 2006, pp. 314-338
 Marquês D.L. & Serrano Gonçalves Henriques D., Avaliação do desempenho organizacional utilizando dados espaciais, Relatório Final de TFC do curso de Licenciatura em Engenharia Informática e de Computadores (LEIC), Ano Lectivo 2005/06, Instituto Superior Tecnico - Departamento de Engenharia Informatica, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa (Portugal), 2006
Marquês D.L. & Serrano Gonçalves Henriques D., Avaliação do desempenho organizacional utilizando dados espaciais, Relatório Final de TFC do curso de Licenciatura em Engenharia Informática e de Computadores (LEIC), Ano Lectivo 2005/06, Instituto Superior Tecnico - Departamento de Engenharia Informatica, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa (Portugal), 2006
 Fry, L. W. & Matherly, L. L., Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Performance, Paper accepted for presentation at the August 2006 meeting of the Academy of Management, Atlanta, Georgia
Fry, L. W. & Matherly, L. L., Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Performance, Paper accepted for presentation at the August 2006 meeting of the Academy of Management, Atlanta, Georgia
 Parida A., Development of a Multi-criteria Hierarchical Framework for Maintenance Performance Measurement. Concepts, Issues and Challenges, Doctoral Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering - Division of Operation and Maintenance Engineering, Luleå University of Technology, 2006
M. Golfarelli, New Trends in Business Intelligence, Invited paper. In Proceedings 1st International Symposium on Business Intelligent Systems (BIS'05), Opatija, Croatia, pp. 15-26, 2005
Parida A., Development of a Multi-criteria Hierarchical Framework for Maintenance Performance Measurement. Concepts, Issues and Challenges, Doctoral Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering - Division of Operation and Maintenance Engineering, Luleå University of Technology, 2006
M. Golfarelli, New Trends in Business Intelligence, Invited paper. In Proceedings 1st International Symposium on Business Intelligent Systems (BIS'05), Opatija, Croatia, pp. 15-26, 2005
 Bernroider, Edward W.N.; Hampel, Alexander and Sumper, Andreas, F., An Application of the Balanced Scorecard as a Strategic IT-Controlling Instrument for E Business Development, Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Electronic Business (ICEB 2003), pp. 42-44, Singapore, December 2003
Bernroider, Edward W.N.; Hampel, Alexander and Sumper, Andreas, F., An Application of the Balanced Scorecard as a Strategic IT-Controlling Instrument for E Business Development, Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Electronic Business (ICEB 2003), pp. 42-44, Singapore, December 2003
 Masson Guerra J.L.& Truñó I Gual J., La Cuarta Generacion de Balanced Scorecard: Revision Critica de la Literatura Conceptual Y Empirica, Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona, 10 Mayo 2006
Masson Guerra J.L.& Truñó I Gual J., La Cuarta Generacion de Balanced Scorecard: Revision Critica de la Literatura Conceptual Y Empirica, Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona, 10 Mayo 2006
 Veras Rodrigues M., Método Para Determinação Da Escala De Prioridade De Ações Estratégicas Fundamentado No Grau De Inter-Relacionamento Entre Os Indicadores Das Perspectivas Do Balanced Scorecard (Bsc) E O Valor Econômico Adicionado (Eva), Universidade Federal De Santa Catarina, Programa De Pós-Graduação Em Engenharia De Produção, Florianópolis (Brasil), 2005
Veras Rodrigues M., Método Para Determinação Da Escala De Prioridade De Ações Estratégicas Fundamentado No Grau De Inter-Relacionamento Entre Os Indicadores Das Perspectivas Do Balanced Scorecard (Bsc) E O Valor Econômico Adicionado (Eva), Universidade Federal De Santa Catarina, Programa De Pós-Graduação Em Engenharia De Produção, Florianópolis (Brasil), 2005
 Tröger M., Konzeption und prototypische Realisierung eines Rollenund Sichtenkonzepts für das FSeMP, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg, Fakultät für Informatik, Institut für Verteilte Systeme, Diplomarbeit, 11. März 2005
Tröger M., Konzeption und prototypische Realisierung eines Rollenund Sichtenkonzepts für das FSeMP, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg, Fakultät für Informatik, Institut für Verteilte Systeme, Diplomarbeit, 11. März 2005
 Hermann A., Paech B., Software Quality by Misuse Analysis, Working Paper 2005-AH-1, University of Heidelberg (Germany), version 1.5, 9 January 2007
Hermann A., Paech B., Software Quality by Misuse Analysis, Working Paper 2005-AH-1, University of Heidelberg (Germany), version 1.5, 9 January 2007
 Saemu J., An Experience on Software Development Organizational Adoption and Implementation of the Preliminary Measurement and Estimation to Appraise Software Projects, Proceedings of METRICS2005 - Industry Track, September 2005, Como (Italy)
Saemu J., An Experience on Software Development Organizational Adoption and Implementation of the Preliminary Measurement and Estimation to Appraise Software Projects, Proceedings of METRICS2005 - Industry Track, September 2005, Como (Italy)
 Universidad Miguel Hernández de Elche, Deliverable 3.2: Guidelines to develop a balanced scorecard in entrepreneurial universities, GLOBALSTART PROJECT (IPS-2001-41038), December 2005
Universidad Miguel Hernández de Elche, Deliverable 3.2: Guidelines to develop a balanced scorecard in entrepreneurial universities, GLOBALSTART PROJECT (IPS-2001-41038), December 2005
 Hong J., Suh E., A Strategic Model for Consolidating BSC Measures Based on the Desirability Function: A Case Study of a Website Company, GESTS Int’l Trans. Computer Science and Engr., Vol.18, No.1, October 2005, pp. 99-110
Hong J., Suh E., A Strategic Model for Consolidating BSC Measures Based on the Desirability Function: A Case Study of a Website Company, GESTS Int’l Trans. Computer Science and Engr., Vol.18, No.1, October 2005, pp. 99-110
 Chang L.C., Tu Y.M., Establishing the Balanced Scorecard of the IC Design Company in Taiwan through System Dynamics, Systems Dynamics
Chang L.C., Tu Y.M., Establishing the Balanced Scorecard of the IC Design Company in Taiwan through System Dynamics, Systems Dynamics
 Lardenoije E.J.H. , van Raaij E.M., van Weele A.J., Performance Management Models and Purchasing: Relevance Still Lost, Proceedings of the 14th IPSERA Conference, Archamps (France), 2005
Lardenoije E.J.H. , van Raaij E.M., van Weele A.J., Performance Management Models and Purchasing: Relevance Still Lost, Proceedings of the 14th IPSERA Conference, Archamps (France), 2005
 Halsti T., Ohjelmistoprosessin kehittäminen, Matemaattisluonnontieteellinen, Tietojenkäsittelytieteenlaitos, UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI, 8.12.2006
Halsti T., Ohjelmistoprosessin kehittäminen, Matemaattisluonnontieteellinen, Tietojenkäsittelytieteenlaitos, UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI, 8.12.2006
 Lee A.H.I., Chen W.C. & Chang C.J., A fuzzy AHP and BSC approach for evaluating performance of IT department in the manufacturing industry in Taiwan, Journal of Expert Systems with Applications, Elsevier, Vol.34 (2008), pp.96–107
Lee A.H.I., Chen W.C. & Chang C.J., A fuzzy AHP and BSC approach for evaluating performance of IT department in the manufacturing industry in Taiwan, Journal of Expert Systems with Applications, Elsevier, Vol.34 (2008), pp.96–107
 Amendola LP., Depool T., F., González M. D., Palacios E., Modelo de Implementacion del Cuadro de Mando Integral en una Oficina de Proyectos, "IX Congreso Internacional De Ingeniería De Proyectos", Málaga (Spain), June 2005
Amendola LP., Depool T., F., González M. D., Palacios E., Modelo de Implementacion del Cuadro de Mando Integral en una Oficina de Proyectos, "IX Congreso Internacional De Ingeniería De Proyectos", Málaga (Spain), June 2005
 Schmidt K., Integrated Cost and Investment Models for Product Family Development, IESE Report no. 067.03/E, Version 1.0, 21 July 2003
Schmidt K., Integrated Cost and Investment Models for Product Family Development, IESE Report no. 067.03/E, Version 1.0, 21 July 2003
 Software Project Metrics, Technical Report, King Saud University, 18 December 2007
Software Project Metrics, Technical Report, King Saud University, 18 December 2007
 Freitas Spinola M. & Prospero dos Santos N.M.A, Sistema de apoio à decisão em contexto espaço-temporal, Relatorio de Trabalho Final de Curso, Curso de Licenciatura en Engenharia Informatica e de Computadores, Ano Lectivo 2005/06, Instituto Superior Tecnico, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa (Portugal)
Freitas Spinola M. & Prospero dos Santos N.M.A, Sistema de apoio à decisão em contexto espaço-temporal, Relatorio de Trabalho Final de Curso, Curso de Licenciatura en Engenharia Informatica e de Computadores, Ano Lectivo 2005/06, Instituto Superior Tecnico, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa (Portugal)
 Abu-Suleiman A., An Analytical Performance Management Framework Enabling Enterprise Strategy Management, Faculty of the Graduate School of The University of Texas at Arlington for the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON (USA), August 2006
Abu-Suleiman A., An Analytical Performance Management Framework Enabling Enterprise Strategy Management, Faculty of the Graduate School of The University of Texas at Arlington for the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT ARLINGTON (USA), August 2006