|
Dense Plasma Focus
For many years, scientists have been attempting to harness thermonuclear fusion (the process that powers the stars) in a controlled manner in the laboratory. Before sixties microsecond time-scale Z-pinch (a kind of pulsed plasma producing device) was a choice to initiate fusion by passing a strong electric current pulse through deuterium gas. The current both ionizes the gas and generates magnetic field that "pinches" the resulting plasma to high temperature and density along the current paths. But the technique proved inadequate to compress the plasma uniformly and the plasma column disintegrates before the current pulse attains its maximum value.
Incidentally, in the early sixties a modified version of the classical Z-pinch device was invented where the existing inherent problems of classical Z-pinch was overcome. This device, a kind of coaxial accelerator, named as plasma focus (PF). Typically, there are two types of this pulsed plasma producing device in accordance with the name of the inventors, that is Mather type and Filippov type PF device.
 | 
CPP Plasma Focus facility |
The highly dense compressed plasma of PF is an efficient source of energetic neutron pulse when operated in deuterium medium. However neutron emission is not the only impetus of this device. It is rich source of X-rays (hard as well as soft), energetic charged particles (electrons and ions) along with varieties of plasma phenomena charge particle acceleration, instability and turbulence development etc. is continuing to fascinate the physicist world over. The manifold emission characteristics of PF has encouraged scientists to explore the possibility of application in various fields such as pulsed neutron activation analysis, neutron radiography, X- lithography, X-ray microscopy, ion implantation, thin film deposition etc.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) photograph of the surface of nitrided high carbon steel (HCS) sample | 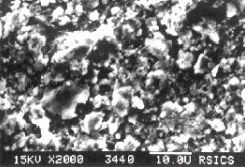 |
At CPP, a low energy 2.2 K.J Mather type PF device has been installed in the mid of 1997. The power to the divice is supplied from a 7.1mF, 40kV energy storage capacitor. In pulsed power supply a high-speed power switch is required to transfer the energy from capacitor to PF machine. A built in spark gap switch at the top of the capacitor serves as the high speed, power switch. The whole elctrode assembly is housed inside a stainless steel chamber, which is evacuated by a Rotary pump.
Research program undertaken in the PF laboratory
of CPP:
- Design and fabrication of high-speed diagnostics tools such as Rogowski coil (current probe), Resistive divider (voltage probe), magnetic probe etc.
- Nitriding of metallic and nonmetallic samples.
- Characterization of the ion emission from PF facility.
- Analysis of soft x-ray emission from PF.
- Study of Temporal evolution of X-ray emission.
- Design and fabrication of a photographic film screen base pinhole camera.
 | 
X-ray pinhole photograph
of PF. (a) End-on view, (b) Side-on view.
|
|