Interferon-beta (IFN-ß) has beneficial effects on the frequency and severity of relapses, as well as on disease progression in patients suffering from Relapsing/Remitting Multiple Sclerosis.
Its mode of action, however, is not completely understood.
Previous studies on T-Lymphocyte bulk cultures and T-Lymphocyte lines with specificity for different Antigens suggested that the drug might partially act via suppression of T-Cell proliferation and secretion of ProInflammatory Cytokines like Interferon-gamma (IFN-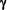 ) and/or Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-
) and/or Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF- ).
).
In this study we investigated the effects of human recombinant IFN-ß 1b on proliferation, Interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor (IL-2R)  -chain upregulation, and Cytokine and Chemokine secretion of Myelin Basic Protein-reactive, MS patient-derived T-Cell clones secreting T-Helper Type 1 (Th1) Cytokines.
-chain upregulation, and Cytokine and Chemokine secretion of Myelin Basic Protein-reactive, MS patient-derived T-Cell clones secreting T-Helper Type 1 (Th1) Cytokines.
IFN-ß partially suppressed both Antigen- and IL-2-driven proliferation of these cells without affecting the expression of either IL-2 or IL-2R  -chain.
-chain.
There was no inhibitory effect on the secretion of IFN-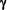 , TNF-
, TNF- , and Macrophage Inflammatory Protein (MIP)-1
, and Macrophage Inflammatory Protein (MIP)-1  , but release was rather slightly enhanced.
, but release was rather slightly enhanced.
In conclusion, while IFN-ß does reduce proliferation of Th1-like, MBP-specific T-Cells in vitro, the drug does not result in overall dysfunction of these cells.
Therefore, the effect of IFN-ß on MS may not depend on a primary inhibition of potentially Encephalitogenic T-Lymphocytes.