|
A large group of Cytokines (IL-1 to IL-35) produced mainly by Leukocytes, although some are made by PolyMorphoNuclear Phagocytes, or by Auxiliary Cells.
They have a variety of functions, but most are involved in directing other Immune Cells to divide and differentiate. Each IL acts on a specific, limited group of cells that express the correct Receptor for that InterLeukin.
- InterLeukin-1 (IL-1)
-
Produced by activated Macrophages, Endothelia Cells, B-Cells, and Fibroblast Cells. IL-1 induces Inflammatory responses, Edema, promotes the production of ProstaGlandins, IL-2, the growth of Leukocytes, and induce the Acute Phase Reaction.
IL-1 also augments CorticoSteroid release, induces fever and shivering - useful responses, because elevated body temperature reduces Bacterial growth.
- InterLeukin-2 (IL-2)
- Also known as T-Cell Growth Factor (TGF), it is secreted by stimulated Helper T-Cells (CD4+), CytoToxic T-Cells (CD8+), and Large Granular Lymphocytes (LGL). IL-2 promotes proliferation (Colonal Expansion) and differentiation of additional CD4+ Cells, B-Cells, and activates Macrophages and Oligodendrocytes.
- InterLeukin-3 (IL-3)
- Produced by activated T-Cells, it stimulates the proliferation of Precursors in all HematoPoietic Cells (Red Cells, Granulocytes, Macrophages, and Lymphocytes).
- InterLeukin-4 (IL-4)
- Stimulates production of AntiBody-producing B-Cells, leading to the production of IgG & IgE. IL-4 also promotes CD8+ Cell growth and promotes Th2 Cell differention.
On Macrophages, IL-4 induces MHC Class II expression, but inhibits production of the ProInflammatory Cytokins (IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha [TNF- ]). ]).
- InterLeukin-5 (IL-5)
- Is chiefly a growth and activation factor for Eosinophil Cells (a subset of Neutrophils).
- InterLeukin-6 (IL-6)
- Is produced by many cell types, including T-Cells, Macrophages, B-Cells, Fibroblasts, and Endothelia Cells. IL-6 stimulates several types of Leukocytes, and the production of Acute Phase Proteins in the Liver. IL-6 is particularly important in inducing B-Cells to differentiate into AntiBody Forming Cells (Plasma Cells).
- InterLeukin-7 (IL-7)
- Is made by Bone Marrow Stroma Cells and acts on Thymocytes. IL-7 is a T-Cell growth and activation factor, and a Macrophage Activation Factor.
- InterLeukin-8 (IL-8)
- Is produced by most cells of the body, especially Macrophages and Endothelia Cells. IL-8 enhances Inflammation, by enabling Immune Cells to migrate into tissue, and is a powerful inducer of Chemotaxis for Neutrophil Cells.
- InterLeukin-9 (IL-9)
- Up-regulates Th1 responses (Enhancing Inflammation) by inhibiting T-Cell Apoptosis.
- InterLeukin-10 (IL-10)
- Down-regulates AntiViral Responses by inhibiting: the production of Interferon-gamma (IFN-
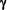 ), Antigen Presentation, and Macrophage production of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF- ), Antigen Presentation, and Macrophage production of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF- . IL-10 is also very important in B-Cell activation. . IL-10 is also very important in B-Cell activation.
- InterLeukin-12 (IL-12)
- Acts in a contrasting manner to IL-10; it promotes Th1 Type Response in Macrophages, NK Cells, and induces IFN-
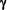 production. production.
- InterLeukin-13 (IL-13)
- Has structural and functional similarities to IL-4 and promotes B-Cell differentiation, inhibits Th1 Cells and the production of Macrophage Inflamatory Cytokines.
- Interleukin-15 (IL-15)
- Shares several biological activities with IL-2 and is produced by both Epithelial Cells and Monocytes. IL-15 also induces T-Cell proliferation, enhances NK Cell CytoToxicity and stimulates B-Cells to proliferate and secrete ImmunoGlobulins.
- InterLeukin-17 (IL-17)
- Induces production of inflammatory Cytokines.
- InterLeukin-18 (IL-18)
- Induces Interferon-gamma (IFN-
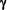 ) production. #30 ) production. #30
- InterLeukin-23 (IL-23)
- One of the essential factors required for the expansion of pathogenic CD4+ T-Cells, which is characterized by the production of IL-17, IL-6, and Tumor Necrosis Factor.
|