I
Immune System - The Immune System is a collection of Cells and Proteins that works to protect the body from potentially harmful, infectious Microorganisms (microscopic life-forms), such as Bacteria, Viruses and Fungi.
- It is a defense mechanism characterized by recognition of Nonself, Specificity, and Memory. It has two basic components: Innate Immunity and Acquired Immunity. #22
- The Immune System plays a role in the control of Cancer and other diseases, but also is the culprit in the phenomena of Allergies, HyperSensitivity, the rejection of Transplanted Organs, AutoImmune Diseases, and Medical Implants.
Immunity
- Having protection or resistance to a particular disease or poison, ie, Gamma Globulin. #09
ImmunoGlobulin - A group of GlycoProteins (AntiBodies), present in Serum and tissue fluids that recognize and bind to Antigens. They are produced by Plasma Cells and are integral in Adaptive Immune Responses. There are five classes of ImmunoGlobulins (Ig): IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE. #22, #25
ImmunoSuppression
- Any form of treatment or drug, which slows or inhibits the body's usual Immune Responses. Some examples used to treat MS are: Cyclosporin, Methotrexate, and Azathioprine. #28
Impairment
- Any loss or abnormality of Psychological, Physiological, or Anatomical structure or function. It is a deviation from the person's usual biomedical state. An impairment is thus any loss of function directly resulting from injury or disease. #28
Impotence - Poor or Absent erection of the Penis. #25
(See: Sexuality)
Incidence - The number of new cases of a disease in a specified population over a defined time period. #28
Incontinence - The inability to hold urine or stool until urination or defecation is intended. #25
Inflammation - A tissue's Immunological response to trauma, injury, or invasion; characterized by mobilization of Leukocytes, AntiBodies, and increased body temperature, with fluid accumulation. #28
Insulin - One of many Hormones which helps the body, change the food we eat into energy; Insulin helps us store energy for later use. After we eat, it causes sugar (Glucose) to leave the blood and enter the body's cells - to make fat, sugar, and protein. Between meals, it aids in the utilization of stored fat, sugar, and protein.
Integrins - Are transmembrane proteins capable of binding externally to matrix and other cell-membrane Proteins and internally to signal-transferring Proteins, thereby positioning themselves to communicate ExtraCellular signals.
Interferon - An interfering Protein that neutralizes Virus, it is produced by CytoToxic T-Cells of the Immune System, in response to foreign Nucleic Acids (produced by Viruses and Bacteria), thereby protecting uninfected cells.
- Interferon-alpha ( ) and Interferon-beta (ß), form the Type 1 class of Interferons; while Interferon-gamma ( ) and Interferon-beta (ß), form the Type 1 class of Interferons; while Interferon-gamma (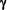 ) is a Type 2 Interferon. These Proteins are AntiViral Cytokines that are also, potent Immune Regulators and Growth Factors. #09, #25, #30 ) is a Type 2 Interferon. These Proteins are AntiViral Cytokines that are also, potent Immune Regulators and Growth Factors. #09, #25, #30
- Three Interferons
alpha ( ) ) |
is produced by Leukocytes in response to Viruses or Nucleic Acids; |
|
beta (ß) |
is produced by Fibrobasts in response to Viruses or Nucleic Acids; |
gamma (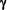 ) ) |
is produced by Lymphocytes, both T-Cells and Large Granular Lymphocytes (LGL), in response to Immune stimuli. It is produced by activated T-Cells and Natural Killer Cells.
- A degree of Immune Activation leads to the production of IFN-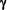 , an increase in Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) function, activates Macrophages in general, and probably enhances their capacity to act as APCs. #30 , an increase in Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) function, activates Macrophages in general, and probably enhances their capacity to act as APCs. #30 |
InterLeukins (IL-1 to IL-23) - A well-characterized group of Cytokines, mainly produced by Leukocytes, which mostly act upon other Leukocytes. Their main targets for actions, vary from T-Cells and B-Cells, to Fibroblasts and Endothelium.
- They have a broad spectrum of functional activities that regulate the activities and capabilities of many cell types and regulate Inflammation and Immune Responses. #30
InterNuclear Ophthalmoplegia - UnCoordinated Eye movements, where the outward turning Eye looking towards the side develops Nystagmus, and the other Eye fails to turn completely inward.
- To produce synchronous Eye movements, Cranial Nerves III, IV and VI communicate through the Fasciculus, Medial Longitudinal (MLF). In INO, a lesion disrupts this pathway, preventing communication between Nuclei.
- To gaze to the left, the left SupraNuclear control center of horizontal Eye movements [Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation (PPRF)] must signal the left CN VI Nucleus to turn the left Eye outwards (abduct).
- At the same time, the PPRF must signal the right CN III Nucleus, via the right MLF, to simultaneously turn the right Eye inwards (adduct).
- A lesion of the right MLF would not allow the Neural impulse to reach the Right Medial Rectus. In this case, the left Eye would abduct, but the right Eye would not adduct. Further, the left Eye would go into an Abducting Nystagmus.
- Most lesions of the MLF are located in the Pons and with INO, you will be able to converge. However, if the lesion affects the MLF within the MidBrain and involves the CN III Nucleus, then you will not be able to converge. #31
(Also See: Diplopia, Afferent Pupillary Defect, Retrobulbar Neuritis, Nystagmus, Oscillopsia, Dyschromatopsia, Optic Neuritis, & Diagnosing MS)
Intrathecal - Occurring in the space under the Arachnoid membrane, which surrounds the Brain and Spinal Cord (generally within the CerebroSpinal Fluid). #15
Ischemia - Is an insufficient Blood Supply to an Organ or Tissue. #17
|
 since August 10, 1999.
since August 10, 1999.