|
OUROBOROS
Pathfinder |
Home to OUROBOROS
Contents
Architecture
Psychology professor James Alcock's theory of the Belief Engine (decribed by Jane Goldman in her fascinating companion books to the series The X-Files) may help to explain whyvpeople throughout history have come to believe in a number of religious and/or paranormal phenomena--or why they haven't! The Belief Engine is capable of creating beliefs that are just as false as others are true. The Belief Engine works thus:
The concept of the angel is common to the three current monotheistic religions of the West: Judaism, Christinaity, and Islam. Various prophets, theologians, and mystics have added to the lore of angels over several thousand years. There are countless informal sources, including folklore and popular stories, as well as material from traditions like Zoroastrianism and the religions of ancient Sumer and Babylon that have contributed to the concept of the angel. Furthermore, religions from other parts of the world, particularly India, contain similar concepts that may have influenced or been influenced by the Western angelic traditions. The following list is a broad outline of some of the best known and most important written sources of angelic lore in the West.
Judaism
The Heavenly Choirs
Orders
Gary Goldschneider's "personology" system is based on the supposition that people born on the same day of the year tend to share personality traits. The system depends on the symbolic associations of the astrological signs and other related symbols for its structure. I am not a believer in astrology, but I found this system offered some interesting personality insights and a plethora of personal symbols drawn from traditional occult sources. It is somewhat less hokey than most astrological systems, and is fun to play with.
I have always loved games that allowed players to engage their own creativity and knowledge in the gameplay. This has been espacially true for role-playing games and customizable card games. I also enjoy a good game of chance and skill, like poker!
The word philosophy literally means "love of wisdom". The term is applied to any sustained reflection, the goal of which is to better understand things. Scholastically, studying philosophy provides training in disciplined analysis and clarification.
Maya
Teotihuacan
Machu Picchu
Lascaux
Glastonbury
Egypt
Belief Systems
The Belief Engine
A similar effect is pareidolia, which is what psychologists call our mind's tendency to find meaning in anything. If we see something that appears to create a pattern, we'll associate another event of the same type with it, even if they aren't actually connected. And if we expect to find something, more than likely we will. Our minds will find meaning where there is none so that we can understand what is going on around us.
Our Belief Engine can be overcome by not leaping to conclusions, but keeping an open mind.
Terms for Describing Belief Systems

Angelology
Primary Sources
Christianity
Islam
Non-orthodox Sources
Secondary Sources
Choirs and Orders
 In the Middle Ages, a system was developed by which scholars could organize the angels. Eventually Nine Choirs were developed, each Choir taking its name from the names of angelic groupings in the Bible. The Nine were divided into Three Hierarchies. Each Choir represented one step closer to mankind. Different angels from both Jewish and Christian texts were assigned a place in the Choirs. This particular configuration of the angelic hierarchy is that of Pseudo-Dionysius.
In the Middle Ages, a system was developed by which scholars could organize the angels. Eventually Nine Choirs were developed, each Choir taking its name from the names of angelic groupings in the Bible. The Nine were divided into Three Hierarchies. Each Choir represented one step closer to mankind. Different angels from both Jewish and Christian texts were assigned a place in the Choirs. This particular configuration of the angelic hierarchy is that of Pseudo-Dionysius.
 Throughout the millennia, people have been interested in knowing why there is evil in the world. One explanation, created over centuries by theologians, writers, priests, and prophets is the story of the Fallen, angels who rejected the Divine Plan and have sought dominion over the world. The most common tale is that the angel Lucifer, or Satan, greatest of all angels, gave in to pride, coveting God's kingdom. Lucifer and one third of the angels in heaven rebelled and a war was fought in Heaven between Lucifer's followers and the loyal angels lead by Michael. Michael's troops prevailed and the Rebels were cast into Hell. However, Lucifer was not willing to accept defeat and the battle has raged on ever since. The idea of a separate entity controlling evil grew necessary in Christian theology because orthodox doctrine indicated that God was perfectly good and therefore incapable of doing evil. The paradox of believing in One God and at the same time believing in an equally powerful being responsible for evil has plagued Christianity for practically its entire history.
Throughout the millennia, people have been interested in knowing why there is evil in the world. One explanation, created over centuries by theologians, writers, priests, and prophets is the story of the Fallen, angels who rejected the Divine Plan and have sought dominion over the world. The most common tale is that the angel Lucifer, or Satan, greatest of all angels, gave in to pride, coveting God's kingdom. Lucifer and one third of the angels in heaven rebelled and a war was fought in Heaven between Lucifer's followers and the loyal angels lead by Michael. Michael's troops prevailed and the Rebels were cast into Hell. However, Lucifer was not willing to accept defeat and the battle has raged on ever since. The idea of a separate entity controlling evil grew necessary in Christian theology because orthodox doctrine indicated that God was perfectly good and therefore incapable of doing evil. The paradox of believing in One God and at the same time believing in an equally powerful being responsible for evil has plagued Christianity for practically its entire history.
Paranormal Phenomena
Reincarnation
 Reincarnation, the rebirth of the soul in different bodies, is a tenant of many major religions. Instances of reincarnation are found in Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Judaism, and even Christianity. Dr. Ian Stevenson, the father of modern "scientific" research into reincarnation, puts forth several kind of evidence in favor of this phenomenon. Some interpret child prodigies and intense phobias as evidence of past life experiences, but these are easily explained as differences in talent and psychological make-up in this life. Mediumistic information about past lives and past life memories brought to the surface by hypnotic regression or spontaneously remembered can be invented inadvertently or fraudulently—or read from someone else’s mind if you believe in telepathy! Some children may talk about things they have never seen or experienced. Or they may tell you about the manner of their previous death. Usually by the age of six to ten, these "memories" have ceased or been forgotten. This category is quite controversial and is Dr. Stevenson's greatest source of evidence. These cases are most common in countries where reincarnation is a strongly held belief. Nevertheless, there are plenty of Western cases. Another counter-argument is crytomnesia ("hidden memory"), the notion that our minds record everything we see or hear for later retrieval, which could explain how children and adults know information they did not know they knew. An interesting question remains even if one believes in reincarnation: there are always more people in the next generation than in the last, so where do new souls come from as the population grows?
Reincarnation, the rebirth of the soul in different bodies, is a tenant of many major religions. Instances of reincarnation are found in Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Judaism, and even Christianity. Dr. Ian Stevenson, the father of modern "scientific" research into reincarnation, puts forth several kind of evidence in favor of this phenomenon. Some interpret child prodigies and intense phobias as evidence of past life experiences, but these are easily explained as differences in talent and psychological make-up in this life. Mediumistic information about past lives and past life memories brought to the surface by hypnotic regression or spontaneously remembered can be invented inadvertently or fraudulently—or read from someone else’s mind if you believe in telepathy! Some children may talk about things they have never seen or experienced. Or they may tell you about the manner of their previous death. Usually by the age of six to ten, these "memories" have ceased or been forgotten. This category is quite controversial and is Dr. Stevenson's greatest source of evidence. These cases are most common in countries where reincarnation is a strongly held belief. Nevertheless, there are plenty of Western cases. Another counter-argument is crytomnesia ("hidden memory"), the notion that our minds record everything we see or hear for later retrieval, which could explain how children and adults know information they did not know they knew. An interesting question remains even if one believes in reincarnation: there are always more people in the next generation than in the last, so where do new souls come from as the population grows?
Ghosts
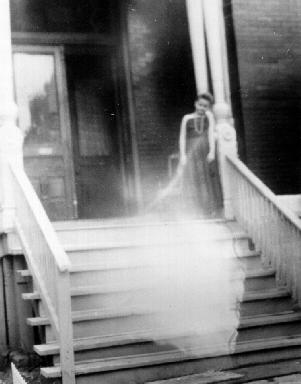 Jane Goldman describes several types of "ghost" phenomena in her books. Ghosts are commonly thought to be the souls of the dead, but new theories have emerged about the nature and meaning of these experiences in recent decades. The following is a list of different ghost types and possible explanations of them.
Jane Goldman describes several types of "ghost" phenomena in her books. Ghosts are commonly thought to be the souls of the dead, but new theories have emerged about the nature and meaning of these experiences in recent decades. The following is a list of different ghost types and possible explanations of them.
Personology
The Seasons and Signs
The four seasons of the northern hemisphere represent the four stages of human life. Each season has its own characteristics, and it is on this foundation that the rest of the system is built. For purposes of this system, the spring equinox is considered the beginning of the year. Each sign is subdivided into three phases, with a cusp on either side in which blends the personalities of the two adjoining signs.
 ARIES (March 21-April 20)- ELEMENT: Fire QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: Mars SYMBOL: The Ram MODE: Intuition MOTTO: I Am HUMAN AGE: 0-7 THE ARIES PERSONALITY: Aries people, like young children, are spontaneous, frank, open, self-centered, and willful. They are innocent and see the world with awe and wonder. They also want to be the center of attention and explore the world around them.
ARIES (March 21-April 20)- ELEMENT: Fire QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: Mars SYMBOL: The Ram MODE: Intuition MOTTO: I Am HUMAN AGE: 0-7 THE ARIES PERSONALITY: Aries people, like young children, are spontaneous, frank, open, self-centered, and willful. They are innocent and see the world with awe and wonder. They also want to be the center of attention and explore the world around them.
 TAURUS (April 21-May 21)- ELEMENT: Earth QUALITY: Fixed RULER: Venus SYMBOL: The Bull MODE: Sensation MOTTO: I Have HUMAN AGE: 7-14 THE TAURUS PERSONALITY: These people are maintainers and sharers. They crave autonomy and love physical activities. Taureans are observers and strategists who live for their loved ones. They are good team players.
TAURUS (April 21-May 21)- ELEMENT: Earth QUALITY: Fixed RULER: Venus SYMBOL: The Bull MODE: Sensation MOTTO: I Have HUMAN AGE: 7-14 THE TAURUS PERSONALITY: These people are maintainers and sharers. They crave autonomy and love physical activities. Taureans are observers and strategists who live for their loved ones. They are good team players.
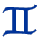 GEMINI (May 22-June 21)- ELEMENT: Air QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Mercury SYMBOL: The Twins MODE: Thought MOTTO: I Communicate HUMAN AGE: 14-21 THE GEMINI PERSONALITY: Geminis are very individual. They seek excitement and travel, having energy to burn. They are group people who, however, don't form emotional attachments easily.
GEMINI (May 22-June 21)- ELEMENT: Air QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Mercury SYMBOL: The Twins MODE: Thought MOTTO: I Communicate HUMAN AGE: 14-21 THE GEMINI PERSONALITY: Geminis are very individual. They seek excitement and travel, having energy to burn. They are group people who, however, don't form emotional attachments easily.
 CANCER (June 22-July 22)- ELEMENT: Water QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: The Moon SYMBOL: The Crab MODE: Feeling MOTTO: I Feel HUMAN AGE: 21-28 THE CANCER PERSONALITY: Those born under Cancer are patient. They seek strong friendships with a high degree of trust and sharing. They are set apart, and express themselves nonverbally. They require much emotional support from their loved ones. Appreciation is not as important as expression to Cancer people.
CANCER (June 22-July 22)- ELEMENT: Water QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: The Moon SYMBOL: The Crab MODE: Feeling MOTTO: I Feel HUMAN AGE: 21-28 THE CANCER PERSONALITY: Those born under Cancer are patient. They seek strong friendships with a high degree of trust and sharing. They are set apart, and express themselves nonverbally. They require much emotional support from their loved ones. Appreciation is not as important as expression to Cancer people.
 LEO (July 23-August 23)- ELEMENT: Fire QUALITY: Fixed RULER: The Sun SYMBOL: The Lion MODE: Intuition MOTTO: I Create HUMAN AGE: 28-35 THE LEO PERSONALITY: Leo people bring the full force of their personalities to bare on the world. They have a strict sense of honor, and the will to stick to what they believe and reject what they don't. They are big-hearted, often giving in grand gestures. Leos like to be admired for their looks as well as for their accomplishments. Leo people love their homes and have a fierce protectiveness towards friends and family. However, they can be in danger of clinging to outdated arrangements.
LEO (July 23-August 23)- ELEMENT: Fire QUALITY: Fixed RULER: The Sun SYMBOL: The Lion MODE: Intuition MOTTO: I Create HUMAN AGE: 28-35 THE LEO PERSONALITY: Leo people bring the full force of their personalities to bare on the world. They have a strict sense of honor, and the will to stick to what they believe and reject what they don't. They are big-hearted, often giving in grand gestures. Leos like to be admired for their looks as well as for their accomplishments. Leo people love their homes and have a fierce protectiveness towards friends and family. However, they can be in danger of clinging to outdated arrangements.
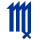 VIRGO (August 24-Sept 22)- ELEMENT: Earth QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Mercury SYMBOL: The Virgin MODE: Sensation, Thought MOTTO: I Serve HUMAN AGE: 35-42 THE VIRGO PERSONALITY: People born under this sign are very particular about what they reveal of themselves. Their inner worlds are focused on solving problems. The future is an important goal to Virgos. A structure is very important to these people and they make excellent family-persons and co-workers. They contribute greatly to the group effort, sometimes to a fault. Virgos tend to take things literally, although they do sometimes expect that others will know their needs without having to say them verbally.
VIRGO (August 24-Sept 22)- ELEMENT: Earth QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Mercury SYMBOL: The Virgin MODE: Sensation, Thought MOTTO: I Serve HUMAN AGE: 35-42 THE VIRGO PERSONALITY: People born under this sign are very particular about what they reveal of themselves. Their inner worlds are focused on solving problems. The future is an important goal to Virgos. A structure is very important to these people and they make excellent family-persons and co-workers. They contribute greatly to the group effort, sometimes to a fault. Virgos tend to take things literally, although they do sometimes expect that others will know their needs without having to say them verbally.
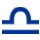 LIBRA (Sept 23-Oct 22)- ELEMENT: Air QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: Venus SYMBOL: The Scales MODE: Thought, Sensation MOTTO: I Weigh HUMAN AGE: 42-49 THE LIBRA PERSONALITY: Those born under Libra pay considerable attention to how they relate to others. They like harmony, but can stir up trouble with their controversial views. Libras are generous, but may be blind to others' needs and therefore isolate themselves. When making decisions, Libras see both sides of the issue. They do not react well to pressure, but will assert it on others if they feel justified. Libras are full of energy, but must be careful of depression and extremes in opinion.
LIBRA (Sept 23-Oct 22)- ELEMENT: Air QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: Venus SYMBOL: The Scales MODE: Thought, Sensation MOTTO: I Weigh HUMAN AGE: 42-49 THE LIBRA PERSONALITY: Those born under Libra pay considerable attention to how they relate to others. They like harmony, but can stir up trouble with their controversial views. Libras are generous, but may be blind to others' needs and therefore isolate themselves. When making decisions, Libras see both sides of the issue. They do not react well to pressure, but will assert it on others if they feel justified. Libras are full of energy, but must be careful of depression and extremes in opinion.
 SCORPIO (Oct 23-Nov 21)- ELEMENT: Water QUALITY: Fixed RULER: Pluto SYMBOL: The Scorpion MODE: Feeling MOTTO: I Control HUMAN AGE: 49-56 THE SCORPIO PERSONALITY: Scorpio people want to have full dominance in social roles. They can be dark, sexual, and belligerent people. They are serious types, but prefer to keep their formidable weapons in reserve. Scorpios often undergo dramatic transformation, and their lives are influenced by the death/rebirth theme. They are highly connected to the unconscious. Scorpios are humorous and appreciate ironies. They must be weary of self-destructive, controlling behavior and addiction to people and ideas.
SCORPIO (Oct 23-Nov 21)- ELEMENT: Water QUALITY: Fixed RULER: Pluto SYMBOL: The Scorpion MODE: Feeling MOTTO: I Control HUMAN AGE: 49-56 THE SCORPIO PERSONALITY: Scorpio people want to have full dominance in social roles. They can be dark, sexual, and belligerent people. They are serious types, but prefer to keep their formidable weapons in reserve. Scorpios often undergo dramatic transformation, and their lives are influenced by the death/rebirth theme. They are highly connected to the unconscious. Scorpios are humorous and appreciate ironies. They must be weary of self-destructive, controlling behavior and addiction to people and ideas.
 SAGITTARIUS (Nov 22-Dec 21)- ELEMENT: Fire QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Jupiter SYMBOL: The Archer MODE: Intuition MOTTO: I Philosophize HUMAN AGE: 56-63 THE SAGITTARIUS PERSONALITY: These people want to see the whole picture of life. They are energetic, expansive, optimistic, honest, and ethical. Sagittarians are eternal students and may reject society in favor of a higher truth. They must not be too judgmental of those who don't share their beliefs though. Although loving travel, if a Sagittarian feels at home he will certainly stay.
SAGITTARIUS (Nov 22-Dec 21)- ELEMENT: Fire QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Jupiter SYMBOL: The Archer MODE: Intuition MOTTO: I Philosophize HUMAN AGE: 56-63 THE SAGITTARIUS PERSONALITY: These people want to see the whole picture of life. They are energetic, expansive, optimistic, honest, and ethical. Sagittarians are eternal students and may reject society in favor of a higher truth. They must not be too judgmental of those who don't share their beliefs though. Although loving travel, if a Sagittarian feels at home he will certainly stay.
 CAPRICORN (Dec 22-Jan 20)- ELEMENT: Earth QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: Saturn SYMBOL: The Goat MODE: Sensation MOTTO: I Master HUMAN AGE: 63-70 THE CAPRICORN PERSONALITY: Capricorns tend to be conservative, but that doesn't stop them from achieving the heights no matter how long it takes. Capricorns acknowledge difficulty and suffering to be part of life's package. This fatalism leads them to accept their role in life, but can also lead them to be inflexible. Those born under this sign have an instinctive knowledge of power and how it works and may have a tendency to be dictatorial.
CAPRICORN (Dec 22-Jan 20)- ELEMENT: Earth QUALITY: Cardinal RULER: Saturn SYMBOL: The Goat MODE: Sensation MOTTO: I Master HUMAN AGE: 63-70 THE CAPRICORN PERSONALITY: Capricorns tend to be conservative, but that doesn't stop them from achieving the heights no matter how long it takes. Capricorns acknowledge difficulty and suffering to be part of life's package. This fatalism leads them to accept their role in life, but can also lead them to be inflexible. Those born under this sign have an instinctive knowledge of power and how it works and may have a tendency to be dictatorial.
 AQUARIUS (Jan 21-Feb 19)- ELEMENT: Air QUALITY: Fixed RULER: Uranus SYMBOL: The Water Bearer MODE: Thought MOTTO: I Universalize HUMAN AGE: 70-77 THE AQUARIUS PERSONALITY: Aquarians transcend restrictions and limitations with their somewhat childlike wisdom. These people have many idiosyncrasies and function best in unregulated environments. Aquarians are naturally open and accepting and are unable to understand when others aren't. When confronted with hostility they may fight or simply disappear. Aquarians are promoters of high ideals (scientific and universal) and are always looking for happiness in life. They are objective, and sometimes too superficial.
AQUARIUS (Jan 21-Feb 19)- ELEMENT: Air QUALITY: Fixed RULER: Uranus SYMBOL: The Water Bearer MODE: Thought MOTTO: I Universalize HUMAN AGE: 70-77 THE AQUARIUS PERSONALITY: Aquarians transcend restrictions and limitations with their somewhat childlike wisdom. These people have many idiosyncrasies and function best in unregulated environments. Aquarians are naturally open and accepting and are unable to understand when others aren't. When confronted with hostility they may fight or simply disappear. Aquarians are promoters of high ideals (scientific and universal) and are always looking for happiness in life. They are objective, and sometimes too superficial.
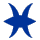 PISCES (Feb 20-March 20)- ELEMENT: Water QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Neptune SYMBOL: The Fish MODE: Feeling MOTTO: I Believe HUMAN AGE: 77-84 THE PISCES PERSONALITY: Those born under this sign can be masters of abstract expression and highly emotional. They like to be with others and alone at times too, but run the risk of becoming escapists. Extreme sensitivity make Pisceans vulnerable to depression. These people have excellent memories and are empathic and compassionate. But they must beware that others don't take advantage of them.
PISCES (Feb 20-March 20)- ELEMENT: Water QUALITY: Mutable RULER: Neptune SYMBOL: The Fish MODE: Feeling MOTTO: I Believe HUMAN AGE: 77-84 THE PISCES PERSONALITY: Those born under this sign can be masters of abstract expression and highly emotional. They like to be with others and alone at times too, but run the risk of becoming escapists. Extreme sensitivity make Pisceans vulnerable to depression. These people have excellent memories and are empathic and compassionate. But they must beware that others don't take advantage of them.
The Four Elements
The Three Qualities
The Ten Planets
Cosmology
 According to The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, cosmology is: "the study of the physical universe considered as a totality of phenomena in time and space; the astrophysical study of the history, structure, and constituent dynamics of the universe; a specific theory or model of this structure and these dynamics."
According to The American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, cosmology is: "the study of the physical universe considered as a totality of phenomena in time and space; the astrophysical study of the history, structure, and constituent dynamics of the universe; a specific theory or model of this structure and these dynamics."
Cosmological Models
The Nature of the Universe
 How did our universe begin? What will be its fate? How is it structued and how does it function?
How did our universe begin? What will be its fate? How is it structued and how does it function?
Black Holes
 A black hole is created when a very large star, many times the size of our own Sun, collapses in on itself as it dies into a tiny super-dense point called a singularity. The collapsed star's gravity is so great that nothing, not even light, can escape once it comes close enough. The barrier where this happens is called the event horizon, and it is the lack of escaping light at the event horizon that makes the star appear as a perfect black sphere. Thus far, no theory of even quantum physics can explain what happens inside the singularity.
A black hole is created when a very large star, many times the size of our own Sun, collapses in on itself as it dies into a tiny super-dense point called a singularity. The collapsed star's gravity is so great that nothing, not even light, can escape once it comes close enough. The barrier where this happens is called the event horizon, and it is the lack of escaping light at the event horizon that makes the star appear as a perfect black sphere. Thus far, no theory of even quantum physics can explain what happens inside the singularity.
Time Travel
Consider the following mind-bender: if you traveled into the past and killed your own parents before you were born, how could you then have lived to travel back in time in the first place?
Extrasolar Planets
 Astronomers continue to discover extrasolar planets, planets in solar systems other than our own, on a regular basis.
Astronomers continue to discover extrasolar planets, planets in solar systems other than our own, on a regular basis.
Alien Intelligence and Contact
Even into the twentieth century, people posited that civilizations existed on the Moon and Mars. Modern investigation has proved otherwise, but tantalizing clues like the announcement in 1996 of the discovery of possible microscopic Martian fossils have given new hope to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. If humans were to one day make contact with another species of intelligent beings in the universe, how might it affect us? We might experience a sense of kinship and connection with this other species, perhaps helping us to overcome our own internal differences (as Star Trek creator Gene Roddenberry imagined). We might come to devalue our own civilization in the face of a technologically superior species (a scenario touched on by J. Michael Strascynski on Babylon 5) or to lose sight of the value of our existence and that of our own planet as simply one meaningless biosphere among many; on the other hand, if we found Earth to be the only inhabited world in the universe, we might come to view our planet and our species as precious and unique, worth protecting and nurturing. Religious believers might come to view the aliens as messengers of their divinities, as "evil" opponents to their beliefs, or as evidence that their beliefs were unjustified if the aliens were not able to provide spiritual insights beyond our own. Maybe it wouldn’t change us in any profound way. In fact, some scientists feel that alien physiology and psychology would be so different from ours that we couldn't reach a common ground of understanding for communication. For now, it’s all just fascinating speculation.
Evolution Science
Human Evolution
Games
Languages
Painting
Philosophy
Branches of Philosophy
Philosophical Approaches
Linked closely with changes in the theories by which philosophers question and explore the world has been the evolution of religion and science. The Classical Schools
The four major Classical Schools of philosophy developed by the Greeks after the fall of Athens (listed hrer in ordering of founding) continue to be relevant today.
The Fathers of Western Philosophy
Socrates, considered the father of Western philosophy; his student Plato; and Plato's pupil Aristotle set the stage for Western philosophy. The debate between the Platonian and Aristotelian viewpoints has remained the central debate in philosophy for 2,000 years.
Socrates
 Socrates was born in 469 BCE and lived in the city-state of Athens. Socrates encouraged people to think about and challenge accepted notions of the world. According to Plato's Dialogues, from which most of what we know about him comes, Socrates would use ironic statements to goad people into speaking with him about issues such as government and beauty. By allowing them to talk themselves into a corner, Socrates would politely point out the flaws in their reasoning his goal was not to tell people what to think, but to help them think for themselves.
Socrates was born in 469 BCE and lived in the city-state of Athens. Socrates encouraged people to think about and challenge accepted notions of the world. According to Plato's Dialogues, from which most of what we know about him comes, Socrates would use ironic statements to goad people into speaking with him about issues such as government and beauty. By allowing them to talk themselves into a corner, Socrates would politely point out the flaws in their reasoning his goal was not to tell people what to think, but to help them think for themselves.
Plato
 Plato described everything in the world as being an ephemeral, decaying copy of some ideal form that existed outside space/time--a reality perceptible through mathematical equations. Plato is also famous for his great work the Republic, in which he described the perfect society based on order, harmony, and reason. The Myth of the Cave from the Republic tells of men trapped in a cave with only the shadows of the outside world to show them what is really going on all around them. They assume that the shadows are the real world. If one of these men were suddenly thrust out into the bright light of day, he would be unable to accept the revelation at first. And, if after finally understanding the truth of the situation, he returned to the cave, no one there would be able to understand or accept what he had to say. This allegory seeks to teach us that our direct experience is not of reality, but what is in our minds.
Plato described everything in the world as being an ephemeral, decaying copy of some ideal form that existed outside space/time--a reality perceptible through mathematical equations. Plato is also famous for his great work the Republic, in which he described the perfect society based on order, harmony, and reason. The Myth of the Cave from the Republic tells of men trapped in a cave with only the shadows of the outside world to show them what is really going on all around them. They assume that the shadows are the real world. If one of these men were suddenly thrust out into the bright light of day, he would be unable to accept the revelation at first. And, if after finally understanding the truth of the situation, he returned to the cave, no one there would be able to understand or accept what he had to say. This allegory seeks to teach us that our direct experience is not of reality, but what is in our minds.
Aristotle
 Aristotle believed that the ultimate truth could only be found in this world. He went on to create the fundamentals of logic, physics, political science, economics, psychology, metaphysics, meteorology, rhetoric, and ethics. Aristotle taught that what defines a thing its structure and purpose. Aristotle believed that experience was the best guide to learning about something. He also believed that what every person wants is to live a happy life to the fullest extent possible. To this end, he developed the doctrine of the "golden mean" which says that moderation is the key to a balanced life and happiness. The government of a people should ensure the ability of each person to pursue this happiness. Aristotle also believed that drama, rather than history, provided the best insight into life.
Aristotle believed that the ultimate truth could only be found in this world. He went on to create the fundamentals of logic, physics, political science, economics, psychology, metaphysics, meteorology, rhetoric, and ethics. Aristotle taught that what defines a thing its structure and purpose. Aristotle believed that experience was the best guide to learning about something. He also believed that what every person wants is to live a happy life to the fullest extent possible. To this end, he developed the doctrine of the "golden mean" which says that moderation is the key to a balanced life and happiness. The government of a people should ensure the ability of each person to pursue this happiness. Aristotle also believed that drama, rather than history, provided the best insight into life.
Places of Interest
Central and South America
A civilization that flourished in present-day Mexico and northern Central America from the 19th century BCE to the 17th century CE.
Ancient ritual city located in present-day Mexico, largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas.
The enigmatic Inca city high in the Andes Mountains in Peru.
Europe,Africa, and Asia
Site in France of prehistoric cave paintings dating to c. 15,000 BCE
Site of a ruined Christian monastery and supposed repository of the Holy Grail and the remains of King Arthur.
A breathtakingly beautiful landscape of lakes, waterfalls, caverns, and forest inhabited by unique and fascinating flora and fauna
Symbols
Reviewed Works
OUROBOROS - Films
OUROBOROS - Literature
OUROBOROS - Music
OUROBOROS - Television